Summary
-
1.
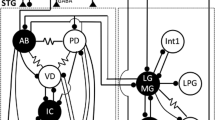
Electrical properties of neurons involved in the production of the pyloric output pattern of the stomatogastric ganglion of the crab,Cancer pagurus, as well as characteristics of synaptic connections of these neurons were investigated.
-
2.
The bursting discharge activity of the medium sized pyloric dilator neurons (m-PD) is found to be of endogenous origin. The ionic mechanism of the bursting activity is suggested to consist of a coactivated sodium-calcium inward current opposed by a calcium dependent potassium outward current. The small-sized pyloric dilators (s-PD), lateral pyloric (LP) and pyloric neurons (PY) also have the capability to discharge spontaneously.
-
3.
Low-pass properties of the neurite segment connecting the spike trigger zone to the soma is indicated. This seems to account for the small amplitudes of action potentials recorded usually at the soma.
-
4.
The values of different electronic length parameters suggest differences in the collateral properties. The effect of passive collateral properties on synaptic parameters is discussed.
-
5.
The pyloric neurons can be driven by excitatory synaptic (EPSP) input. With increased stimulus strength additional input fibres are recruited. Increasing the stimulus frequency augments the burst-frequency and spike-frequency per burst, however, the number of spikes per burst stays relatively constant.
-
6.
The time-course and amplitude of EPSPs recorded from pacemaker neurons are reduced shortly after the burst. EPSP's late in the interburst phase however were prolonged. Active membrane processes underlying the pacemaker activity appear to be responsible for these modifications of synaptic parameters.
-
7.
Hyperpolarizing current injection reduces EPSP-amplitude and shortens the time-course of EPSPs. Since no anomalous conductance changes of the soma membrane were found, it is presumed that the anomalous conductance changes occur at the collateral membrane.
-
8.
Intraganglionic chemical synaptic interaction of the pyloric neurons is exclusively inhibitory. The IPSPs for the various neurons show characteristic differences in delay, amplitude and time-course. This may contribute to the sequencing of the LP-PY discharge in the pyloric pattern. The ionic mechanism of the postsynaptic inhibition of pyloric neurons is found to be chlorid-dependent.
-
9.
It is concluded that the endogenous discharge properties of the pyloric neurons produces a basic level of activity and that the differences in passive and active membrane properties and their effect on synaptic parameters contributes to the generation of the pyloric output pattern.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PD :
-
pyloric dilator
- LP :
-
lateral pyloric neuron
- PY :
-
pyloric neuron
- m-PD :
-
medium-sized pyloric dilator neuron
- s-PD :
-
small-sized pyloric dilator neuron
References
Alving, B.O.: Spontaneous activity in isolated somata ofAplysia pacemaker neurons. J. Gen. Physiol.51, 29–45 (1968)
Arvanitaki, A., Chalazonitis, N.: Electrical properties and temporal organization in oscillatory neurons (Aplysia). In: Neurobiology of invertebrates. Salanki, J. (ed.). Budapest: Akademiai Kiado and New York: Plenum Press 1967, pp. 169–199
Baylor, D.A., Nicholls, J.G.: Chemical and electrical synaptic connections between cutaneous mechanoreceptor neurons in the central nervous system of the leech. J. Physiol.203, 391–609 (1969)
Eccles, J.C.: The physiology of synapses. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1964
Eckert, R.O., Lux, H.D.: A voltage-sensitive persistent calcium conductance in neuronal somata ofHelix. J. Physiol.254, 129–151 (1976)
Getting, P.A.: Modification of neuron properties by electrotonic synapses I. Input resistance, time constant, and integration. J. Neurophysiol.37, 846–857 (1974)
Getting, P.A., Willows, A.O.D.: Modification of neuron properties by electrotonic synapses II. Burst formation by electrotonic synapses. J. Neurophysiol.37, 858–868 (1974)
Gola, M.: Electrical properties of bursting pacemaker neurones. Neurobiology of invertebrates. Salanki, J. (ed.), pp. 387–423. Tihany: Akademiai Kiado 1976
Gorman, A.L.F., Mirolli, M.: Axonal localization of an excitatory postsynaptic potential in a molluscan neuron. J. Exp. Biol.53, 727–736 (1970)
Gorman, A.L.F., Thomas, M.V.: Changes in the intracellular concentration of free calcium ions in a pacemaker neurone, measured with the metallochromic indicator dye Arsenazo III. J. Physiol.275, 357–376 (1978)
Hagiwara, S.: Nervous activities of the heart in Crustacea. Ergeb. Biol.24, 287–311 (1961)
Hagiwara, S.: Ca spike. Adv. Biophys.4, 71–102 (1973)
Hermann, A.: Generation of a fixed motor pattern. I. Details of synaptic interconnections of pyloric neurons in the stomatogastric ganglion of the crab,Cancer pagurus. J. comp. Physiol.130, 221–228 (1979)
