Summary
This report deals with the clinical and neuropathological findings in two cases of subacute spongiform encephalopathy. Cerebral biopsies were performed in both cases and electron microscopy studies carried out.
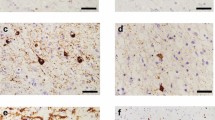
The cavities were lined by a membrane and were assumed therefore to have originated in the cytoplasm of nervous tissue elements. The presence of transitional stages between dilated astrocytic processes and large cavities makes it probable that the cavities originated from enlarged astroglial cytoplasm.
No abnormalities were found in small blood vessels.
Zusammenfassung
Die klinischen und neuropathologischen Befunde von 2 Fällen von „Encephalopathia spongiformis subacuta” werden berichtet. Beide Fälle wurden durch Hirnbiopsie verifiziert und elektronenmikroskopisch untersucht.
Die Hohlräume, welche das pathologische Bild der Hirnrinde kennzeichnen, sind von einer Membran begrenzt und werden daher vom Cytoplasma nervöser Gewebselemente abgeleitet. Der Nachweis von Übergangsformen zwischen Astrocytenfortsätzen und den Hohlräumen macht ihre Entstehung aus dem Cytoplasma vergrößerter Astrocyten wahrscheinlich. Die kleinen Blutgefäße zeigen keine pathologischen Veränderungen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crompton, M. R.: A case of sub-acute spongiform encephalopathy supporting a vascular pathogenesis. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)2, 291 (1963).
De Robertis, E., andH. M. Gerschenfeld: Submicroscopic morphology and function of glial cells. Int. Rev. Neurobiol.3 (1961).
Farquhar, M. G., andJ. F. Hartmann: Neuroglia structure and relationship as revealed by electron microscopy. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.16, 18 (1957).
Foley, J. M., andD. Denny-Brown: Sub-acute progressive encephalopathy with bulbar myoclonus. Excerpta. med. (Amst.), Sect. VIII,8, 782 (1955).
Heidenhain, A.: Klinische und anatomische Untersuchungen über eine eigenartige organische Erkrankung des Zentralnervensystems im Praesenium. Z. ges. Neurol. Psychol.118, 49 (1928).
Hallervorden, J.: In: Handbuch der Geisteskrankheiten Vol. II Spezieller Teil VII. Ed.O. Bumke: Berlin: Springer 1930.
Ishii, S., andE. Tany: Electron microscopic study of the blood-brain-barrier in brain swelling. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)1, 474 (1962).
Jakob, A.: Über eigenartige Erkrankungen des Zentralnervensystems mit bemerkenswertem anatomischem Befunde. Z. ges. Neurol. Psychiat.64, 147 (1921).
Jones D. P., andS. Nevin: Rapidly progressive cerebral degeneration (Sub-acute vascular encephalopathy) with mental disorder, focal disturbances and myoclonic epilepsy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.17, 148 (1954).
Meyer, A., D. Leigh, andC. E. Bagg: A rare presenile dementia associated with cortical blindness (Heidenhain's syndrome). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.17, 129 (1954).
Nevin, S., W. H. McMenemey, S. Behrman, andD. P. Jones: Sub-acute spongiform encephalopathy. A sub-acute form of encephalopathy attributable to vascular dysfunction (spongiform cerebral atrophy). Brain83, 519 (1960).
Pallis, C. A., andJ. D. Spillane: A sub-acute progressive encephalopathy with mutism, hypokinesia rigidity and myoclonus. A clinical and pathological account of three cases. Quart. J. Med.26, 349 (1957).
Siedler, H., andN. Malamud: Creutzfeldt-Jakob's disease. Clinico-pathologic report of 15 cases and review of the literature. (With special references to a related disorder designated as sub-acute spongiform encephalopathy.) J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.22, 381 (1963).
Schultz, R. L., E. A. Maynard, andD. C. Pease: Electron microscopy of neurons and neuroglia of cerebral cortex and corpus callosum. Amer. J. Anat.100, 369 (1957).
Torack, R. M., R. D. Terry, andH. M. Zimmerman: The line structure of cerebral fluid accumulation. I. Swelling secondary to cold injury. Amer. J. Path.35, 1135 (1959).
———: The line structure of cerebral fluid accumulation. II Swelling produced by triethyl tin poisoning and its comparison with that in the human brain. Amer. J. Path.36, 273 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 7 Figures in the Text
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marin, O., Vial, J.D. Neuropathological and ultrastructural findings in two cases of subacute spongiform encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol 4, 218–229 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00684130
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00684130