Abstract
The transepithelial voltage (Ψ ms) of rat rectum in vivo increases for several hours in experiments under general anaesthesia. So far this was attributed by indirect evidence to increasing aldosterone plasma levels during the course of the experiment.
We performed direct measurements of aldosterone and corticosterone plasma concentrations during intestinal perfusion experiments on barbiturate anaesthetized rats. Experiments were terminated for blood sampling at 10, 75, 300, 400, 800, or 1,800 min, respectively.
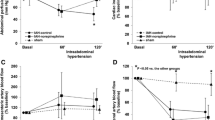
(i) After 75 min of anaesthesia, surgical preparation was finished and plasma levels of aldosterone and of corticosterone were found increased by the factors 5 and 3, respectively, as compared to conscious controls. (ii) During the following 12 h, aldosterone further increased to levels 10 times as high as those of controls. In contrast, during the same period corticosterone slowly decreased but still remained elevated as compared to controls. (iii) The increase of both hormones was attenuated when abdominal surgery was omitted. (iv) The use of pentobarbital (Nembutal) instead of thiobarbital (Inactin) did not influence the adrenal response. (v) In adrenalectomized rats a continous substitution with 65 ng·h−1·kg−1 BWT aldosterone resulted in plasma levels as high as in conscious intact animals. (vi) RectalΨ ms started to move to higher lumen-negative values with a time delay of 1–1 1/2 h as compared with the increase of hormone levels.Ψ ms then stayed elevated until to the end of the experiments.
We conclude that in vivo experiments of several hours duration in thio- or pentobarbital anaesthetized rats take place under conditions of aldosterone and corticosterone plasma levels which are high as compared to those of conscious unstressed animals. The different time course of aldosterone and corticosterone plasma levels after the end of surgery would be in accord with a stimulatory effect of anaesthesia on both renin and ACTH, plus an additional stimulatory effect of abdominal surgery on ACTH alone.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Allen MB, Mahesh VB (1977) The pituitary. A current review. Proceedings of a Symposium on the pituitary. NY Acad Sci Press, New York
Bastl CP, Binder HJ, Hayslett JP (1980) Role of glucocorticoids and aldosterone in maintenance of colonic cation transport. Am J Physiol 238:F181-F186
Blair-West JR, Coghlan JP, Denton DA, Scoggins BA, Wintour EM, Wright RD (1970) The onset of effects of ACTH, angiotensin II and raised plasma potassium concentration on the adrenal cortex. Steroids 15:433–448
Cade R, Perenich P (1965) Secretion of aldosterone by rats. Am J Physiol 208:1026–1030
Cooper CE, Nelson DH (1962) ACTH levels in plasma in preoperative and surgically stressed patients. J Clin Invest 41:1599–1605
Crabbé J (1961) Stimulation of active sodium transport by the isolated toad bladder with aldosterone in vitro. J Clin Invest 40:2103–2110
Edmonds CJ, Marriott J (1967) The effect of aldosterone and adrenalectomy on the electrical potential difference of rat colon and on the transport of sodium, potassium, chloride and bicarbonate. J Endocrinol 39:517–531
Edmonds CJ, Marriott J (1968) Factors influencing the electrical potential across the mucosa of rat colon. J Physiol 194:457–478
Efstratopoulos AD, Peart WS, Wilson GA (1974) The effect of aldosterone on colonic potential difference and renal electrolyte excretion in normal man. Clin Sci Molec Med 46:489–499
Eilers EA, Peterson RE (1964) Aldosterone secretion in the rat. In: Bauliev EE, Robel P (eds) Aldosterone. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 251–264
Frizzell RA, Schultz SG (1978) Effect of aldosterone on ion transport by rabbit colon in vitro. J Membr Biol 39:1–26
Fromm M, Hegel U (1978) Segmental heterogeneity of epithelial transport in rat large intestine. Pflügers Arch 378:71–83
Fromm M, Lüderitz S, Hegel U (1980) Mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid action on epithelial transport in the rectum of adrenalectomized rats. Fed Proc 39:492
