Summary
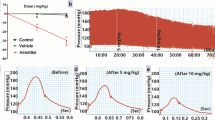
Seven patients with acutely elevated diastolic blood pressure (DBP≧135 mmHg) were treated with repeated injections of diazoxide 1 mg/kg body weight i. v. at 10-min intervals. If the DBP was not reduced to 110 mmHg or less after 5 injections, a dose of 5 mg/kg was given. Serum diazoxide (total and unbound) was determined by high pressure liquid chromatography. In all the patients it was possible to reduce the blood pressure to a satisfactory level (i.e. DBP<110 mmHg). The individual plasma diazoxide concentrations necessary to achieve the desired response ranged from 20 to 85 µg/ml. A significant correlation was found between the initial venous concentration and the initial reduction in blood pressure (p<0.02). A high initial concentration in venous blood was associated with high protein binding (“transport function”,p<0.05), and so were the elimination half-lives, which ranged from 14.7 to 61.3 h (“depot function”,p<0.05). It is concluded that the previously recommended therapy of injection of 5 mg/kg as a bolus should be given only to patients who do not respond to small repeated doses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreasen F (1969) Protein binding and initial distribution of diazoxide. Fed Proc 28: 614
Andreasen F, Kjeldahl Christensen C, Kjær-Jakobsen F, Mogensen CE (1981) The use of HPLC to elucidate the metabolism and urinary excretion of furosemide and its metabolic products. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 49: 223–229
Black J (1968) Diazoxide and the treatment of hypoglycemia: An historical review. Ann NY Acad Sci 150: 194–203
Boerth RC, Long WR (1977) Dose-response relation of diazoxide in children with hypertension. Circulation 56: 1062–1066
Cove DH, Seddon M, Fletches RF (1979) Blindness after treatment for malignant hypertension. Br Med J 2: 245–245
Crout JR, Andreasen F, Parks RI, Heimbach DM (1970) Intravenous diazoxide in hypertension. Clin Res 18: 337
Finnerty FA, Kakaviatos N, Tuckman J, Magill J (1963) Clinical evaluation of diazoxide. A new treatment for acute hypertension. Circulation 28: 203–208
Finnerty FA (1974) Hypertensive Crisis. J Am Med Assoc 229: 1479–1480
Garrett BN, Kaplan N (1982) Efficacy of slow infusion of diazoxide in the treatment of severe hypertension without organ hypoperfusion. Am Heart J 103: 390–394
Heinrich WL, Cronin R, Miller PD, Anderson RJ (1977) Hypotensive sequelae of diazoxide and hydralazine therapy. J Am Med Assoc 237: 264–265
Johnson BF, Kapur M (1972) The influences of rate of injection upon the effects of diazoxide. Am J Med Sci 263: 481–488
Leadingham JGG, Rajagopalau B (1979) Cerebral complications in the treatment of accelerated hypertension. Q J Med 48: 25–41
Lee WR, Mroczek WJ, Davidov ME, Finnerty FA (1975) Nonemergency use of slow infusions of diazoxide. Clin Pharmacol Ther 18: 154–157
McLaine PN, Drummond KN (1971) Intravenous diazoxide for severe hypertension in childhood. J Pediatr 79: 829–832
Miller WE, Gifford RW, Humphrey DC, Vidt DG (1969) Management of severe hypertension with intravenous injections of diazoxide. Am J Cardiol 24: 870–875
Mroczek WJ, Leibel BA, Davidov ME (1971) The importance of the rapid administration of diazoxide in accelerated hypertension. N Engl J Med 285: 603–606
Nielsen PE, Krogsgaard AR, McNair A, Hilden T (1980) Emergency treatment of severe hypertension evaluated in a randomized study. Acta Med Scand 208: 473–480
Sadee W, Segal J, Finn C (1973) Diazoxide urine and plasma levels in humans by stable-isotope dilution-mass fragmentography. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 1: 295–305
Sellers EM, Koch-Weser J (1969) Protein binding and vascular activity of diazoxide. N Engl J Med 281: 1141–1145
Sellers EM, Koch-Weser J (1973) Influence of intravenous injection rate on protein binding and vascular activity of diazoxide. Ann NY Acad Sci 226: 319–332
Sellers EM, Koch-Weser J (1974) Binding of diazoxide and other benzothiadiazines to human albumin. Biochem Pharmacol 23: 553–556
Thien TA, Huysmans FTM, Gerlag PGG, Koene RAP, Wijdeveld PGAB (1979) Diazoxide infusion in severe hypertension and hypertensive crisis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 25: 795–799
Weder HG, Schildknecht J, Kesselring P (1971) A new equilibrium dialyzing system. Am Lab 10: 15–21
Wohl AJ, Hausler LM, Roth FE (1967) Studies on the mechanism of antihypertensive action of diazoxide: In vitro vascular pharmacodynamics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 158: 531–538
Wohl AJ, Hausler LM, Roth FE (1968) Mechanism of the antihypertensive effects of diazoxide: In vitro vascular studies in the hypertensive rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 162: 109–114
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McNair, A., Andreasen, F. & Nielsen, P.E. Antihypertensive effect of diazoxide given intravenously in small repeated doses. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24, 151–156 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613809
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613809