Conclusions
-
1.
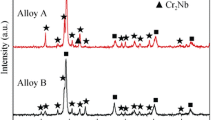
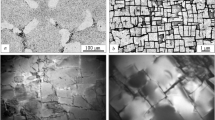
The phase composition of Nb−W−Zr−Ta−C alloys is more stable than that of Nb−W−Zr−Mo−C alloys at 1100°C.
-
2.
One can expect greater hardening of Nb−W−Zr−Ta−C alloys because the precipitating carbide phase, of the MC type rich in zirconium, is a more effective hardening phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
L. N. Kuz'minskaya and I. A. Sosulina, "Phase analysis of alloys based on niobium," Zavod. Lab., 9, 1029–1032 (1971).
G. Brauer and R. Lesser, Z. Metallk.,50, 8, 487–492 (1959).
F. Ostermann and F. Bollenrath, "On the precipitation behavior of niobium alloy D-43," Sixth Plansee Seminar, Vol. 22, 1–39 (1968).
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 11, pp. 45–46, November, 1974.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuz'minskaya, L.N., Sosulina, I.A. Effect of heat treatment of phase composition of niobium alloys. Met Sci Heat Treat 16, 951–952 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00663804
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00663804