Abstract
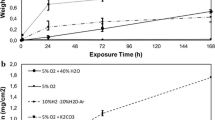
A commercial 18% Cr-11% Ni steel and a laboratory-made 21% Cr-11% Ni alloy have been oxidized in steam at 50 atm pressure and with approximately 0.2 ppm O2 at 800°C for 50–1000 hr. The oxide scales have been studied by optical microscopy, replica electron microscopy, x-ray, and selected-area-electron diffraction and microprobe analysis. The diffusion processes have been studied by gold markers and autoradiography by means of the reaction18O (p, n)18F. On both materials internal oxidation in combination with external scale formation is observed. The interface between the external scale and the inner internally oxidized scale coincides very closely with the original metal surface. The oxide phases present have been identified. The scale is of fairly even thickness on the 21% Cr-11% Ni alloy and grows by a cubic rate law. The scale on the commercial steel is of very irregular thickness; areas with protective Cr-oxide alternate with areas of the above-mentioned structure, so-called nodules. The zones of internal oxidation in the nodules are frequently intersected by bands of compact oxide. The growth mechanism of the nodules is discussed in terms of the theory for internal oxidation. The reason for the beneficial effect of increased Ni content with constant Cr content is discussed briefly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Eberle and C. H. Anderson,J. Eng. Power Trans. ASME 84, 223 (1962).
W. E. Ruther and S. Greenberg,J. Electrochem. Soc. 111, 1116 (1964).
G. P. Wozaldo and W. L. Pearl,Corrosion 21, 355 (1965).
M. J.-Ph. Berge,European Coal and Steel Community IV Congress (1968).
S. Jansson, W. Hübner, G. Östberg, and M. de Pourbaix,Brit. Corrosion J. 4, 21 (1969).
J. C. Bokros and W. P. Wallace,Corrosion 16, 73A (1960).
H. T. Daniel, J. E. Antill, and K. A. Peakall,J. Iron Steel Inst. 201, 154 (1963).
H. E. McCoy,Corrosion 21, 84 (1965).
H. Loriers, D. Leclercq, and R. Darras,Mem. Sci. Rev. Met. 60, 177 (1963).
D. Caplan and M. Cohen,Corrosion 15, 141A (1959).
J. Decroix,Appl. Mater. Res. 3, 35 (1964).
G. C. Wood and M. G. Hobby,J. Iron Steel Inst. 203, 54 (1965).
G. C. Wood, M. G. Hobby, and B. Vaszko,J. Iron Steel Inst. 202, 685 (1964).
D. Lai, R. J. Borg, M. J. Brabers, J. D. Mackenzie, and C. E. Birchenall,Corrosion 17, 357 t (1961).
G. C. Wood and D. P. Whittle,Corrosion Sci. 7, 763 (1967).
W. Hubner,5th Scandinavian Corrosion Congress (Copenhagen, 1968).
T. Ericsson,4th International Congress on Metallic Corr. (Amsterdam, 1969).
M. Warzee, J. Hennaut, M. Maurice, C. Sonnen, and J. Waty,J. Electrochem. Soc. 112, 670 (1965).
J. Philibert,X-Ray Optics and Microanalysis (Academic Press, New York, 1963), p. 379.
S. J. B. Reed,Brit. J. Appl. Phys. 16, 913 (1965).
K. F. J. Heinrich,The Electron Microprobe (Wiley, New York, 1966).
R. H. Condit and J. B. Holt,J. Electrochem. Soc. 111, 1192 (1964).
W. B. Pearson,Handbook of Lattice Spacings and Structures of Metals and Alloys (Pergamon Press, New York, 1958).
R. K. Di Cerbo and A. U. Seybolt,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 42, 430 (1959).
H. J. Yearian, J. M. Kortright, and R. H. Langenheim,J. Chem. Phys. 22, 1196 (1954).
J. M. Francis,Brit. Corrosion J. 3, 113 (1968).
J. Paidassi and J. Lopez,Mem. Sci. Rev. Met. 58, 677 (1961).
A. U. Seybolt,J. Electrochem. Soc. 107, 147 (1960).
O. Kubaschewski and E. Ll. Evans,Metallurgical Thermochemistry (Pergamon Press, New York, 1958).
J. D. Tretjakow and H. Schmalzried,Ber. Bunsenges. Physik. Chem. 69, 396 (1965).
D. P. Whittle, G. C. Wood, D. J. Evans, and D. B. Scully,Acta Met. 15, 1747 (1967).
J. E. Castle and P. L. Surman,J. Phys. Chem. 73, 632 (1969).
J. I. Goldstein, R. E. Hanneman, and R. E. Ogilvie,Trans. AIME 233, 812 (1965).
K. Hauffe,Oxidation of Metals (Plenum Press, New York, 1965).
C. T. Fujii and R. A. Meussner,J. Electrochem. Soc. 110, 1195 (1963).
C. T. Fujii and R. A. Meussner,J. Electrochem. Soc. 111, 1215 (1964).
P. K. Kofstad and A. Z. Hed,J. Electrochem. Soc. 116, 224 (1969).
Y. Adda and J. Philibert,La Diffusion dans les Solides II (Presse Univ. de France, 1966).
C. Wagner,Z. Elektrochem. 63, 772 (1959).
L. B. Pfeil,J. Iron Steel Inst. 119, 501 (1929).
K. Sachs,Metallurgia 54, 11 (1956).
R. A. Rapp,Corrosion 21, 382 (1965).
G. C. Wood,Corrosion Sci. 2, 173 (1961).
T. Ericsson, L-G. Liljestrand, S. Sehlstedt, and H. Sterner (submitted toJ. Iron Steel Inst.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ericsson, T. Stratified oxide scale growth on two Cr-Ni steels oxidized in high-pressure steam at 800°C. Oxid Met 2, 173–205 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00603656
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00603656