Hermann, A., Dando, M.R.: Mechanism of command fibre operation onto bursting pacemaker neurons in the stomatograstric ganglion of the crab,Cancer pagurus. J. comp. Physiol.114, 15–33 (1977)
Hermann, A., Gorman, A.L.F.: Blockade of the Ca2+-induced K+-current by TEA in molluscan bursting pacemaker neurons. J. Biophys.21, 52a (1978a)
Hermann, A., Gorman. A.L.F.: Effects of Ba2+ and Cs+ on voltage and calcium dependent potassium currents in molluscan neurons. J. Biophys.21, 178a (1978b)
Heyer, C.B., Lux, H.D.: Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pacemaker neurons of the snail,Helix pomatia. J. Physiol.262, 349–382 (1976)
Junge, D., Stephens, C.L.: Cyclic variation in potassium conductance in a burst generating neurone inAplysia. J. Physiol.235, 155–181 (1973)
Kandel, E.R., Kupfermann, I.: The functional organization of invertebrate ganglia. Ann. Rev. Physiol.32, 193–258 (1970)
Kandel, E.R., Tauc, L.: Anomalous rectification in the metacerebral giant cells and its consequences for synaptic transmission. J. Physiol.183, 287–304 (1966)
Kater, S.B.: Feeding inHelisoma trivolis: The morphological and physiological bases of a fixed action pattern. Am. Zool.14, 1017–1036 (1974)
King, D.G.: Organization of crustacean neuropil. I. Patterns of synaptic connections in lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J. Neurocytol.5, 207–237 (1976a)
King, D.G.: Organization of crustacean neuropil. II. Distribution of synaptic contacts on identified motor neurons in lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J. Neurocytol.5, 239–266 (1976b)
Koester, J., Kandel, E.R.: Further identification of neurons in the abdominal ganglion ofAplysia using behavioral criteria. Brain Res.121, 1–20 (1977)
Lux, H.D., Schubert, P.: Some aspects of the electroanatomy of dendrites. Adv. Neurol.12, 29–44 (1975)
Lux, H.D., Schubert, P., Kreutzberg, G.W.: Direct matching of morphological and electrophysiological data in cat spinal motoneurons. In: Excitatory synaptic mechanisms. Andersen, P., Jansen, J.K.S. (eds.), pp. 189–198. Oslo: Universitetsforlaget 1970
Magherini, P.C., Precht, W., Schwindt, P.C.: Evidence for electrotonic coupling between frog motoneurons in the in situ spinal cord. J. Neurophysiol.39, 474–483 (1976)
Maynard, D.M.: Simpler networks. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.193, 59–72 (1972)
Maynard, D.M., Walton, K.D.: Effects of maintained depolarization of presynaptic neurons on inhibitory transmission in lobster neuropile. J. comp. Physiol.97, 215–234 (1975)
Maynard, E.A.: Electron microscopy of stomatogastric ganglion in the lobsterHomarus americanus. Tissue and Cell3, 137–160 (1971)
Murayama, K., Lakshminarayanaiah, N.: Some electrical properties of the membrane of the barnacle muscle fibers under internal perfusion. J. Membr. Biol.35, 257–283 (1977)
Pantin, C.F.A.: In: Notes on microscopical technique for zoologists. London: Cambridge University Press 1961
Prior, D.J., Gelperin, A.: Autoactive molluscan neuron: Reflex function and synaptic modulation during feeding in the terestrial slug,Limax maximus. J. comp. Physiol.114, 217–232 (1977)
Rall, W.: Time constants and electrotonic length of membrane cylinders and neurons. J. Biophys.9, 1483–1508 (1969)
Rall, W.: Cable properties of dendrites and effects of synaptic location. In: Excitatory synaptic mechanisms. Andersen, R., Jansen, J.K.S. (eds.), pp. 175–187. Oslo: Universitetsforlaget 1970
Russel, D.F., Hartline, D.K.: Bursting neural networks: A reexamination. Science200, 453–456 (1978)
Sandeman, D.C.: Integrative properties of a reflex motoneuron in the brain of the crab,Carcinus maenas. Z. vergl. Physiol.64, 450–464 (1969)
Selverston, A.L.: The use of intracellular dye injections in the study of small neural networks. In: Intracellular staining in neurobiology. Kater, S.B., Nicholson, C. (eds.), pp. 255–280. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1973
Selverston, A.L., Russel, D.F., Miller, J.P., King, D.G.: The stomatogastric nervous system: structure and function of a small neural network. Prog. Neurobiol.7, 215–290 (1976)
Smith, T.G., Barker, J.L., Gainer, H.: Requirements for bursting pacemaker potential activity in molluscan neurons. Nature253, 450–452 (1975)
Wine, J.J., Mistick, D.C.: Temporal organization of crayfish escape behavior: delayed recruitment of peripheral inhibition. J. Neurophysiol.40, 904–925 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The author is particularely grateful to Dr. H.D. Lux for his support and advise throughout the course of this work and would also like to thank Dr. A.L.F. Gorman and Dr. M.C. Cornwall for helpful criticism on the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hermann, A. Generation of a fixed motor pattern. J. Comp. Physiol. 130, 229–239 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614609
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614609