Summary
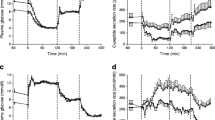
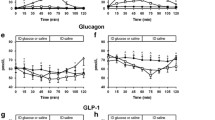
The influence of sulfonylurea on the secretion, disposal and effect of insulin was studied in 9 Type 2 diabetics during 3 one-month courses of treatment with a) chlorpropamide (t1/2>24 h) once daily, b) glipizide (t1/2=2–4 h) once daily, and c) glipizide in divided doses. Food intake by each patient was identical during each period. Blood concentrations of immunoreactive insulin (IRI) and C-peptide (radioimmunoassays), and of glucose (enzymatic assay), chlorpropamide (gas chromatography) and glipizide (high-pressure liquid chromatography) were determined before and after breakfast and lunch on the 4th day of each examination period. All comparisons were intraindividual. Despite the lunch-time dose of glipizide given during the divided dose treatment, once-daily administration of this drug led to higher drug concentrations not only after breakfast but also for the first few hours after lunch. Divided dosage, on the other hand, led to higher concentrations later. In contrast to once-daily dosage, continuous exposure to glipizide was found in most patients. Chlorpropamide gave the most continuous sulfonylurea exposure. The blood glucose levels were inversely related to the concurrent sulfonylurea concentrations; glucose levels after breakfast and lunch were lowest during once-daily glipizide, whereas the fasting level was lowest during chlorpropamide treatment. The IRI response to breakfast was 60%–70% higher during once-daily glipizide than during the other two treatments, but the C-peptide responses to breakfast were almost identical. Thus, the greater after-breakfast availability of peripheral insulin appeared to be due to an effect of glipizide on the extrapancreatic disposal of the hormone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marshall A, Gingerich RL, Wright PH (1970) Hepatic effect of sulfonylureas. Metabolism 19:1046–1052
Feldman JM, Lebovitz HE (1969) Appraisal of the extrapancreatic actions of sulfonylureas. Arch Int Med 123:314–322
Blumenthal SA, Whitmer KR (1979) Hepatic effects of chlorpropamide. Inhibition of glucagon-stimulated gluconeogenesis in perfused livers of fasted rats. Diabetes 28:646–650.
Greenstein BD (1979) Improved insulin receptor assay: effects of an antidiabetic sulfonylurea on liver membrane insulin receptors from obese hyperglycaemic mice. Br J Pharmacol 66:217–222
Lebovitz HE, Feinglos MN, Bucholtz HK, Lebovitz FL (1977) Potentiation of insulin action: a probable mechanism for the anti-diabetic action of sulfonylurea drugs. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 45:601–604
Tanese T, Lazarus NR, Devrim S, Recant L (1979) Synthesis and release of proinsulin and insulin by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. J Clin Invest 49:1394–1404
Dunbar JC, Foa PP (1974) An inhibitory effect of tolbutamide and glibenclamide (glyburide) on the pancreatic islets of normal animals. Diabetologia 10:27–35
Marks V (1959) An improved glucose-oxidase method for determining blood, C.S.F. and urine glucose levels. Clin Chim Acta 4:395–4000
Heding LG (1966) A simplified insulin radioimmonoassay method. In: Donato et al. (eds) Labelled proteins in tracer studies. Euratom, Brussels, pp 345–351
Heding LG (1975) Radioimmonological determination of human C-peptide in serum. Diabetologia 11:541–548
Prescott LF, Redman DR (1972) Gas-liquid chromatographic estimation of tolbutamide and chlorpropamide in plasma. J Pharm Pharmacol 24:713–716
Wåhlin-Boll E, Melander A (1979) High-pressure liquid chromatographic determination of glipizide and some other sulfonylurea drugs in serum. J Chromatogr 164:541–546
Wåhlin-Boll E, Sartor G, Melander A, Scherstén B (1982) Impaired effect of sulfonylurea following increased dosage. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22:21–25
Blundell T, Dodson G, Hodgkin D, Mercola D (1972) Insulin: The structure in the crystal and its reflection in chemistry and biology. In: Anfinsen et al. (eds) Advances in protein chemistry. Academic Press, New York, pp 279–402
Howell SL, Tyhurst M, Duvefelt H, Andersson A, Hellerström C (1978) Role of zinc and calcium in the formation and storage of insulin in the pancreatic B-cell. Cell Tissue Res 188:107–118
Arquilla ER, Thiene P, Brugman T, Ruess W, Sugiyama (1978) Effects of zinc ion on the conformation of antigenic determinants on insulin. Biochem J 175:289–297
Arquilla ER, Packer S, Tarmas W, Miyamoto S (1978) The effect of zinc on insulin metabolism. Endocrinology 103:1440–1449
Zermatten A, Heptner W, Delaloye B, Séchaud R, Felber J-P (1977) Extrapancreatic effect of glibenclamide: stimulation of duodenal insulin-releasing activity (DIRA) in man. Diabetologia 13:85–87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almér, L.O., Johansson, E., Melander, A. et al. Influence of sulfonylureas on the secretion, disposal and effect of insulin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22, 27–32 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00606421
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00606421