Abstract
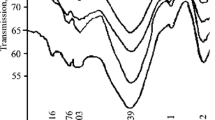
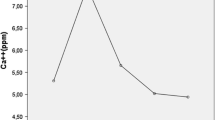
It was established that in the initial stage of heating enamel frit (below 200°C), its surface mainly desorbs water vapors. In further heating, carbon dioxide is desorbed more intensely. After the frit is softened (∼ 500°C), the evolution of steam becomes predominant again. The intensity of hydrogen and carbon dioxide evolution is insubstantial.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Steklo i Keramika, No. 12, p. 22, December, 1995.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shardakov, N.T., Kurumchin, É.K., Vdovin, G.K. et al. Gassing in heating of glass enamel frit. Glass Ceram 52, 346–347 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00679294
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00679294