Abstract
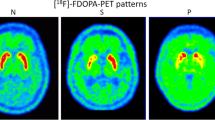
Positron emission tomography (PET) studies using [18F]-l-dopa were carried out in 9 patients with supranuclear palsy and 13 controls. For quantification of PET data a rate constant Ki was calculated for the radiotracer using a graphical method. Corrections for nonspecific activity were performed in both arterial plasma and brain tissue. The purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis that parametric images of the rate constant K mapping can be obtained on a pixel-by-pixel basis using an appropriate mathematical algorithm. Ki values from these parametric images and the graphical approach were compared. Both correlated closely, with y=0.013+0.947*x, r=0.992 and y=−0.052+1.048*x, r=0.965 in patients and controls, respectively. Contrast measurements were also performed and showed a striking increase in contrast on parametric images. K mapping offers several advantages over the graphical approach, since parametric images are time-independent, i. e. one image represents the quantitative result of the study. In addition, parametric images of the rate constant are normalized to arterial plasma radioactivity and corrected for tissue metabolites. Thus, parametric images of Ki in different individuals can be compared directly without further processing in order to assess the nigrostriatal integrity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin WRW, Palmer MR, Patlak CS, Calne DB (1989) Nigrostriatal function in humans with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 26: 535–542
Garnett ES, Firnau G, Nahmias C, Sood, S, Belbeck L (1980) Blood-brain barrier transport and cerebral utilization of dopa in living monkeys. Am J Physiol 238: 318–327
Patlak CS, Blasberg RG, Fenstermacher JD (1983) Graphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple-time uptake data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3: 1–7
Patlak CS, Blasberg RG (1985) Graphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple-time uptake data: generalizations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5: 584–590
Bloomfield PM, Sawle GV, Frackowiak RSJ (1991) A method for inter-subject comparison of [18F]-6-l-fluordopa positron emission tomography studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11: S 609
Ruth TJ (1985) The production of 18F-F2 and 150-02 sequentially from the same target chamber. Int J Appl Radiat Isot 36: 107–110
Adam MJ, Jivan S (1988) Synthesis and purification of L-6-[18F]fluorodopa. Appl Radiat Appl Instrum 39: 1203–1206
Evans B, Harrop R, Heywood D, Mackintosh J, Moore, RW, Pate BD, Rogers JG, Ruth TJ, Sayre C, Sprenger H, Van Oers N, Yao XG (1983) Engineering developments on the UBc-TRIUMF modified PETT VI positron emission tomograph. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci NS 30: 707–710
Chan GLY, Hewitt KA, Pate BD, Schofield P, Adam MJ, Ruth TJ (1992) Routine determination of [18F]-l-dopa and its metabolites in blood plasma is essential for accurate PET studies. Life Sci 50: 309–318
Firnau G, Garnett ES, Sourkes TL, Missala K (1975) [18F]-fluorodopa: a unique gamma emitting substrate for dopa decarboxylase. Experementia 31: 1254–1255
Guttman M, Calne DB (1988) In vivo characterization of cerebral dopamine systems in human parkinsonism. In: Jankovic J, Tolosa E (eds) Parkinson's disease and movement disorders. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore, Munich, 1988, pp 49–58
Garnett ES, Firnau G, Nahmias C (1983) Dopamine visualized in the basal ganglia of living man. Nature 305: 137–138
Martin WRW, Boyes BE, Leenders KL, Patlak CS (1985) Method for quantitative analysis of 6-fluoro-dopa uptake data from positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5 [Suppl 1] S 593–594
Bhatt MH, Snow BJ, Martin WRW, Peppard R, Calne DB (1990) Positron emission tomography in supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 28: 101–103
Brooks DJ, Ibanez V, Sawle GV, Quinn N, Lees AJ, Mathias CJ, Bannister R, Marsden CD, Frackowiak RSJ (1990) Differing patterns of striatal 18F-dopa uptake in Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 28: 547–555
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cordes, M., Snow, B.J., Morrison, S. et al. Parametric imaging of the rate constant Ki using [18Fluoro]-l-dopa positron emission tomography in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neuroradiology 35, 404–409 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00602816
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00602816