Summary
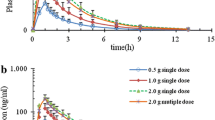
Twenty male volunteers received oral doses (2100, 1050, and 525 mg) of a pivampicillin-probenecid salt in a 1 to 1 molar ratio (MK-356) at 12 hour intervals. After each dose peak serum concentrations of probenecid were observed 2 hours later than peak concentrations of ampicillin. Following the first dose of MK-356 the apparent elimination rate of ampicillin was dose-dependent and did not follow first order kinetics, as it showed a longer apparent half life after a higher dose. An equal dose of MK-356 administered 12 hours later caused an increase in the peak serum ampicillin level greater than expected from the concentration of ampicillin after the preceding dose. In twelve male volunteers who received at random 525 mg of MK-356 or 350 mg of pivampicillin, each three times daily for 4 days, the areas under the ampicillin concentration curve were the same after the first or last dose of either drug. When 2100 or 1050 mg of MK-356 was taken as an initial dose, 30 to 40 per cent of the ampicillin was recovered from urine in the ensuing 12 hours. The results indicate that when at least 400 mg probenecid was coadministered twice daily with 700 mg pivampicillin (MK-356), the peak serum concentrations of ampicillin were increased and its elimination rate slowed following successive doses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daehne, W. von, Godtfredsen, W.O., Roholt, K., Tybing, L.: Pivampicillin, a new orally active ampicillin ester. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1970 (ed. Hobby, G.L.), pp. 431–437. Bethesda: Amer. Soc. Microbiol. 1971
Foltz, E.L., West, J.W., Breslow, J.H., Wallick, H.: Clinical pharmacology of pivampicillin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1970 (ed. Hobby, G.L.), pp. 442–454. Bethesda: Amer. Soc. Microbiol. 1971
Hultberg, E.R., Backelin, B.: Studies on the absorption of pivampicillin and ampicillin. Scand. J. infect. Dis.4, 149–153 (1972)
Jordan, M.C., de Maine, J.B., Kirby, W.M.M.: Clinical pharmacology of pivampicillin as compared with ampicillin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1970 (ed. Hobby G.L.) pp. 438–441. Bethesda: Amer. Soc. Microbiol. 1971
Daehne, W. von, Fredricksen, E., Jundersen, E., Lund, F., Morch, P., Petersen, H.J., Roholt, K., Tybing, L., Godtfredsen, W.O.: Acyloxymethyl esters of ampicillin. J. med. Chem.13, 607–612 (1970)
Beyer, K.H., Russo, H.F., Tillson, E.K., Miller, A.K., Verwey, W.F., Gass, S.R.: Benemid, p (di-n-propylsulfamyl)-benzoic acid: its renal affinity and its elimination. Amer. J. Physiol.166, 625–640 (1951)
Eickhoff, Th.C., Kislak, J.W., Finland, M., Wilcox, C.: Sodium ampicillin: Absorption and excretion of intramuscular and intravenous doses in normal young men. Amer. J. med. Sci.249, 163–176 (1965)
Kampman, J., Lindahl, F., Mølhom Hansen, J., Siersbaek-Nielsen, K.: Effect of probenecid on the excretion of ampicillin in human bile. Brit. J. Pharmacol.47, 782–786 (1973)
Zacchei, A.G., Weidner, L.: GLC — determination of probenecid in biological fluids. J. pharm. Sci.62, 1972–1974 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kampffmeyer, H.G., Hartmann, I., Metz, H. et al. Serum concentrations of ampicillin and probenecid and ampicillin excretion after repeated oral administration of a pivampicillin-probenecid salt (MK-356). Eur J Clin Pharmacol 9, 125–129 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614008
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614008