Abstract
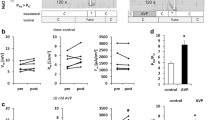
The effect of cAMP on transepithelial and transmembrane potential differences and resistances was examined in isolated in vitro perfused mouse medullary thick ascending limbs of Henle's loop (mTAL). The effects of furosemide and barium were tested. Stimulation of NaCl transport by ADH 10−9+dbcAMP 4·10−4+forskolin 10−6 mol·l−1 (paired experiments) resulted in: a) an increase in transepithelial potential difference, referenced to the grounded bath, from +6.7±0.3 mV to +12.0±0.4 mV (n=47); b) a decrease in transepithelial resistance from 25±1 Ω cm2 to 20±1 Ω cm2 (n=47); c) a depolarization of the basolateral membrane by 12 mV and of the apical membrane by 7 mV (n=36); d) a decrease in the fractional resistance of the basolateral membrane from 0.27±0.005 to 0.15±0.06 (n=12). Furosemide (10−4 mol·l−1) abolished the active transepithelial transport potential and hyperpolarized the basolateral membrane potential to values which were similar in both control and cAMP treated mTAL segments. Barium increased the transepithelial resistance and depolarizedPD bl to similar values in both functional states. An increase in the fractional conductance of the basolateral membrane was also seen, if, prior to the cAMP treatment, the luminal Na+2Cl−K+ contransport was inhibited by furosemide. Thus, we propose that stimulation of active NaCl reabsorption in the mTAL segment of the mouse by ADH, mediated via cAMP, increases primarily the basolateral chloride conductance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakker-Grunwald T (1981) Hormone-induced diuretic-sensitive potassium transport in turkey erythrocytes is anion dependent. Biochim Biophys Acta 641:427–431
Burg M, Grantham J, Abramow M, Orloff J (1966) Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol 210:1293–1298
Cook DI, Frömter E (1985) Is the voltage divider ratio a reliable estimate of the resistance ratio of the cell membranes in tubular epithelia? Pflügers Arch 403:388–395
Eveloff J, Kinne R (1983) Sodium-chloride transport in the medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop: evidence for a sodium-chloride cotransport system in plasma membrane vesicles. J Membr Biol 72:173–181
Frizzell RA, Field M, Schultz SG (1979) Sodium-coupled chloride transport by epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol 236:F1-F8
Grantham JJ, Burg MB (1966) Effect of vasopressin and cyclic AMP on permeability of isolated collecting tubules. Am J Physiol 211:255–259
Greger R (1981) Cation selectivity of the isolated perfused cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 390:30–37
Greger R (1981) Chloride reabsorption in the rabbit cortical thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. A sodium dependent process. Pflügers Arch 390:38–43
Greger R, Hampel W (1981) A modified system for in vitro perfusion of isolated renal tubules. Pflügers Arch 389:175–176
Greger R, Schlatter E (1981) Presence of luminal K+, a prerequisite for active NaCl transport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 392:92–94
Greger R, Schlatter E (1983) Properties of the basolateral membrane of the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. A model for secondary active chloride transport. Pflügers Arch 396:325–334
Greger R, Schlatter E (1983) Properties of the lumen membrane of the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 396:315–324
Greger R, Schlatter E (1983) Cellular mechanism of the action of loop diuretics on the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Klin Wochenschr 61:1019–1027
Greger R, Schlatter E (1984) Mechanism of NaCl secretion in rectal gland tubules of spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias). II. Effects of inhibitors. Pflügers Arch 402:364–375
Greger R, Oberleithner H, Schlatter E, Cassola AC (1983) Chloride activity in cells of isolated perfused cortical thick ascending limbs of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 399:29–34
Greger R, Schlatter E, Gögelein H (1985) Cl−-channels in the apical cell membrane of the rectal gland “induced” by cAMP. Pflügers Arch 403:446–448
Greger R, Schlatter E, Lang F (1983) Evidence for electroneutral sodium chloride cotransport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 396:308–314
Greger R, Schlatter E, Wang F, Forrest JN Jr (1984) Mechanism of NaCl secretion in rectal gland tubules of spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias). III. Effects of stimulation of secretion by cyclic AMP. Pflügers Arch 402:376–384
