Summary
-
1.
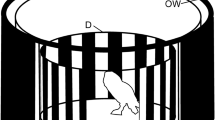
The compensatory eyestalk movements ofPalinurus vulgaris have been measured in response to oscillations of the body, substrate and patterned visual surround about a body-parallel horizontal axis. The stimuli were delivered alone, and in fourteen different combinations (Fig. 2).
-
2.
Responses are greatest (amplitude gain ca. 1.5) when the mechanical inputs, substrate and gravity, are combined synergistically (Fig. 3 a). The effect of the optokinetic stimulus is gain-limiting (Fig. 3b, c).
-
3.
When analysed over a wide frequency range (0.001–0.4 Hz), substrate and optokinetic drum movements result in quite different response curves (Figs. 4a, c), combinations of these stimuli produce responses at an intermediate level when synergistic (Fig. 4b), but at a low level when antagonistic (Fig. 4d).
-
4.
Turning the animal inside a stationary optokinetic drum, to produce synergistic action of vision and statocyst input, improves the compensatory response (Fig. 5: P8).
-
5.
The threefold stimulus combination which simulates an external disturbance (condition 3, Fig. 2) elicits eye responses which are exactly compensatory at all frequencies tested (Fig. 6).
-
6.
When the visual surround is devoid of pattern (but presents a gradient of light intensity, centred above) the eye response to substrate movement is attenuated (Fig. 7), whereas the gravity response is enhanced (Fig. 8).
-
7.
Timing relationships display consistent phase advances with decreasing frequency (Fig. 9, Fig. 10).
-
8.
These results are discussed in terms of the gain-limiting properties of the optokinetic system, and the action of a visual factor responsive to the vectorial component of the stimulating light.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birkner H (1978) Versuche an Langusten (Palinurus vulgaris) zur Orientierung nach Schwerkraft und Substrat. Zulassungsarbeit für die Wissenschaftliche Prüfung für das Lehramt an den Gymnasien in Bayern, München
Collewijn H (1981) The oculomotor system of the rabbit and its plasticity. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Fraenkel G, Gunn DL (1961) The orientation of animals: Kineses, taxes and compass reactions. Dover, New York
Higuchi T, Hisada M (1973) Visual and geotactic contributions to oculomotor responses in the crayfish,Procambarus clarki. J Fac Sci Hokkaido Univ (Ser 6) 18:495–506
Hisada M, Sugawara K, Higuchi T (1969) Visual and geotactic control of compensatory eyecup movement in the crayfish,Procambarus clarki. J Fac Sci Hokkaido Univ (Ser 6) 17:224–239
Marrelli JD, Hsiao HS (1976) Miniature angle transducer for marine arthropods. Comp Biochem Physiol[A] 54:121–123
Mellon DeF, Lorton ED (1977) Reflex actions of the functional divisions in the crayfish oculomotor system. J Comp Physiol 121:367–380
Neil DM (1982) Compensatory eye movements. In: Atwood HL, Sandeman DC (eds) Biology of the Crustacea, vol IV. Academic Press, New York, pp 133–163
Neil DM, Schöne H (1979) Reactions of the spiny lobster,Palinurus vulgaris to substrate tilt. II. Input-output analysis of eystalk responses. J Exp Biol 79:59–67
Neil DM, Schöne H, Scapini F (1979) Leg resistance reaction as an output and an input. Reactions of the spiny lobster,Palinurus vulgaris, to substrate tilt VI. J Comp Physiol 129:217–221
Neil DM, Schöne H, Scapini F (1983) Optokinetic responses, visual adaptation and multisensory control of eye movements in the spiny lobster,Palinurus vulgaris. J Exp Biol (submitted)
Olivo RF, Jazak MM (1980) Proprioception provides a major input to the horizontal oculomotor system of the crayfish. Vision Res 20:349–353
Sandeman DC (1977) Compensatory eye movements in crabs. In: Hoyle G (ed) Identified neurons and behavior in arthropods. Plenum, New York, pp 131–147
Scapini F, Neil DM, Schöne H (1978) Leg-to-body geometry determines eyestalk reactions to substrate tilt. Substrate orientation in spiny lobsters IV. J Comp Physiol 126:287–291
Schöne H (1953) Die optische Lageorientierung von Dekapoden. Naturwissenschaften 39:554
Schöne H (1980) Orientierung im Raum. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart
Schöne H, Neil DM (1977) The integration of leg position receptors and their interaction with statocyst inputs in spiny lobsters (Reactions ofPalinurus vulgaris to substrate tilt). Mar Behav Physiol 5:45–59
Schöne H, Neil DM, Stein A, Carlstead MK (1976) Reactions of the spiny lobster,Palinurus vulgaris to substrate tilt. I. J Comp Physiol 107:113–128
Schöne H, Neil DM, Scapini F (1978) The influence of substrate contact on gravity orientation. Substrate orientation in spiny lobsters V. J Comp Physiol 126:293–295
Stein A, Schöne H (1972) Über das Zusammenspiel von Schwereorientierung und Orientierung zur Unterlage beim Flußkrebs. Verh Dtsch Zool Ges 65:225–229
Verheijen FJ (1982) Environmental features and orientation. In: Addink ADF, Spronk N (eds) Exogenous and endogenous influences on metabolic and neural control, vol 1. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 371–382
Zacharias GL, Young LR (1981) Influence of combined visual and vestibular cues on human perception and control of horizontal rotation. Exp Brain Res 41:159–171
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. H. Autrum on the occasion of his 75th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schöne, H., Neil, D.M., Scapini, F. et al. Interaction of substrate, gravity and visual cues in the control of compensatory eye responses in the spiny lobster,Palinurus vulgaris . J. Comp. Physiol. 150, 23–30 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00605284
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00605284