Summary
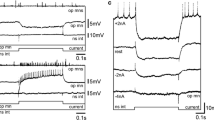
We have investigated the connectivity of four classes of mechanosensory afferents to giant interneurons in the earthwormLumbricus. Three of these classes of afferents change their specification for connection to medial giant (MGF) and lateral giant (LGF) fibers along the length of the animal. Near the caudal end, stimulation of touch, pressure and small tactile fibers generates excitatory post-synaptic potentials, epsp's, in the two LGF's but not in the MGF. Near the rostral end these afferents produce much smaller epsp's in the LGFs but produce large epsp's in the MGF. In the middle region of the animal an overlap region exists where both giant fibers receive approximately equal inputs from these afferents. The amplitude of these inputs are reduced compared to the maxima seen at either end. The fourth class of sensory afferents investigated, the stretch neurons, have no synaptic effect on the giant fibers anywhere in the nerve cord.
These results explain at least part of the basis, in neuronal connectivity, for the differences in response to tactile stimulation of the head and tail segments previously characterized in terms of behavior and giant fiber impulse activity. In this system developmental mechanisms generating synaptic connectivity patterns have coded certain classes of homologous afferent neurons and interneurons to make different connections in different segments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MGF :
-
medial giant fiber
- LGF :
-
lateral giant fiber
- SN1 :
-
first segmental root
- SN2 :
-
second segmental root
- SN3 :
-
third segmental root
- RIN :
-
giant interneuron
References
Beleslin. B.B.: Lack of electrotonic transmission between Retzius nerve cells in the fifth and sixth free ganglion of horse leechHaemopis sanguisuga. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.56A, 509–512 (1977)
Brink, P., Barr, L.: The resistance of the septum of the medial giant axon of the earthworm. J. Gen. Physiol.69, 517–536 (1977)
Brown, P.B.: An inexpensive mechanical stimulator incorporating a new optoelectric device. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. BME-21, 428–429 (1974)
Bullock, T.H.: Functional organization of the giant fiber system ofLumbricus. J. Neurophysiol.8, 57–71 (1945)
Coggeshall, R.E.: A fine structural analysis of the ventral nerve cord and associated sheath ofLumbricus terrestris L. J. Comp. Neurol.125, 393–438 (1965)
Drewes, C.D., Fourtner, C.R.: Stretch-sensitive neural units in the body wall of the earthworm,Lumbricus terrestris L. J. Exp. Biol.65, 39–50 (1976)
Drewes, C.D., Pax, R.A.: Neuromuscular physiology of the longitudinal muscle of the earthworm,Lumbricus terrestris. I. Effects of different physiological salines. J. Exp. Biol.60, 445–452 (1974)
Friedländer, B.: Altes und Neues zur Histologie des Bauchstranges des Regenswurms. Z. Wiss. Zool.48, 661–693 (1894)
Goldman, L.: The effects of stretch on cable and spike parameters of single nerve fibers; some implications for the theory of impulse propagation. J. Physiol.175, 425–444 (1964)
Günther, J.: On the organization of the exteroceptive afferents in the body segments of the earthworm. Verb. Dtsch. Zool. Ges.64, 261–265 (1970)
Günther, J.: Der cytologische Aufbau der dorsalen Riesenfasern vonLumbricus terrestris L. Z. Wiss. Zool.183, 51–70 (1971a)
Günther, J.: Microanantomie des Bauchmarks vonLumbricus terrestris L. Z. Morphol. Tiere70, 141–182 (1971b)
Günther, J.: Overlapping sensory fields of the giant fiber systems in the earthworm. Naturwissenschaften60, 521–522 (1973)
Günther, J., Schürmann, F.W.: Zur Feinstruktur des dorsalen Riesenfasersystems im Bauchmark des Regenwurms. II. Synaptische Beziehungen der proximalen Riesenfaserkollateralen. Z. Zellforsch.139, 369–396 (1973)
Günther, J., Walther, J.B.: Funktionelle Anatomie der dorsalen Riesenfaser-Systeme vonLumbricus terrestris L. (Annelida, Oligochaeta). Z. Morphol. Tiere70, 253–280 (1971)
Hesse, R.: Zur vergleichenden Anatomie der Oligochaeten. Z. Wiss. Zool.58, 394–439 (1894)
Kao, C.Y., Grundfest, H.: Post-synaptic electrogenesis in septate giant axons. I. Earthworm median giant axon. J. Neurophysiol.20, 558–573 (1957)
Langdon, F.E.: The sense organs ofLumbricus agricola. Hoffm. J. Morphol.11, 193–234 (1895)
Mill, P.J., Knapp, M.F.: Efferent sensory impulses and the innervation of tactile receptors inAllolobophora longa andLumbricus terrestris L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.23, 263–276 (1967)
Mittenthal, J.E., Wine, J.J.: Connectivity patterns of crayfish giant interneurons: Visualization of synaptic regions with cobalt dye. Science179, 182–184 (1973)
Mittenthal, J.E., Wine, J.J.: Segmental homology and variation in flexor motoneurons of the crayfish abdomen. J. Comp. Neurol.177, 311–334 (1978)
Mulloney, B.: Structure of the giant fibers of earthworms. Science168, 994–996 (1970)
Retzius, G.: Das Nervensystem der Lumbriciden. Biol. Untersuch. N. F.3, 1–16 (1892)
Rushton, W.A.H.: Motor response from giant fibers in the earthworm. Nature156, 109–110 (1945)
Rushton, W.A.H.: Reflex conduction in the giant fibers of the earthworm. Proc. R. Soc. (London) Ser. B133, 109–120 (1946)
Stough, H.B.: Polarization of the giant fibers of the earthworm. J. Comp. Neurol.50, 217–229 (1930)
Takeuchi, A., Takeuchi, N.: Electrical changes in pre- and postsynaptic axons of the giant synapse of Loligo. J. Gen. Physiol.45, 1181–1193 (1962)
Taylor, W.G.: The optical properties of the earthworm giant fiber sheath as related to fiber size. J. Cell. Comp. Physiol.15, 363–371 (1940)
Thompson, W.J., Stent, G.S.: Neuronal control of heartbeat in the medicinal leech. III. Synaptic relations of the heart interneurons. J. Comp. Physiol.111, 309–333 (1976)
Wilson, D.M.: The connections between the lateral giant fibers of earthworms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.1, 274–284 (1961)
Wilson, J.A., Hoyle, G.: Serially homologous neurons as concomitants of functional specialization. Nature274, 377–379 (1978)
Youlton, L.W.: The effects of cutting the giant fibers in the earthworm,Eisenia foetida (Sav.). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA9, 383–385 (1923)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, P.H., Mittenthal, J.E. Intersegmental variation of afferent pathways to giant interneurons of the earthworm,Lumbricus terrestris L.. J. Comp. Physiol. 140, 351–363 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00606275
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00606275