Abstract
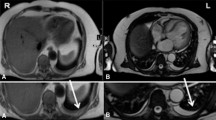
MR angiography (MRA) is a promising completion of MR imaging in the preoperative assessment of pulmonary and mediastinal tumours. Scan acquisition was done by sequential FLASH 2D angiograms (TR = 30 ms, TE = 10 ms, FA = 30°), one section per breathhold, section thickness 5 mm with 1 mm overlap between sequential sections. An automated control procedure allowed individiual continuation of the examination. Postprocessing by a maximum-intensity-projection algorithm using angiograms of interest (AOI) resulted in 3D reconstructions illustrating vascular anatomy and avoiding superimposition. This technique was evaluated in a prospective study of 15 patients with malignant intrathoracic tumours. The results were validated by conventional angiographic procedures such as pulmonary angiography, digital subtraction angiography or cavography. Complementing spin-echo (SE) imaging, MRA provided diagnostic information about vessel displacement, stenosis and perfusion defects due to space-occupying lesions. Thus MRA was helpful in planning thoracic surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edelman RR, Wentz KU, Mattle H, Zhao B, Liu C, Kim D, Laub G (1989) Projection arteriography and venography: initial clinical results with MR. Radiology 172: 351
Kauczor H-U, Layer G, Schad LR, Müller-Schimpfle M, Tuengerthal SJ, Vogt-Moykopf I, Semmler W, Kaick G van (1991) Clinical applications of MR angiography in intrathoracic masses. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14: 409
Tuengerthal SJ, Clorius JH (1989) Radiology in thoracic surgery: the role of conventional radiography. In: Martini N, Vogt-Moykopf I (eds) Thoracic surgery: frontiers and uncommon neoplasms. The Mosby Company, St. Louis, pp 55–76
Frahm J, Haase A, Matthaei D (1986) Rapid NMR imaging of dynamic processes using the FLASH technique. Magn Reson Med 3: 321
Haase A, Frahm J, Matthaei KD (1986) FLASH imaging: rapid NMR imaging using low flip angle pulses. J Magn Reson 67: 258
Haacke EM, Lenz G (1987) Improving MR image quality in the presence of motion by using rephasing gradients. AJR 148: 1251
Lenz GW, Haacke EM, Masaryk TJ, Laub G (1988) In-plane vascular imaging: pulse sequence design and strategy. Radiology 166: 875
Felmlee JP, Ehman RL (1987) Spatial presaturation: a method for suppressing flow artifacts and improving depiction of vascular anatomy in MR imaging. Radiology 164: 559
Laub GA, Kaiser WA (1988) MR angiography with gradient motion refocusing. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12: 377
Anderson CM, Saloner D, Tsuruda JS, Shapeero LG, Lee RE (1990) Artifacts in maximum-intensity-projection display of MR angiograms. AJR 154: 623
Arlart IP, Guhl L, Fauser L, Laub G, Edelman RR (1991) MR-Angiographie der Abdominalaorta: Erste Erfahrungen. Fortschr Röntgenstr 154: 488
Gehl H-B, Bohndorf K, Klose K-C, Günther RW (1990) Two-dimensional MR angiography in the evaluation of abdominal veins with gradient motion refocused sequences. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14: 619
Kim D, Edehnan RR, Kent KC, Porter DH, Skillman JJ (1990) Abdominal aorta and renal artery stenosis: evaluation with MR angiography. Radiology 174: 727
Müller-Schimpfle M, Layer G, Köster A, Brix G, Kimmig B, Kauczor H-U, Wannenmacher M, Semmler W, Kaick G van (1992) MRI and MRA in treatment planning of subdiaphragmatic radiation therapy. J Comput Assist Tomogr 16: 110
Wallner B, Edelman RR, Kim D, Finn JP (1991) Darstellung thorakaler und abdomineller Aortenaneurysmen mit MR-Angiographie. Fortschr Röntgenstr 154: 11
Lewin JS, Laub G, Hausmann R (1991) Three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography: applications in the abdomen and thorax. Radiology 179: 261
Hatabu H, Gefter WB, Kressel HY, Axel L, Lenkinski RE (1989) Pulmonary vasculature: high-resolution MR imaging. Radiology 171: 391
Edelman RR, Wentz KU, Mattle HP, O'Reilly GV, Candia G, Liu C, Zhao B, Kjellberg RN, Davis KR (1989) Intracranial arteriovenous malformations: evaluation with selective MR arteriography and venography. Radiology 173: 831
Musset D, Grenier P, Carette MF, Frija G, Hauuy MP, Desbleds MT, Girard P, Bigot JM, Lallemand D (1986) Primary lung cancer staging: prospective comparative study of MR imaging with CT. Radiology 160: 607
Webb R (1989) The role of magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of patients with lung cancer: a comparison with computed tomography. J Thorac Imag 4: 65
Masaryk TJ, Modic MT, Ruggieri PM, Ross JS, Laub G, Lenz GW, Tkach JA, Haacke EM, Selman WR, Harik SI (1989) Three-dimensional (volume) gradient-echo imaging of the carotid bifurcation: preliminary clinical experience. Radiology 171: 801
Podolak MJ, Hedlund LW, Evans AJ, Herfkins RJ (1989) Evaluation of flow through simulated vascular stenoses with gradient echo magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 24: 184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kauczor, H.U., Gamrothe, A.H., Tuengerthal, S.J. et al. MR Angiography: clinical applications in thoracic surgery. Eur. Radiol. 2, 214–222 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00595833
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00595833