Summary
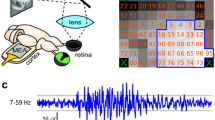
Visual unit activity, EEG changes and sustained potential shifts (SPS) were recorded from the toad tectum whilst the animal was presented with a visual stimulus. Telencephalic EEGs were also recorded.
On the surface of the tectum, retinal unit activity preceded a sustained negative shift in potential and an increase in the amplitude and dominant frequency of the EEG. In deeper layers of the tectum, T5 units with configurational selectivity for ‘wormlike’ stimuli were found. The activity of these units followed a pronounced SPS and EEG change.
Visual unit activity was most pronounced during the negative-going phase of the synchronised EEG, when there was also a small decrease in amplitude of neuronal spikes. Similarities between the latencies and durations of EEGs and SPSs, and their response decrements, on repeated stimulus presentation, implies a close relationship between them not shared by the visual units studied. The specific activity of tectal units is discussed in relation to the correlated EEG and SPS changes, which may form part of an adaptive sensitizing mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EEG :
-
electroencephalogram
- ERF :
-
excitatory receptive field
- SPS :
-
sustained potential shift
- T4, T5 :
-
tectal neurons
References
Adrian ED, Matthews BHC (1934) The interpretation of potential waves in the cortex. J Physiol 81:440–471
Borchers HW, Ewert JP (1979) Correlation between behavioral and neuronal activities of toads,Bufo bufo (L.) in response to moving configurational prey stimuli. Behav Processes 4:99–106
Buchwald JS, Halas ES, Schramm S (1966) Relationship of neuronal spike populations and EEG activity in chronic cats. EEG Clin Neurophysiol 21:227–238
Caspers H (1961) Changes of cortical DC potentials in the sleep-wakefulness cycle. In: Wolstenholme GE, O'Connor M (eds) The Nature of Sleep. Ciba Foundation Symposium, Little Brown & Co., Boston, pp 125–139
Elul R (1964) Specific site of generation of brain waves. Physiologist 7:125
Elul R (1968) Brain waves: Intracellular recording and statistical analysis help clarify their physiological significance. In: Einstein K (ed) Data acquisition and processing in biology and medicine, vol 5. Pergamon, Oxford, p 93
Elul R (1972) The genesis of the EEG. In: Pfeiffer CC, Smythies JR (eds) International review of neurobiology, vol 15. Academic Press, New York London, pp 228–272
Enger PS (1957) The electroencephalogram of the codfish. Acta Physiol Scand 39:55–72
Ewert JP (1968) Der Einfluß von Zwischenhirndefekten auf die Visuomotorik im Beutefang- und Fluchtverhalten der Erdkröte (Bufo bufo). Z Vergl Physiol 61:41–70
Ewert JP (1969) Quantitative Analyse der Reiz-Reaktionsbeziehungen bei visuellem Auslösen der Beutefang-Wendereaktion der Erdkröte (Bufo bufo). Pflügers Arch 308:225–243
Ewert JP (1974) The neural basis of visually guided behavior. Sci Am 230:34–42
Ewert JP (1980) Neuroethology. An introduction to the neurophysiological fundamentals of behavior. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Ewert JP (1981) Neural coding of ‘worms’ and ‘antiworms’ in the brain of toads: the question of hardwired and soft-wired systems. In: Laming PR (ed) Brain mechanisms of behaviour in lower vertebrates. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 137–168
Ewert JP, Hock FJ (1972) Movement sensitive neurons in the toad's retina. Exp Brain Res 16:41–59
Ewert JP, Wietersheim A von (1974) Musterauswertung durch Tectum- und Thalamus/Praetectum-Neurone im visuellen System der Kröte,Bufo bufo. J Comp Physiol 92:131–148
Ewert JP, Arend B, Becker V, Borchers HW (1979a) Invariants in configurational prey selection byBufo bufo. Brain Behav Evol 16:38–51
Ewert JP, Borchers HW, Wietersheim A von (1979b) Directional sensitivity, invariance and variability of tectal T5 neurons in response to moving configurational stimuli in the toadBufo bufo. J Comp Physiol 132:191–201
Fujita Y, Sato T (1964) Intracellular records from hippocampal pyramidal cells in rabbit during theta rhythm activity. J Neurophysiol 27:1011–1025
Grüsser OJ, Grüsser-Cornehls U (1976) Neurophysiology of the anuran visual system. In: Llinás R, Precht W (eds) Frog Neurobiology, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 297–385
Hayward JN, Fairchild MD, Stuart DG (1966) Hypothalamic and cortical DC potential changes induced by stimulation of the midbrain reticular formation. Exp Brain Res 1:205–219
