Summary
-
1.
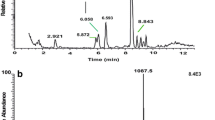
The molecular characteristics and physiological role of a partially purified small cardioactive neuropeptide (SCP) of the freshwater pulmonate snailLymnaea stagnalis were studied and compared with those of FMRFamide, an SCP discovered in clam ganglia.Lymnaea SCP, extracted from the central nervous system, and commercial FMRFamide co-elute on Sephadex G-15 columns, but SCP behaves differently from FMRF-amide, when chromatographed on the ion exchanger CM-Sephadex C-25. Moreover, it has a lowerR f value (0.60) on thin layer chromatograms than FMRFamide (0.75). SCP is sensitive to proteolytic enzymes. These data indicate thatLymnaea SCP is a small peptide which is not identical to FMRFamide.
-
2.
Lymnaea SCP is involved in the physiological regulation of the activity of various muscles. It stimulates the frequency of beat as well as the amplitude of the auricle and ventricle. It also stimulates the peristalsis of the oesophagus and causes contractions of the penis retractor muscle. These excitatory effects are similar to those of FMRFamide, suggesting thatLymnaea SCP and FMRFamide must be closely related.
-
3.
The role of SCP as a neurotransmitter is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNS :
-
central nervous system
- FMRFamide :
-
Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2
- SCP :
-
small cardioactive peptide
References
Boer HH, Schot LPC, Veenstra JA, Reichelt D (1980) Immunocytochemical identification of neural elements in the central nervous system of a snail, some insects, a fish and a mammal with an antiserum to the molluscan cardio-excitatory tetrapeptide FMRF-amide. Cell Tissue Res 213:21–27
Cottrell GA (1981) FMRFamide neuropeptides simultaneously increase and decrease K+ currents in an identified neurone. Nature 296:87–89
Cottrell GA (1983) Actions of FMRFamide and related peptides on snail neurones. In: Lever J, Boer HH (eds) Molluscan neuro-endocrinology. Mon R Neth Acad Sci. North-Holland, Amsterdam Oxford, pp 213–221
Contrell GA, Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1981) FMRFamide-like activity in the brain ofHelix aspersa and in a simple identified neurone. Comp Biochem Physiol [C] 70:103–107
Dockray GJ, Vaillant C, Williams RC (1981) New vertebrate brain-gut peptide related to a molluscan neuropeptide and an opioid peptide. Nature 292:656–657
Geraerts WPM, Leeuwen JPThM van, Nuyt K, de With ND (1981) Cardioactive peptides of the CNS of the pulmonate snailLymnaea stagnalis. Experientia 37:1168–1169
Geraerts WPM, With ND de, Ebberink RHM, Casteleijn E, Hogenes ThM (1983) Cardioactive peptides in the freshwater pulmonateLymnaea stagnalis. In: Lever J, Boer HH (eds) Molluscan neuro-endocrinology. Mon R Neth Acad Sci. North-Holland, Amsterdam Oxford, pp 196–202
Greenberg MJ, Price DA (1980) Cardioregulatory peptides in molluscs. In: Bloom FE (ed) Peptides: integrators of cell and tissue function. Raven Press, New York, pp 107–126
Hill RB, Welsh JH (1966) Heart, circulation, and blood cells. In: Wilbur KM, Yonge CM (eds) Physiology of mollusca, vol II. Academic Press, New York London, pp 126–174
Hughes J, Beumont A, Fuentes JA, Malfroy B, Unsworth C (1980) Opioid peptides: aspects of their origin, release and metabolism. J Exp Biol 89:239–255
Joosse J, Geraerts WPM (1983) Endocrinology. In: Wilbur K, Saleuddin ASM (eds) The mollusca, vol 4, Physiology, part I. Academic Press, New York, pp 317–406
Lehman H (1983) The distribution of an FMRFamide-like peptide inHelix aspersa. In: Lever J, Boer HH (eds) Molluscan neuroendocrinology. Mon R Neth Acad Sci. North-Holland, Amsterdam Oxford, pp 235–236
Lloyd PE (1982) Cardioactive neuropeptides in gastropods. Fed Proc 41:2948–2952
Morris HR, Panico M, Karplus A, Lloyd PE, Riniker B (1982) Elucidation by FAB-MS of the structure of a new cardioactive peptide fromAplysia. Nature 300:643–645
Owen G (1966) Digestion. In: Wilbur KM, Yonge CM (eds) Physiology of mollusca, vol II. Academic Press, New York London, pp 53–96
Plesch BEC, Jance C, Boer HH (1975) Gross morphology and histology of the musculature of the freshwater pulmonateLymnaea stagnalis (L.). Neth J Zool 25:332–352
Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1977) Purification and characterization of a cardioexcitatory neuropeptide from the central ganglia of a bivalve mollusc. Prep Biochem 7:261–281
Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1980) Pharmacology of the molluscan cardioexcitatory neuropeptide FMRFamide. Gen Pharmacol 11:237–241
Scheerboom JEM, Geldof AA (1978) A quantitative study of the assimilation of different diets in the pond snailLymnaea stagnalis (L.), introducing a method to prevent coprophagy. Proc K Ned Akad Wet Ser C 81:173–183
Schot LPC, Boer HH (1982) Immunocytochemical demonstration of peptidergic cells in the pond snailLymnaea stagnalis with an antiserum to the molluscan cardioactive tetrapeptide FMRF-amide. Cell Tissue Res 225:347–354
Wabnitz RW (1975) Functional states and fine structure of the contractile apparatus of the penis retractor muscle (PRM) ofHelix pomatia L. Cell Tissue Res 156:253–265
Wabnitz RW (1979) Neurogenic contractile activity of the penis retractor muscle ofHelix pomatia L.. Malacologia 18:533–538
Weber E, Evans CJ, Samuelson SJ, Barchas JP (1981) Novel peptide neuronal system in rat brain and pituitary. Science 214:1248–1251
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geraerts, W.P.M., de With, N.D., Vreugdenhil, E. et al. Studies on the physiological role of a partially purified small cardioactive neuropeptide ofLymnaea stagnalis . J Comp Physiol B 154, 29–34 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00683213
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00683213