Abstract
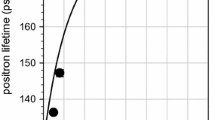
Positron lifetime measurements have been made on graphite powders, grafoils, and pyrolytic graphite crystals with different surface areas in the temperature range between 25° and 600 °C. Three positron lifetimes were found in these systems: a short-lived component (∼0.2 ns) due to positrons in the bulk; a component (∼0.45 ns) due to surface-trapped positrons; and a long-lived component (∼2 ns) ofo-Ps in the voids or the interfacial spaces of powders. Both bulk and surface positron lifetimes increase as a function of temperature. Correlations between the intensity of surface-trapped positrons and the surface area and between Ps formation and the surface area of graphite are found. The Ps formation probability increases as a function of temperature. A thermal desorption model interprets the emission process of Ps atoms from the surface of graphite to the vacuum and gives an activation energy of 0.23±0.02 eV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
See, for example, J.G. Dash:Films on Solid Surfaces (Academic Press, New York 1975)
J.P. McTague, M. Nielsen, L. Passell: InPhase Transitions in Surface Films ed. by J.G. Dash, J. Ruvaldo (Plenum Press, New York 1980)
See, for example, G.A. Somorjai:Chemistry in Two Dimensional Surfaces (Cornell Press, Ithaca, NY 1982)
See examples, P. Hautojärvi (ed.):Positrons in Solids, Topics Current Phys.12 (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York 1979)
W. Brandt, A. Dupasquier:Positron Solid-State Physics (North-Holland, Amsterdam 1983)
A.P. Mills, Jr.: Appl. Phys. Lett.35, 427 (1979)
R.H. Howell, R.A. Alvarez, M. Stanek: Appl. Phys. Lett.40, 75 (1982)
W. Brandt, R. Paulin: Phys. Rev. Lett.21, 193 (1968)
S.Y. Chuang, S.J. Tao: Can. J. Phys.51, 820 (1973)
R. Paulin, R. Ripon, W. Brandt: Phys. Rev. Lett.31, 1214 (1973); Appl. Phys.4, 343 (1974)
M. Debowska, A. Baranowski: Acta Phys. Pol. A60, 679 (1981)
Y. Tsuchija, S. Noguchi, M. Hasegawa: Philos. Mag. B39, 181 (1979)
H. Morinaga, Y. Matsuoka, M. Okochi: Phys. Lett.77A, 353 (1980)
A. Gainotti, C. Ghezzi: Phys. Rev. Lett.24, 349 (1970); J. Phys. C5, 779 (1972)
See examples, W.N. Reynolds:Physical Properties of Graphite, (Elsevier, Amsterdam 1968)
A.R. Ubbelohde, F.A. Lewis:Graphite and its Crystal Compounds (Oxford 1960)
B.T. Kelly:Physics of Graphite (Applied Science, London 1981)
M. Shinotomai, T. Takahashi, H. Fukushima, M. Doyama: J. Nucl. Mater.103, 779 (1981); J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.52, 694 (1983)
S. Berko, R.E. Kelly, J.S. Plaskett: Phys. Rev.106, 824 (1957)
D.H.D. West, V.J. McBrierty, C.F.G. Delaney: Appl. Phys.18, 85 (1979)
T. Iwata, H. Fukushima, M. Shimotomai, M. Doyama: Jpn. J. Appl. Phys.20, 1799 (1981)
L. G. Aravin, R.a. Salukvadze, V.P. Shantarovich, A.A. Khomenko: Phys. Stat. Sol.50a, K213 (1978)
E. Cartier, E. Heinoch, Pfluger, H.-J. Güntherodt: Solid State Commun.38 (1981); Phys. Rev. Lett.42, 272 (1981)
P. Kirkegaard, M. Eldrup: Comp. Phys. Commun.7, 401 (1974)
R. Wang, H.R. Danner, H. Taub: InOrdering in Two Dimensions ed. by S.K. Sinha (North-Holland, New York 1980) p. 219
The structures of grafoil were discussed in detail in [1]. The currently used grafoil sheet was a kind gift from H. Taub, the detail information of this grafoil can be found in H. Taub, H.R. Danner, Y.P. Sharma, H.L. McMurry, R.M. Brugger: Surf. Sci.76, 50 (1978)
R.M. Nieminen, M.J. Puska: Phys. Rev. Lett.50, 281 (1983)
W. Brandt: Appl. Phys.5, 1 (1974)
M. Eldrup, V.P. Shantarovich, O.E. Mogensen: Chem. Phys.11, 129 (1975); O.A. Anisimov, YuN. Molin: High Energ. Chem.9, 493 (1976)
I.J. Rosenberg, A.H. Weiss, K.F. Canter: J. Vac. Sci. Technol.17, 753 (1980)
S.Y. Chuang, S.J. Tao: Can. J. Phys.51, 820 (1973)
I.K. MacKenzie: Phys. Lett.77A, 476 (1980)
A.P. Mills, Jr.: Phys. Rev. Lett.41, 1828 (1978)
K.G. Lynn: Phys. Rev. Lett.43, 391 (1979)
A.P. Mills, Jr.: Solid State Commun.31, 623 (1979)
D.E. Gray: (ed.)Am. Inst. Phys. Handbook, 3rd ed. (McGraw-Hill, New York 1982)
J. Suzanne, M. Bienfait: Acta. Cryst. A. (Denmark) A28, 5150 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Preliminary results of this paper were presented at the March Meeting of American Physical Society, Los Angeles. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc.28, 347 (1983)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jean, Y.C., Venkateswaran, K., Parsai, E. et al. Temperature dependence of positron annihilation characteristics on the surfaces of graphite powders. Appl. Phys. A 35, 169–176 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00616971
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00616971