Abstract
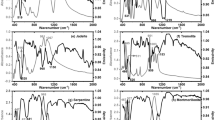
Extinction coefficients were measured for three kind of hydrous silicate minerals, montmorillonite, chlorite and serpentine, from 7 to 140 μm. The infrared extinction coefficients of these minerals show (1) a few broad bands in the mid-infrared region and (2) a less steep wavelength-dependence in the far-infrared region, in contrast to those of high-temperature magnesium silicates. In the far-infrared region, montmorillonite shows a λ−0.8±0.1 dependence (λ, the wavelength) without any band structure, chlorite has a double maxima structure around 80 μm, and serpentine shows a rather steep dependence with a small peak at 77 μm.
The changes of mid-infrared spectra by heating were measured. Change in chlorite spectrum is the most significant. Many fine features appear by heating and then they disappear. Above 900°C one broad feature remains around 10 μm. Fine features of the montmorillonite spectrum disappear by heating. For serpentine, many new peaks appear and the spectrum resembles the spectrum of olivin. In near-infrared a band around 2.72 μm disappears by heating.
Extinction coefficients at very low temperatures were measured in the far-infrared region. For montmorillonite and serpentine, the spectrum is the same as that at room temperature. The double peaks of chlorite around 80 μm become higher.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell, M. F., Elias, J. H., Gezari, D. Y., Harvey, P. M., Hoffman, W. F., Hudson, H. S., Neugebauer, G., Soifer, B. T., Werner, M. W., and Westbrook, W. E.: 1976,Astrophys. J. 208, 396.
Gillett, F. C. and Forrest, W. J.: 1973,Astrophys. J. 179, 483.
Knacke, R. F. and Krätschmer, W.: 1980,Astron. Astrophys. 92, 281.
Koike, C., Hasegawa, H., and Manabe, A.: 1980,Astrophys. Space Sci. 67, 495.
Koike, C., Hasegawa, H., Asada, N., and Hattori, T.: 1981,Astrophys. Space Sci. 79, 77.
Merrill, K. M., Russell, R. W., and Soifer, B. T.: 1976,Astrophys. J. 207, 763.
Noguchi, K., Maihara, T., Okuda, H., Sato, S., and Mukai, T.: 1977,Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 29, 511.
Seki, J. and Hasegawa, H.: 1981,Proc. 14th ISAS Lunar and Planetary Symposium (Tokyo), 175.
Serratosa, J. M.: 1961,Proc. 9th National Clay Conference, Pergamon Press, London.
Tokunaga, A. T., Erickson, E. F., and Caroff, L. J.: 1978,Astrophys. J. 224, L19.
Zaikowski, A., Knacke, R. F., and Porco, C. C.: 1975,Astrophys. Space Sci. 35, 97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koike, C., Hasegawa, H. & Hattori, T. Mid- and far-infrared extinction coefficients of hydrous silicate minerals. Astrophys Space Sci 88, 89–98 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00648991
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00648991