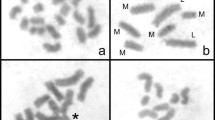
Abstract
Supernumerary chromosomes have been reported in many species particularly in the Orthoptera. Although it is assumed that these chromosomes are ultimately derived from elements of the standard karyotype, in no case recorded is there convincing evidence of even partial homology between true supernumeraries and other chromosomes. In the present paper, a very rare B chromosome in the grasshopperAtractomorpha similis is reported. It associates specifically and persistently with a large segment on Autosome 5 (A5). Associations were seen in 29 out of 288 meiocytes scored, and persisted to Anaphase I. At least four of the 29 associations appear to be of a genuinely chiasmate nature, implying some degree of homology. The A5 segment is itself supernumerary, occurring in 8% of individuals scored. Supernumerary segment polymorphism is extremely common in this species, as is germ line polysomy for Autosome 9. In the light of these pecularities, a possible mode of derivation, involving Autosome 9, is proposed for the B chromosome in question. Supernumeraries of the closely related speciesA. australis are also discussed insofar as they suggest the occurrence of seemingly diverse modes of B chromosome derivation within the genusAtractomorpha.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlow, P., 1973. The influence of inactive chromosomes on human development. Humangenetik 17: 105–136.
Fontana, P. G. & Vickery, V. R., 1975. The B-chromosome system of Tettigldea lateralis (Say) II. New karyomorphs, patterns of pycnosity and giemsa-banding. Chromosoma 50: 371–391.
Hewitt, G. M., 1973. The integration of supernumerary chromosomes into the Orthopteran genome. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 38: 183–194.
Hewitt, G. M. & John, B., 1968. Parallel polymorphism for supernumerary segments in Chorthippus parallelus (Zetterstedt) I. British populations. Chromosoma 25: 319–342.
Jackson, W. D. & Cheung, D. S. M., 1967. Distortional meiotic segregation of a supernumerary chromosome producing differential frequencies in the sexes in the short-horned grass-hopper Phaulacridium vittatum. Chromosoma 23: 24–37.
John, B. & Freeman, M., 1974. Chromosome behaviour in Phaulacridium vittatum. Chromosoma 46: 181–195.
John, B. & King, M., 1983. Population cytogenetics of Atractomorpha similis I. C-band variation. Chromosoma 88: 57–68.
John, B. & Miklos, G. L. G., 1979. Functional aspects of satellite DNA and heterochromatin. Int. Rev. Cytol. 58: 1–114.
Jones, R. N., 1975. B-chromosome systems in flowering plants and animal species. Int. Rev. Cytol. 40: 1–100.
Jones, R. N. & Rees, H., 1982. B chromosomes. Academic Press, New York.
Khush, G. S., 1973. Cytogenetics of aneuploids. Academic Press, New York.
Miklos, G. L. G. & Nakivell, R. N., 1976. Telomeric satellite DNA functions in regulating recombination. Chromosoma 56: 143–167.
Müntzing, A., 1974. Accessory chromosomes. A. Rev. Genet. 8: 243–266.
Nankivell, R. N., 1976. Karyotype differences in the Crenaticeps-group of Atractomorpha (Orthoptera, Acridoidea, Pyrgomorphidae). Chromosoma 56: 127–142.
Peters, G. B., 1981. Germ line polysomy in the grasshopper Atractomorpha similis. Chromosoma 81: 593–617.
Peters, G. B., 1982. The recurrence of chromosome fusion in interpopulation hybrids of the grasshopper Atractomorpha similis. Chromosoma 85: 323–347.
Rees, H., 1974. B chromosomes. Sci. Prog. 61: 535–554.
Shaw, D. D., 1972. Genetic and environmental components of chiasma control. II. The response to selection in Schistocerca. Chromosoma 37: 297–308.
Shaw, D. D. & Wilkinson, P., 1978. ‘Homologies’ between non-homologous chromosomes in the grasshopper Caledia captiva. Chromosoma 68: 241–259.
Webb, G. C. & Neuhaus, P., 1979. Chromosome organisation in the Australian plague locust Chortoicetes terminifera. 2. Banding variants of the B-chromosome. Chromosoma 70: 205–238.
White, M. J. D., 1957. Cytogenetics and systematic entomology. A. Rev. Ent. 2: 71–90.
White, M. J. D., 1973. Animal cytology and evolution. p. 314. Third edition. Cambridge University Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, G.B. Persistent meiotic association of a rare B chromosome and an autosomal segment inAtractomorpha similis (Orthoptera: Acridoidea). Genetica 63, 129–137 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00605897
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00605897