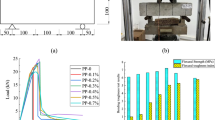
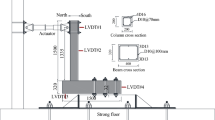
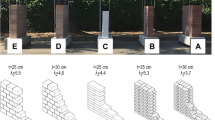
Conclusions
For the optimum choice of pultruded beam members in frameworks there is a need to have a greater understanding of framework behavior under load. Research on the lateral-torsional buckling of a symmetric I-section has shown how much the resistance may be affected by the loading position and the support boundary conditions. By changing the warping at the connections from free, as assumed in the USA design manual, to fixed, as may be achieved with practical connection designs it is shown that there is a potential doubling in the buckling resistance. In addition, practical connections have some initial stiffness and moment resistance, thus the connections behave in a semirigid manner. This connection behavior makes inappropriate the present procedure for choosing beam sections on the basis of limiting deflection for a simply supported member. It is proposed that research be conducted to establish the potential of semirigid design, as now being used with structural steelwork. Results from such research should provide the first stage in the process for the optimum design of frameworks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Barbero and H. V. S. GangaRao, "Structural applications of composites in infrastructure. Pt 1.," SAMPE J.,27, No. 6, 9–16 (1991).
C. Ballinger, "Structural FRP composites," Civ. Eng. ASCE,60, No. 7, 63–65 (1990).
MMFG Design Manual. Extren Fiberglass Structural Shapes Design Manual, MMFG Company, Bristol, Va. (1989).
Creative Pultrusions Design Guide, Creative Pultrasion Inc., Alum Bank, Pa. (1988).
P. W. Meyer, Handbook of Pultrusion Technology, Chapman and Hall (1985).
Structural Plastics Design Manual, ASCE Manuals and Reports on Eng. Practice, No. 63 (1984).
J. T. Mottram, "Evaluation of design analysis for pultruded fibre-reinforced polymeric box beams," The Structural Engineer,69, No. 11, 211–220 (1991).
J. T. Mottram, "Structural properties of pultruded E-glass fibre-reinforced polymeric I-beam," Composite Structures 6, Ed. by I. H. Marshall, Conf. on Composite Structures (9–11 Sept. 1991), Paisley College of Technology, Elsevier Applied Sci., 1–28 (1991).
J. T. Mottram, "Lateral-torsional buckling of a pultruded I-beam," Composites,23, No. 1, 81–93 (1992).
L. C. Bank, "Properties of pultruded fiber reinforced plastic structural members," Transportation Res. Record 1223, Washington DC, 117–124 (1990).
L. C. Bank and A. S. Mosallam, "Creep and failure of a full-size fibre-reinforced plastic pultruded frame," Composites Eng.,2, No. 3, 213–227 (1992).
L. C. Bank, A. S. Mosallam, and G. T. McCoy, "Design and performance of connections for pultruded frame structures," 47th Ann. Conf., Composite Institute, Soc. Plastics Ind., Feb. 3–6, Session 2-B, 8 (1992).
J. T. Mottram, "Lateral-torsional buckling of pultruded thin-walled composite I-beams by the finite difference method," Composites Eng.,2, No. 2, 91–104 (1992).
G. D. Sims, A. F. Johnson, and R. D. Hill, "Mechanical and structural properties of a GRP pultruded section," Composite Structures, No. 8, 173–187 (1987).
El. M. S. Naschie, Stress, Stability and Chaos in Structural Engineering: An Energy Approach. 1st ed., McGraw-Hill, London (1990).
N. R. Bauld and L. S. Tzeng, "A Vlasov theory for fiber-reinforced beams with thin-walled open cross sections," Intern. J. Solids Structures,20, No. 3, 277–297 (1984).
S. P. Timoshenko and J. M. Gere, Theory of Elastic Stability, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York (1961).
Eurocode 3. Design of Steel Structures. Pt 1. General Rules and Rules for Buildings. Edited draft. Issue 5, Committee European Normalization (1990).
D. A. Anderson, A. Coulson, and J.-P. Jaspart, European Connection for Constructions Steelwork, Technical Committee 10. Connections and frame design for economy. Brussels (to be published) (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 29, No. 5, pp. 675–682, September–October, 1993.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mottram, J.T. Recommendations for the optimum design of pultruded frameworks. Mech Compos Mater 29, 503–508 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00611954
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00611954