Abstract
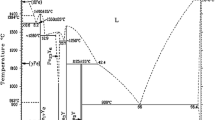
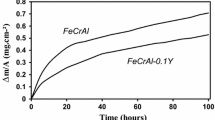
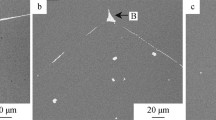
High-temperature sulfidation studies have been carried out on Fe-15Cr-4Al with and without 1% Y in the temperature range 700–1000°C in an H 2-H2 S environment over the sulfur pressure range of 10 −9−10−3 atm. Two-layered and three-layered sulfide scales were observed in both alloys at low and high sulfur pressures, respectively. The pegging phenomenon, similar to that occurring in high-temperature oxidation, across the innermost layer and substrate was observed in the case of the yttrium-containing alloy. Yttrium was found to be associated with aluminum and chromium sulfides. The role of yttrium was more evident at low than at high sulfur pressures and was found to reduce the parabolic rate constants by a factor of about one-half to one-seventh, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. N. Strafford,Met. Rev. 138, 153 (1969).
S. Mrowec, inProceedings of the International Symposium on Properties of High Temperature Alloys, Z. A. Foroulis and F. S. Pettit, eds. The Electrochemical Society, Princeton, 1976, p. 413.
P. Kofstad,High-Temperature Oxidation of Metals (Wiley, New York, 1966).
K. Nishida, T. Narita, T. Tani, and G. Sasaki,Oxid. Met. 14, 65 (1980).
K. Nishida and K. Godlewski,Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on Reactivity of Solids (Cracow, Poland, 1980), p. 170.
K. Nishida, High-Temperature Sulphidation of Iron and Its Alloys in Low Sulphur Pressures,Proceedings of the Japan Institute of Metals, Iron Steel Conference, 1983.
T. Narita and K. Nishida, Grain boundary sulfidation of Fe-Cr alloys in H2S-H2 atmosphere at high temperature,Proceedings of the Japan Institute of Metals, Iron Steel Conference, 1983.
T. Narita and W. W. Smeltzer,Oxid. Met. 21, 39 (1984).
T. Narita and W. W. Smeltzer,Oxid. Met. 21, 57 (1984).
P. C. Patnaik and W. W. Smeltzer,Oxid. Met. 23, 53 (1985).
P. C. Patnaik and W. W. Smeltzer,J. Electrochem. Soc. 132, 1226 (1985).
S. Mrowec, S. Tochowicz, T. Werber, and J. Podhorodecki,Cones. Sci. 7, 697 (1967).
S. Mrowec,Werkst. Korros. 31, 371 (1980).
E. M. Jallouli, J. P. Larpin, M. Lambertin, and J. C. Colson,Oxid. Met. 11, 335 (1977).
E. M. Jallouli, J. P. Larpin, M. Lambertin, and J. C. Colson,J. Electrochem. Soc. 126, 2254 (1979).
S. Mrowec and K. Przybylski,Oxid. Met. 23, 107 (1985).
I. M. Allam, D. P. Whittle, and J. Stringer,Oxid. Met. 12, 35 (1978).
S. Zelouf and G. Simkovid, inHigh-Temperature Metallic Corrosion in Sulfur and Its Compounds, Z. A. Foroulis ed. (The Electrochemical Society, Princeton, 1970), p. 119.
E. J. Vineberg and D. L. Douglass,Proceedings of the Japan Institute of Metals, Iron Steel Conference, 1983, p. 507.
A. S. Kahn, C. E. Lowell, and C. A. Barrett,J. Electrochem. Soc. 127, 670 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, D., Prakash, S., Mehta, M.L. et al. Effect of 1 wt.% yttrium addition on high-temperature sulfidation behavior of Fe-15Cr-4Al alloy. Oxid Met 28, 127–153 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00656703
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00656703