Guillemin R, Dear WE, Liebelt RA (1959) Nycthemeral variations in plasma free corticosteroid levels of the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 101:394–395
Hackl JM, Skrabal F (1975) Das Verhalten von Plasma-reninaktivität, Plasmaaldosteron und Elektrolytbilanz in der postoperativen Phase. Anaesthesist 24:477–482
Hierholzer K, Lange S (1974) The effects of adrenal steroids on renal function. In: Thurau K (ed) Kidney and urinary tract physiology. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 273–333
Hume DM, Bell CC, Bartter F (1962) Direct measurement of adrenal secretion during operative trauma and convalescence. Surgery 52:174–187
Keith LD, Winslow JR, Reynolds RW (1978) A general procedure for estimation of corticosteroid response in individual rats. Steroids 31:523–531
Kinson GA, Singer B (1968) Sensitivity to angiotensin and adrenocorticotrophic hormone in the sodium deficient rat. Endocrinology 83:1108–1116
Komor J, Müller J (1979) Effects of prolonged infusions of potassium chloride, adrenocorticotrophin or angiotensin II upon serum aldosterone concentration and the conversion of corticosterone to aldosterone in rats. Acta Endocrinol 90:680–691
Lindström CG, Rosengren J-E, Fork F-T (1979) Colon of the rat. An anatomic, histologic and radiographic investigation. Acta Radiol [Diagn] 20:523–536
Oyama T, Takiguchi M (1970) Plasma levels of ACTH and cortisol in man during halothane anaesthesia and surgery. Anesth Analg Curr Res 49:363–366
Oyama T, Saito T, Nakai Y, Imura H (1974) Effects of anaesthesia and surgery on plasma ACTH levels in man. Anesth Analg Curr Res 54:430–438
Oyama T, Taniguchi K, Jin T, Satone T, Kudo T (1979) Effects of anaesthesia and surgery on plasma aldosterone concentration and renin activity in man. Br J Anaesth 51:747–751
Palmore WP, Mulrow PJ (1967) Control of aldosterone secretion by the pituitary gland. Science 158:1482–1484
Parsons DS (1968) Methods for investigation of intestinal absorption. In: Handbook of physiology, sect VI, vol 3: Cade CF (ed) Intestinal absorption. Am Physiol Soc, Washington DC, pp 1177–1216
Pettinger WA, Tanaka K, Keeton K, Campbell WB, Brooks SN (1975) Renin release, an artifact of anesthesia and its implications in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 148:625–630
Schöneshöfer M (1975) Suitability of four standard curve models for computer evaluation of steroid and peptide radioimmunoassays. Acta Endocrinol (Kbh) Suppl 193:116
Schöneshöfer M (1977) Simultaneous determination of eight adrenal steroids in human serum by radioimmunoassay. J Steroid Biochem 8:995–1009
Sharp GWG, Leaf A (1964) Biological action of aldosterone in vitro. Nature 202:1185–1188
Singer B, Stack-Dunne MP (1955) The secretion of aldosterone and corticosterone by the rat adrenal. J Endocrinol 12:130–145
Stricker EM, Vagnucci AH, McDonald RH, Leenen FH (1979) Renin and aldosterone secretions during hypovolemia in rats: relation to NaCl intake. Am J Physiol 237:R45–R51
Ullrich JK, Frömter E, Baumann K (1969) Micropuncture and microanalysis in kidney physiology. In: Passow H, Staempfli R (eds) Laboratory techniques in membrane biophysics. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 106–129
Wernze H, Hilfenhaus M, Rietbrock R, Schuettke R, Kuehn K (1975) Plasma-Renin-Aktivität und Plasma-Aldosteron unter Narkose sowie Operationsstress und Beta-Receptoren-Blockade. Anaesthesist 24:471–476
Yun JCH, Donahue JJ, Bartter FC, Kelly GD (1978) Effect of pentobarbital anesthesia and laparotomy on plasma renin activity in the dog. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 57:412–416
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fromm, M., Oelkers, W., Hegel, U. et al. Time course of aldosterone and corticosterone plasma levels in rats during general anaesthesia and abdominal surgery. Pflugers Arch. 399, 249–254 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652747
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652747