Hall DA, Varney DM (1980) Effect of vasopressin on electrical potential difference and chloride transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. J Clin Invest 66:792–802
Hebert SC, Andreoli TE (1982) Salt and water transport in the mouse medullary thick ascending limb. Role of antidiuretic hormone. In: Martonosi A (ed) Membranes and Transport. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 187–196
Hebert SC, Andreoli TE (1984) Control of NaCl transport in the thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol 246:F745-F756
Hebert SC, Andreoli TE (1984) Effects of antidiuretic hormone on cellular conductive pathways in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs of Henle. II. Determinants of the ADH-mediated increases in transepithelial voltage and in net Cl− absorption. J Membr Biol 80:221–233
Hebert SC, Culpepper RM, Andreoli TE (1981) NaCl transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs. I. Functional nephron heterogeneity and ADH-stimulated NaCl cotransport. Am J Physiol 241:F412-F431
Hebert SC, Culpepper RM, Andreoli TE (1981) NaCl transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs. II. ADH enhancement of transcellular NaCl cotransport; origin of transepithelial voltage. Am J Physiol 241:F432-F442
Hebert SC, Friedman PA, Andreoli TE (1984) Effects of antidiuretic hormone on cellular conductive pathways in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs of Henle. I. ADH increases transcellular conductance pathways. J Membr Biol 80:201–219
Heintze K, Stewart CP, Frizzell RA (1983) Sodium-dependent chloride secretion across rabbit descending colon. Am J Physiol 244:G357-G365
Hoshi T, Kawahara K, Yokoyama R, Suenaga K (1981) Changes in membrane resistances of renal proximal tubule induced by cotransort of sodium and organic solute. In: Takacs L (ed) Kidney and body fluids, vol 11. Pergamon Press, Budapest, pp 403–407
Imai M, Torikai S, Takeda K (1984) Regulation of ion transport in the thick ascending limbs of Henle's loop. In: Hoshi T (ed) Coupled transport in nephron. Miura Foundation, Tokyo, pp 119–130
Koenig B, Ricapito S, Kinne R (1983) Chloride transport in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop: potassium dependence and stoichiometry of the NaCl cotransport system in plasma membrane vesicles. Pflügers Arch 399:173–179
Peterson KU, Reuss L (1983) Cyclic AMP-induced chloride permeability in the apical membrane ofNecturus gallbladder epithelium. J Gen Physiol 81:705–729
Reuss L, Reinach P, Weinman SA, Grady TP (1983) Intracellular ion activities and Cl−-transport mechanisms in bullfrog corneal epithelium. Am J Physiol 244:C336-C347
DeRouffignac C, Corman B, Roinel N (1983) Stimulation by antidiuretic hormone of electrolyte tubular reabsorption in rat kidney. Am J Physiol 244:F156-F164
Sasaki S, Imai M (1980) Effects of vasopressin on water and NaCl transport across the in vitro perfused medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mouse, rat, and rabbit kidneys. Pflügers Arch 383:215–221
Shorofsky SR, Field M, Fozzard HA (1982) The cellular mechanism of active chloride secretion in vertebrate epithelia: studies in intestine and trachea. Philos Trans R Soc (Lond) B299:597–607
Smith PL, Welsh MJ, Stoff JS, Frizzell RA (1982) Chloride secretion by canine tracheal epithelium. I. Role of intracellular cAMP levels. J Membr Biol 70:217–226
Stokes JB (1982) Consequences of potassium recycling in the renal medulla. Effects on ion transport by the medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. J Clin Invest 70:219–229
Stokes JB (1984) Regulation of NaCl transport by the loop of Henle. In: Robinson RR (ed) Nephrology, vol 1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 208–223
Welsh MJ, Smith PL, Frizzell RA (1983) Chloride secretion by canine tracheal epithelium. III. Membrane resistances and electromotive forces. J Membr Biol 71:209–218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft Gr 480/6-2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlatter, E., Greger, R. cAMP increases the basolateral Cl−-conductance in the isolated perfused medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of the mouse. Pflugers Arch. 405, 367–376 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00595690
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00595690