Summary
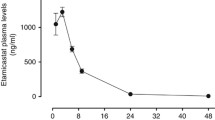
Acute sublingual administration of nifedipine 10–20 mg to 13 hypertensive patients caused a rapid decrease in blood pressure (BP) and a concomitant increase in heart rate (HR), plasma noradrenaline (NA) and plasma renin activity (PRA); there was no significant change in plasma adrenaline (A) or aldosterone (ALDO). Basal PRA was the major determinant of the rise in PRA, as a close correlation was present between the basal value and the increase caused by nifedipine (r=0.92, p<0.001). The rise in PRA was also correlated with the plasma concentration of nifedipine after 60 min (r=0.80, p<0.01), but it was not correlated with the decrease in BP, the rise in HR or the increase in NA. Nifedipine 30–60 mg daily for 6 weeks caused a reduction in mean BP from 133 to 113 mmHg (p<0.001). Body weight and serum potassium decreased but no consistent change was noted in NA, PRA, ALDO or 24 h-excretion of catecholamines. A significant correlation was present between the change in NA and that in PRA (r=0.74, p<0.01). The alterations in the various parameters in the acute and chronic studies were not correlated. The findings indicate that different regulatory mechanisms are activated during acute and chronic administration of nifedipine. It is suggested that an initial rise in sympathetic activity gradually decreases during prolonged therapy, but it still remains a determinant of PRA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki, K., Yoshida, T., Kato, S., Tazumi, K., Sato, I., Takikawa, K., Hotta, K.: Hypotensive action and increased plasma renin activity by Ca2+ antagonist (Nifedipine) in hypertensive patients. Jpn. Heart J.17, 479–484 (1976)
Christensen, N.J.: Plasma noradrenaline and adrenaline in patients with thyrotoxicosis and myxoedema. Clin. Sci. Mol. Med.45, 163–171 (1973)
Davis, J.O., Freeman, R.H.: Mechanisms regulating renin release. Physiol. Rev.56, 1–56 (1976)
Giese, J., Jørgensen, M., Nielsen, M.D., Lund, J.O., Munck, O.: Plasma renin concentration measured by use of radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest.26, 355–367 (1970)
Ibsen, H., Rasmussen, K., Ærenlund Jensen, H., Leth, A.: Changes in plasma volume and extracellular fluid volume after addition of hydralazine to propranolol treatment in patients with hypertension. Acta Med. Scand.203, 419–423 (1978)
Klütsch, K., Schmidt, P., Grosswendt, J.: Der Einfluß von BAY a 1040 auf die Nierenfunktion des Hypertonikers. Arzneim.-Forsch.22, 377–380 (1972)
Koch-Weser, J.: Vasodilator drugs in the treatment of hypertension. Arch. Intern. Med.133, 1017–1027 (1974)
Lederballe Pedersen, O., Mikkelsen, E.: Acute and chronic effects of nifedipine in arterial hypertension. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.14, 375–381 (1978)
O'Malley, K., Velasco, M., Wells, J., McNay, J.L.: Control plasma renin activity and changes in sympathetic tone as determinants of minoxidil-induced increase in plasma renin activity. J. Clin. Invest.55, 230–235 (1975)
Pettinger, W.A., Mitchell, H.C.: Renin release, saralasin, and the vasodilator-beta-blocker drug interaction in man. N. Engl. J. Med.292, 1214–1217 (1975)
Rask-Madsen, J., Bruusgaard, A., Munck, O., Nielsen, M.D., Worning, H.: The significance of bile acids and aldosterone for the electrical hyperpolarization of human rectum in obese patients treated with intestinal bypass operation. Scand. J. Gastroenterol.9, 417–426 (1974)
Rämsch, K.D.: Nifedipine: Fluoreszenzspektroskopische Nachweismethode der unveränderten Substanz im Blutplasma nach Gabe therapeutischer Dosen. (To be published, 1979)
Williams, G.H., Dluhy, R.G.: Aldosterone biosynthesis. Interrelationship of regulatory factors. Am. J. Med.53, 595–605 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedersen, O.L., Mikkelsen, E., Christensen, N.J. et al. Effect of nifedipine on plasma renin, aldosterone and catecholamines in arterial hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 15, 235–240 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00618511
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00618511