Abstract
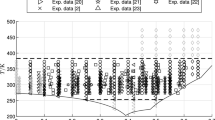
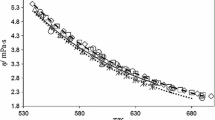
Viscosity measurements of a series of univalent electrolytes in water have been performed with an automatic dual viscometer system, covering the temperature range of 5 to 95°C. Results are discussed in terms of Jones-DoleB andD coefficients. TheB coefficients of the salts are divided into their ionic contributions according toB(K+)=B(Cl−) at all temperatures. On a simple model intrinsic and structural contributions inB are calculated for the different ions. The structural term depends exponentially on the temperature in a unique manner, independent of the ion (except for Li+).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Jones and M. Dole,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 51, 2950 (1929).
G. Jones and S. K. Talley,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 55, 4124 (1933).
H. Falkenhagen,Theorie der Elektrolyte (S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart, 1971), p. 256.
G. Jones and S. K. Talley,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 55, 624 (1933).
M. Kaminsky,Z. Phys. Chem. N.F. 5, 154 (1955).
M. Kaminsky,Z. Phys. Chem. N.F. 8, 173 (1956).
M. Kaminsky,Z. Phys. Chem. N.F. 12, 206 (1957).
E. Hückel and H. Schaaf,Z. Phys. Chem. N.F. 21, 326 (1959).
R. H. Stokes and R. Mills,Viscosity of Electrolytes and Related Properties (Pergamon, New York, 1965), Chapters 2 and 4.
R. L. Kay, T. Vituccio, C. Zawoyski, and D. F. Evans,J. Phys. Chem. 70, 2336 (1966).
J. E. Desnoyers and G. Perron,J. Solution Chem. 1, 199 (1972).
G. S. Kell,J. Chem. Eng. Data 12, 66 (1967).
R. C. Hardy and R. L. Cottington,J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 42, 573 (1949);
J. F. Swindels, J. R. Coe, Jr., and T. B. Godfrey,J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 48, 1 (1952)
R. S. Marvin and D. L. Hogenboom inAmerican Institute of Physics Handbook, D. E. Gray, ed. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1972), 3rd edn., pp. 2–187.
J. Kestin, M. Sokolov, and W. A. Wakeham,J. Phsy. Chem. Ref. Data 7, 941 (1978).
K. G. Lawrence,Chem. Ind., 1338 (1966).
L. D. Eicher and B. J. Zwolinski,J. Phys. Chem. 75, 2016 (1971).
W. M. Cox and J. H. Wolfenden,Proc. Roy. Soc. A 145, 475 (1934).
G. Jones and R. E. Stauffer,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 59, 1630 (1937).
M. R. Cannon, R. E. Manning, and J. D. Bell,Anal. Chem. 32, 355 (1960).
R. S. Marvin,J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand Sect. A 75, 535 (1971).
D. Eagland and G. Pilling,J. Phys. Chem. 76, 1902 (1972).
Gmelin,Handbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (Springer Verlag, Berlin, 8th edition).
S. Schiavo, B. Scrosati, and A. Tommasini,Ric. Sci. 37, 211 (1967).
O. Kratky, H. Leopold, and H. Stabinger,Angew. Phys. 27, 273 (1969).
P. Picker, E. Tremblay, and C. Jolicoeur,J. Solution Chem. 3, 377 (1974).
F. A. Goncalves and J. Kestin,Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 81, 1156 (1977).
N. Martinus, C. D. Sinclair, and C. A. Vincent,Electrochim. Acta 22, 1183 (1977).
W. D. Kraeft and J. Einfeldt,Z. Phys. Chem. 237, 267 (1968);239, 415 (1968).
A. Einstein,Ann. Phys. 19, 289 (1906);34, 591 (1911).
R. Simha,J. Phys. Chem. 44, 25 (1940).
R. W. Gurney,Ionic Processes in Solution (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1953), p. 168.
H. S. Frank and W. Y. Wen,Discuss. Faraday Soc. 24, 133 (1957).
M. Kaminsky,Discuss. Faraday Soc. 24, 171 (1957).
G. K. Batchelor,Introduction to Fluid Dynamics (Cambridge University Press, 1967), Chapter XVIII, p. 253.
T. F. Ford,J. Phys. Chem. 64, 1168 (1960).
S. Glasstone, K. J. Laidler, and H. Eyring,The Theory of Rate Processes (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1941), Chapter IX.
J. H. Hildebrand,Viscosity and Diffusivity (Wiley, New York, 1977).
H. S. Frank and M. W. Evans,J. Chem. Phys. 13, 507 (1945).
R. A. Robinson and R. H. Stokes,Electrolyte Solutions, 2nd rev. edn. (Butterworths, London, 1965), p. 128.
D. G. Thomas,J. Colloid Sci. 20, 267 (1965).
V. Vand,J. Phys. Chem. 52, 277 (1948).
A. T. Hagler, H. A. Scheraga, and G. Némethy,J. Phys. Chem. 76, 3229 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Out, D.J.P., Los, J.M. Viscosity of aqueous solutions of univalent electrolytes from 5 to 95°C. J Solution Chem 9, 19–35 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00650134
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00650134