Hobson JA (1967) Respiration and EEG synchronisation in the frog. Nature 213:988–989
Karmanova IG, Belekhova MG, Tchurnosov EV (1971) Specifics of behavioral and electrographic patterns of natural sleep and wakefulness in reptiles. Sechenov Physiol J USSR 57:504–511
Kelly JP, Van Essen DC (1974) Cell structures and function in the visual cortex of the cat. J Physiol 238:515–547
Klemm WR (1969) Animal electroencephalography. Academic Press, New York
Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1978) The command neuron concept. Behav Brain Sci 1: 3–39
Laming PR (1980) Electroencephalographic studies on arousal in the goldfish (Carassius auratus). J Comp Physiol Psychol 94:238–254
Laming PR (1981) The physiological basis of alert behaviour in fish. In: Laming PR (ed) Brain mechanisms of behaviour in lower vertebrates. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 203–224
Laming PR (1982) Electroencephalographic correlates of behavior in the anurans,Bufo regularis andRana temporaria. Behav Neural Biol 34:296–306
Laming PR, Savage GE (1980) Physiological changes observed in the goldfish (Carassius auratus) during behavioral arousal and fright. Behav Neural Biol 29:255–275
Laming PR, Savage GE (1981) Seasonal differences in brain activity and responsiveness shown by the goldfish (Carassius auratus). Behav Neural Biol 32:386–389
Li CL, Jasper HH (1953) Microelectrode studies of the electrical activity of the cerebral cortex in the cat. J Physiol 121:117–140
Li CL, Cullen C, Jasper HH (1956) Laminar microelectrode analysis of cortical unspecific recruiting responses and spontaneous rhythms. J Physiol 19:131–143
Livingstone MS, Hubel DH (1981) Effects of sleep and arousal on the processing of visual information in the cat. Nature 291:554–561
Morruzzi G, Magoun HW (1949) Brain-stem reticular formation and activation of the EEG. EEG Clin Neurophysiol 1:455–473
Orkand RK, Nicholls JG, Kuffler SW (1966) Effect of nerve impulses on the membrane potential of glial cells in the central nervous system of Amphibia. J Neurophysiol 29:788–806
Pagano RR, Gault FP (1964) Amygdala activity: A central measure of arousal. EEG Clin Neurophysiol 17:255–260
Parker RE (1973) Introductory Statistics for Biology. Edward Arnold, London
Parmeggiani PL (1967) On the functional significance of the hippocampalθ-rhythm. In: Adey WR, Tokizane T (eds) Structure and function of the limbic system. Prog Brain Res 27:413–441
Pickenhain L, Klingberg F (1967) Hippocampal slow wave activity as a correlate of basic behavioral mechanisms in rat. In: Adey WR, Tokizane T (eds) Structure and function of the limbic system. Prog Brain Res 27:218–227
Ransom BR, Goldring S (1973a) Ionic determinants of membrane potential of cells presumed to be glia in cerebral cortex of cat. J Neurophysiol 36:879–892
Ransom BR, Goldring S (1973b) Slow depolarisation in cells presumed to be glia in cerebral cortex of cat. J Neurophysiol 36:869–878
Rowland V, Dines G (1973) Cortical steady potential shift in relation to the rhythmic electrocorticogram and multiple unit activity. In: Thompson RF, Patterson MM (eds) Bioelectric recording techniques: Part A, Cellular processes and brain potentials. Academic Press, New York, pp 369–385
Schade JP, Weiler PJ (1959) EEG patterns of the goldfish. J Exp Biol 36:435–452
Schürg-Pfeiffer E (1979) Quantitative neurophysiologische Untersuchungen zur Frage nach Gestaltdedektoren im visuellen System des FroschesRana temporaria (L.). Dissertation, Universität Kassel
Segura ET, De Juan A (1966) Electroencephalographic studies in toads. EEG Clin Neurophysiol 21:373–380
Shepherd GM (1979) The synaptic organization of the brain. Oxford University Press, New York Oxford
Thompson RF, Groves PM, Teyler PJ, Roemer RA (1973) A dual process theory of habituation: Theory and behavior. In: Peeke HVS, Herz MJ (eds) Habituation, vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 16–43
Winer BJ (1962) Statistical principles in experimental design. McGraw-Hill- London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laming, P.R., Ewert, J.P. Visual unit, EEG and sustained potential shift responses to biologically significant stimuli in the brain of toads (Bufo bufo). J. Comp. Physiol. 154, 89–101 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00605394
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00605394