Abstract
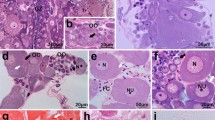
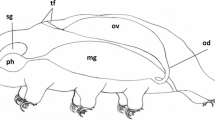
We describe a provitellogenic stage, a previously unrecognized stage of follicle development in moths, and show that oocytes begin yolk sphere formation prior to the development of patency by the follicular epithelium. The vitellogenic activities of follicles from pharate adult femalePlodia interpunctella (Hübner) were determined by visualizing the subunits of vitellin (YP1 and YP3) and the follicular epithelium yolk protein (YP2 and YP4) using monospecific antisera to each subunit to immunolabel whole-mounted ovaries or ultrathin sections. At 92 h after pupation, yolk spheres that contained only YP2 began to proliferate in the oocytes. The inter-follicular epithelial cell spaces were closed at 92 h making vitellogenin inaccessible to the oocyte, and consequently, the vitellin subunits were not observed in the yolk spheres. YP2 uptake most likely occurred across the brush border from the follicular epithelial cells to the oocyte at this time. At 105 h, the inter-follicular epithelial cell spaces appeared closed yet trace amounts of labeling for vitellin were observed in the spaces and also in the yolk spheres along with YP2. Equivalent labeling for all four YPs in yolk spheres was finally observed at 112 h after pupation when the follicular epithelium had become patent. These data indicate that the provitellogenic stage is an extended transition period between the previtellogenic and vitellogenic stages that lasts for approximately 13 h, and it is marked at the beginning by YP2 yolk sphere formation in the oocyte and at the end by patency in the follicular epithelium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bast RE, Telfer WH (1976) Follicle cell protein synthesis and its contribution to the yolk of theCecropia moth oocyte. Dev Biol 52:83–97
Bean DW, Shirk PD, Brookes VJ (1988) Characterization of yolk proteins from the eggs of the Indianmeal moth,Plodia interpunctella. Insect Biochem 18:199–210
Brennan MD, Weiner AJ, Goralski TJ, Mahowald AP (1982) The follicle cells are a major site of vitellogenin synthesis inDrosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol 89:225–236
Butterworth FM, Burde VS, Bownes M (1992) Mutant yolk proteins lead to female sterility inDrosophila. Dev Biol 154:182–194
Cruickshank WJ (1971) Follicle cell protein synthesis in moth oocytes. J Insect Physiol 17:217–232
Cruickshank WJ (1972) Ultrastructural modification in the follicle cells and egg membranes during development of flour moth oocytes. J Insect Physiol 18:485–498
Cummings MR, King RC (1970) The cytology of the vitellogenic stages of oogenesis inDrosophila melanogaster. II. Ultrastructural investigations on the origin of protein yolk spheres. J Morphol 130:467–478
Davey KG (1981) Hormonal Control of vitellogenin uptake inRhodnius prolixus Stal. Am Zool 21:701–705
Engelmann F (1979) Insect vitellogenin: Identification, biosynthesis, and role in vitellogenesis. Adv Insect Physiol 14:49–108
Giorgi F, Jacob J (1977) Recent findings on oogenesis ofDrosophila melanogaster. I. Ultrastructural observations on the developing ooplasm. J Embryol Exp Morphol 38:115–124
Hagedorn HH, Kunkel JG (1979) Vitellogenin and vitellin in insects. Ann Rev Entomol 24:475–505
Irie K, Yamashita O (1983) Egg-specific protein in the silkworm,Bombyx mori: Purification, properties, localization and titre changes during oogenesis and embryogenesis. Insect Biochem 13:71–80
Issac PG, Bownes M (1982) Ovarian and fat-body vitellogenin synthesis inDrosophila melanogaster. Eur J Biochem 123:527–534
King RC, Aggarwal SK (1965) Oogenesis inHyalophora cecropia. Growth 29:17–83
Kunkel JG, Nordin JH (1985) Yolk proteins. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology, vol. 1. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 84–111
Leung H, Palli SR, Locke M (1989) The localization of arylphorins in an insect,Calpodes ethlius. J Insect Physiol 35:223–231
Mahowald AP (1972) Ultrastructural observations on oogenesis inDrosophila. J Morphol 137:29–48
Mollenhauer HH (1964) Plastic embedding mixtures for use in electron microscopy. Stain Technol 39:111–114
Pratt GE, Davey KG (1972) The corpus allatum and oogenesis inRhodnius prolixus (Stal.). J Exp Biol 56:201–214
Raikhel AS, Dhadialla TS (1992) Accumulation of yolk proteins in insect oocytes. Ann Rev Entomol 37:217–251
Raikhel AS, Lea AO (1985) Hormone-mediated formation of the endocytic complex in mosquito oocytes. Gen Compar Endocrinol 57:422–433
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Shaaya E, Shirk PD, Zimowska G, Plotkin S, Young NJ, Rees HH, Silhacek DL (1993) Declining ecdysteroid levels are temporally correlated with the initiation of vitellogenesis during pharate adult development in the Indianmeal moth,Plodia interpunctella. Insect Biochem Molec Biol 23:153–158
Silhacek DL, Miller GL (1972) Growth and development of the Indian meal moth,Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera: Phycitidae), under laboratory mass-rearing conditions. Ann Entomol Soc Am 65:1084–1087
Shirk PD (1987) Comparison of yolk production in seven pyralid moth species. Int J Invert Reprod Dev 11:173–188
Shirk PD, Bean DW, Brookes VJ (1990) Ecdysteroids control vitellogenesis and egg maturation in pharate adult females of the Indianmeal moth,Plodia interpunctella. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 15:183–199
Shirk PD, Bean D, Millemann AM, Brookes VJ (1984) Identification, synthesis, and characterization of the yolk polypeptides ofPlodia interpunctella. J Exp Zool 232:87–98
Shirk PD, Zimowska G, Silhacek DL, Shaaya E (1992) Initiation of vitellogenesis in pharate adult females of the Indianmeal moth,Plodia interpunctella. Arch Insect Physiol Biochem 21:53–64
Telfer WH (1961) The route of entry and localization of blood proteins in the oocytes of saturniid moths. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:747–759
Telfer WH (1965) The mechanism and control of yolk formation. Ann Rev Entomol 10:161–184
Telfer WH, Huebner E, Smith DS (1982) The cell biology of vitellogenic follicles inHyalophora andRhodnius. In: King RC, Akai H (eds) Insect ultrastructure, vol. 1. Plenum Press, New York and London, pp 118–149
Woodruff RI, Telfer WH (1990) Activation of a new physiological state at the onset of vitellogenesis inHyalophora follicles. Dev Biol 138:410–420
Yamauchi H, Yoshitake N (1984) Developmental stages of ovarian follicles in the silkworm,Bombyx mori L. J Morphol 179:21–31
Zimowska G, Silhacek DL, Shaaya E, Shirk PD (1991) Immunofluorescent analysis of follicular growth and development in whole ovaries of the Indian-meal moth. J Morphol 209:215–228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimowska, G., Shirk, P.D., Silhacek, D.L. et al. Yolk sphere formation is initiated in oocytes before development of patency in follicles of the moth,Plodia interpunctella . Roux's Arch Dev Biol 203, 215–226 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636337
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636337