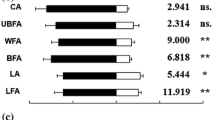
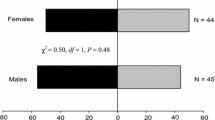
Summary
A method for measuring the attractive effect of odorous compounds on a population of pine weevilsHylobius abietis L. is described. Three substances, which strongly activated different groups of sensory cells (Mustaparta, 1975) were examined. Trans-verbenol, which excited selectively certain trichodeal cells had the highest attraction and dominated the attractive effect of α-pinene. The latter activated a special group of basiconic cells which indicated its importance as food attractant. The third compound, 5-hexen-2-one, activated a large number of olfactory receptor cells, but had almost no attractive effect on the weevils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brand, J. M., Bracke, J. W., Markovetz, A. J., Wood, D. L., Browne, L. E.: Production of verbenol pheromone by a bacterium isolated from bark beetles. Nature (Lond.)254, 136–137 (1975)
Hughes, P. R.: Effect of α-pinene exposure on trans-verbenol synthesis inDendroctonus ponderosae Hopk. Naturwissenschaften60, 261–262 (1973)
Hughes, P. R.:Dendroctonus: Production of pheromones and related compounds in response to host monoterpenes. Z. angew. Ent.73, 294–312 (1973)
Kafka, W. A.: Molekulare Wechselwirkungen bei der Erregung einzelner Riechzellen. Z. vergl. Physiol.70, 105–143 (1970)
Mustaparta, H.: Response of the pine weevil,Hylobius abietis L. (Col.: Curculionidae) to bark beetle pheromones. J. comp. Physiol.88, 395–398 (1974)
Mustaparta, H.: Responses of single olfactory cells in the pine weevilHylobius abietis L. (Col.: Curculionidae). J. comp. Physiol.97, 271–290 (1975)
Renwick, J. A. A., Hughes, P. R., Tantletin, DeJ.Ty: Oxidation products of pinene in the bark beetle,Dendroctonus frontalis. J. Insect Physiol.19, 1735–1740 (1973)
Schneider, D.: Elektrophysiologische Untersuchungen von Chemo- und Mechanorezeptoren der Antenne des SeidenspinnersBombyx mori L. Z. vergl. Physiol.40, 8–41 (1957)
Selander, J., Kalo, P., Kangas, E., Pertunen, V.: Olfactory behaviour ofHylobius abietis L. (Col.: Curculionidae). I. Response to several terpenoid fractions isolated from Scots pine phloem. Ann. Ent. Fenn.40, 108–115 (1974)
Vité, J. P., Bakke, A., Renwick, J. A. A.: Pheromones inIps (Coleoptera: Scolytidae): Occurrence and production. Can. Ent.104, 1967–1975 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was financed by the Norwegian Research Council for Sciences and Humanities NAVF, and also supported by Deutsche Akademische Austauschdienst DAAD.
I would like to thank Dr. S. Gothilf, Israel Institute for Biological Research, Tel Aviv, Dr. J. Jansen, Institute of Physiology, University of Oslo, and Dr. S. Grillner, Institute of Physiology, University of Gothenborg, for discussions. For constantly providing insects I am thankful to Oberforstmeister H. Niemeyer, Niedersächsische Forstliche Versuchsanstalt, Göttingen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mustaparta, H. Behavioural responses of the pine weevilHylobius abietis L. (Col.: Curculionidae) to odours activating different groups of receptor cells. J. Comp. Physiol. 102, 57–63 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657485
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657485