Abstract
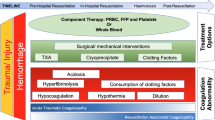
Coagulation disorders in traumatic-haemorrhagic shock need not represent a simple coagulation problem. They may also occur as a complex of local and disseminated intravascular consumption, dilution, extravascular loss and depressed synthesis of coagulation factors. In the severely bleeding patient with a haemorrhagic diathesis heparin is contraindicated because it does not normalize coagulability immediately. Therefore, it fails to stop haemorrhage and the shock becomes untreatable. Fresh frozen plasma, however, has proved to be suitable as a simultaneous substitution therapy for the coagulation disorder and the hypovolaemic shock. 25 patients suffering from severe traumatic-hemorrhagic shock associated with coagulation disorders and haemorrhagic diathesis were successfully treated with fresh frozen plasma, after conventional shock therapy had failed over a period of 2 hours. The success was documented clinically and by numerous laboratory tests. Thrombocytopenia has only a secondary responsibility for the haemorrhagic state.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amuis, A., Amris, C. J.: Turnover and distribution of 131iodine labelled human fibrinogen. Thrombus. Diathes. haemorrh. (Stuttg.) 11, 404–422 (1964)
Benz, J. J.: Clotting factors and fibrinogen split products in the extravascular space. Thrombos. Diathes. haemorrh. (Stuttg.) 19, 226–235 (1968)
Bergentz, S. E., Lewis, D., Ljungqvist, U.: Die Lunge im Schock: Thrombocytenanhäufung nach Trauma und intravasale Gerinnung. Langenbecks Arch. Klin. Chir. 329, 658–664 (1971)
Bergentz, S. E.: Ursachen der disseminierten intravaskulären Gerinnung im Schock. In: Schock, Stoffwechselveränderungen und Therapie, W. E. Zimmermann und I. Staib (Hrsg.), pp. 419–422, Stuttgart: Schattauer 1970
Cafferata, H. T., Aggeler, P. M., Robinson, A. J.: IntravascuJar coagulation in the surgical patient. Amer. J. Surg. 118, 281–291 (1969)
Clauss, A.: Gerinnungsphysiologische Schnellmethode zur Bestimmung des Fibrinogens. Acta haemat. (Basel) 17, 237–246 (1957)
Deykin, D.: The clinical challenge of disseminated intravascular coagulation. New Engl. J. Surg. 283, 636–643 (1970)
Duckert, F.: Diagnostic différentiel de la coagulation intravasculaire et de la fibrinolyse. Schweiz. med. Wschr. 94, 1375–1376 (1964)
Egan, E. L., Bowie, E. J. W., Kazmier, F. J., Gilchrist, G. S., Woods, J. W., Owen, C. A.: Effect of surgical operations on certain tests used to diagnose intravascular coagulation and fibrinolysis. Mayo clin. Proc. 49, 658–664 (1974)
Hardaway, R. M.: Shock and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thrombos. Diathes. haemorrh. (Stuttg.), Suppl. 20, 121–246 (1966a)
Hardaway, R. M.: Pathological evidence of disseminated intravascular coagulation in human shock. Thrombos. Diathes. haemorrh. (Stuttg.), Suppl. 20, 249–254 (1966b)
Hardaway, R. M.: Gerinnungsfaktoren im Schock. In: Schock, Stoffwechselveränderungen und Therapie, W. E. Zimmermann und I. Staib (Hrsg.), pp. 423–426. Stuttgart: Schattauer 1970
Heene, D. L.: Diagnostik der Gerinnungsstörungen im Schock. In: Schock, Stoffwechselveränderungen und Therapie, W. E. Zimmermann und I. Staib (Hrsg.), pp. 413–418. Stuttgart: Schattauer 1970
Herold, R., Maier, W. E., Straub, P. W.: Surface accumulation and reduced survival of J 125 Fibrinogen during wound healing. Helv. med. Acta 37, 57–61 (1973)
Kappeler, R.: Das Verhalten von Faktor V im Serum unter normalen und pathologischen Bedingungen. Z. klin. Med. 153, 103–113 (1955)
Koller, F., Loeliger, A., Duckert, F.: Experiments on a new clotting factor (factor VII). Acta haemat. (Basel) 6, 1–18 (1951)
Lasch, H. G., Heene, D. L., Hutz, K., Sandritter, W.: Pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and therapy of consumption-coagulopathy (“Verbrauchskoagulopathie”). Amer. J. Cardiol. 20, 381–391 (1967)
Lasch, H. G., Huth, K., Heene, D. L., Müller-Berghaus, G., Hörder, M.-H., Janzarik, H., Mittermayer, C., Sandritter, W.: Die Klinik der Verbrauchskoagulopathie. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 96, 715–727 (1971)
Lim, R. C., Olcott, C., Robinson, A. J., Blaisdell, F. W.: Platelet response and coagulation changes following massive blood replacement. J. Trauma 13, 577–581 (1973)
Loew, D.: Das Verhalten der Thrombocyten im Verbrennungsschock. Med. Welt 23, 259–260 (1972)
Matthias, F. R.: Nachweis von Fibrin monomeren und Fibrinogenspaltprodukten im Plasma bzw. Serum durch Adsorption an insolubilisiertes Fibrinogen und Fibrinmonomer. Intensivmedizin 12, 100–104 (1975)
Merskey, C., Johnson, A. J., Pert, J. H., Wohl, H.: Pathogenesis of fibrinolysis in defibrination syndrome. Effect of heparin administration. Blood 24, 701–715 (1964)
Müller, G.: Disseminierte intravaskuläre Gerinnung und Schock. Schweiz. med. Wschr. 102, 986–990 (1972)
Remmle, W., Loew, D.: Pathophysiologie der Thrombocyten im Schock. Klin. Wschr.50, 3–9 (1973)
Silver, D.: Coagulopathies and Surgeons. J. surg. Res. 16, 429–439 (1974)
Straub, P. W.: Diagnose und Therapie der intravasalen Gerinnung. Schweiz. med. Wschr. 101, 1361–1366 (1971)
Straub, P. W.: A case against Heparin therapy of intravascular coagulation. Thrombos. Diathes. haemorrh. (Stuttg.) 33, 107–112 (1974)
String, T., Robinson, A. J., Blaisdell, F. W.: Massive trauma. Effect of intravascular coagulation on prognosis. Arch. Surg. 102, 406–411 (1971)
Wilson, R. F., Mammen, E., Walt, A. J.: Eight years of experience with massive blood transfusions. J. Trauma 11, 275–285 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helme, H.J., Nyman, D., Burri, H. et al. Management of bleeding disorders in traumatic-haemorrhagic shock states with deep frozen fresh plasma. Europ. J. Intensive Care Med 2, 157–161 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00624608
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00624608