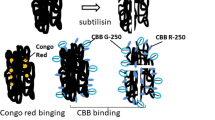
Summary
The permanganate method, the immunoperoxidase method, and a newly developed autoclave method were used to distinguish different types of amyloid fibril proteins in formalin-fixed, paraffinembedded tissue sections. All tissues from permanganate-sensitive cases (AA type) lost the affinity of Congo red and green birefringence under polarized light after incubation with special autoclave treatment. AL type systemic amyloidosis and amyloid plaques of CJD and GSS were permanganate-resistant, but decreased markedly the affinity of Congo red after prolonged autoclaving. On the other hand, prealbumin type systemic amyloidosis and senile plaques of SDAT were resistant to both permanganate oxidation and prolonged autochlaving. Thus, amyloid plaques of CJD and GSS are identical to AL type in systemic amyloidosis, and senile plaques are similar to the prealbumin type. However, anti-prealbumin antiserum did not stain senile plaque amyloid. The anti-human P component stained positively systemic amuyloids and cerebral amyloid plaques of SSE, but failed to stain senile plaques of SDAT. Therefore, the amyloid fibril protein of senile plaues is apparently different from other types of amyloid depositions. Amyloid plaques of SSE are different from senile plaques not only with regard to fibril proteins, but also to globular protein in the amyloid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allsop D, Landon M, Kidd M (1983) The isolation and amino acid composition of senile plaque core protein. Brain Res 259:348–352
Bendheim PE, Barry RA, DeArmond SJ, Stites DP, Prusiner SB (1984) Antibodies to a scrapie prion protein. Nature 310:418–421
Cathcart ES, Skinner M, Cohen AS (1971) Immunogenicity of amyloid. Immunology 20:945–954
Cohen AS, Shirahama T, Sipe JD, Skinner M (1983) Amyloid proteins, precursors, mediator, and enhancer. Lab Invest 48:1–4
Eikelenboom P, Stam FC (1982) Immunoglobulins and complement factors in senile plaques. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 57:239–242
Fujihara S (1982) Differentiation of amyloid fibril proteins in tissue sections. Acta Pathol Jpn 32:771–782
Hasegawa Y, Matsuo T, Ishibashi H, Inoue T, Iwashita A, Isobe T (1984) Amyloid A protein in a case of primary amyloidosis. Jpn J Med 23:190
Ishii T, Haga S, Shimizu F (1975) Identification of components of immunoglobulins in senile plaques by means of fluorescent antibogy technique. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 32:157–162
Mann DMA, Davies JS, Hawkes J, Yates PO (1982) Immunohistochemical staining of senile plaques. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 8:55–61
Merz PA, Somerville RA, Wisnewski HM, Iqbal K (1981) Abnormal fibrils from scrapie-infected brain. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 54:63–74
Merz PA, Somerville RA, Wisniewski HM (1983) Scrapieassociated fibrils in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nature 306:474–476
Merz PA, Rohwer RG, Kascsak R, Wisniewski HM, Somerville RA, Gibbs CJ, Gajdusek DC (1984) Infection-specific particle from the unconventional slow virus diseases. Science 225:437–440
Ogata J, Okayama M, Goto I, Inomata H, Yoshida I, Omae T (1978) Primary amyloidosis with vitreous opacities. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 42:67–70
Pras M, Zaretzky J, Frangione B, Franklin EC (1980) AA protein in a case of primary or idiopathic amyloidosis. Am J Med 68:291–294
Powers JM, Schlaepfer WW, Willingham MC, Hall BJ (1981) An immunoperoxidase study of senile cerebral amyloidosis with pathogenetic considerations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 40:592–612
Powers JM, Sullivan L, Rosenthal CJ (1982) Permanganate oxidation of senile cerebral amyloid and its relationship to AA protein. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 58:275–278
Prusiner SB (1982) Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science 216:136–144
Prusiner SB, McKinley MP, Bowman KA, Bolton DC, Bendheim PE, Groth DF, Glenner GG (1983) Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rod. Cell 35:349–358
Rask L, Peterson PA, Nilsson SF (1971) The subunit strucuture of human thyroxine-binding prealbumin. J Biol Chem 246:6087–6097
Rowe IF, Jensson O, Lewis PD, Candy J, Tennent GA, Pepys MB (1984) Immunohistochemical demonstration of amyloid P component in cerebro-vascular amyloidosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 10:53–61
Shirahama T, Skinner M, Westermark P, Rubinow A, Cohen AS, Brun A, Kemper TL (1982) Senile cerebral amyloidprealbumin as a common constituent in the neuritic plaque, in the neurofibrillary tangle, and in the microangiopathic lesion. Am J Pathol 107:41–50
Tateishi J, Ohta M, Koga M, Sato Y, Kuroiwa Y (1979) Transmission of chronic spongiform encephalopathy with kuru plaques from humans to rodents. Ann Neurol 5:581–584
Tateishi J, Hikita K, Kitamoto T, Nagara H (1985) Experimental Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease inducing amyloid plaques in rodents. In: Prusiner SB (ed) Prions: their structure, biology, and diseases. Academic Press, New York (in press)
Westermark P, Shirahama T, Skinner M, Brun A, Cameron R, Cohen AS (1982) Immunohistochemical evidence for the lack of amyloid P component in some intracerebral amyloids. Lab Invest 46:457–460
Wisniewski HM, Lossinsky AS, Moretz RC, Vorbrodt AW, Lassmann H, Carp RI (1983) Increased blood-brain barrier permeability in scrapie-infected mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 42:615–626
Wright JR, Calkins E, Humphrey RL (1977) Potassium permanganate r reaction in amyloidosis. Lab Invest 36:274–281
Yoshimura T, Tateishi J, Tsujihata M, Muro T, Mameya G, Nagataki S (1984) A case of spongiform encephalopathy with ataxia and amyloid plaques. Brain Nerve 36:789–795
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grant no. 59480215 from the Japanese Ministry of Education
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitamoto, T., Tateishi, J., Hikita, K. et al. A new method to classify amyloid fibril proteins. Acta Neuropathol 67, 272–278 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687812
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687812