Abstract
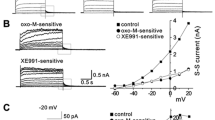
The mechanism of slow muscarinic excitation in bullforg sympathetic ganglia was studied using a singleelectrode voltage clamp technique. The membrane current induced by muscarine (0.01–30 μM:I mus) consisted of a voltage-dependent component (dI M) induced by the inhibition of K+-current (known asI M), a voltage-independent cation-selective current (I D), or both. In the last case, the magnitude of either component varied in different cells. Generation of bothdI M andI D were equally suppressed by pirenzepine with a dissociation constant (K i) of 30 nM, while they were inhibited less by AF-DX116 with aK i of 600 nM.K d values for muscarinic induction ofdI M andI D were 0.35 and 5 μM respectively. This difference was also seen even after reducing the receptor population by pretreatment with propylbenzilylcholine mustard.I D was enhanced after blockade ofdI M by Ba2+ (4 mM), with a little change inK d. This effect was larger when the controlI D was smaller. These results suggest that a single subtype (M1) of muscarinic receptor generates both thedI M andI D with different efficacies and that Ba2+, known as a blocker ofI M (accordingly of a high-efficacy current,dI M), potentiates a low-efficacy current (I D).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams PR, Brown DA, Constanti A (1982a) M-Currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol 330:537–572
Adams PR, Brown DA, Constanti A (1982b) Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol 332:223–262
Akasu T, Gallagher JP, Koketsu K, Gallagher PS (1984) Slow excitatory, post-synaptic currents in bull-frog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol 351:583–593
Brown DA, Adams PR (1980) Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature 283:673–676
Brown DA, Selyanko AA (1985) Two components of muscarinesensitive membrane current in rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol 358:335–363
Cole A, Nicoll RA (1984) Characterization of a slow cholinergic post-synaptic potential recorded in vitro from rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol 352:173–188
Dodd J, Horn JP (1983) A reclassification of B and C neurones in the ninth and tenth paravertebral sympathetic ganglia of the bullfrog. J Physiol 334:255–269
Gil DW, Wolfe BB (1985) Pirenzepine distinguishes between muscarinic receptor-mediated phosphoinositide breakdown and inhibition of adenylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 232:608–616
Goyal RK, Rattan S (1978) Neurohumoral, hormonal and drug receptors for the lower esophageal sphincter. Gastroenterology 74:598–619
Hammer R, Berrie CP, Birdsall NJM, Burgen ASV, Hulem EC (1980) Pirenzepine distinguishes between different sub-classes of muscarinic receptors. Nature 283:90–92
Hammer R, Giraldo E, Schiavi GB, Monferini E, Ladinsky H (1986) Binding profile of a novel cardioselective muscarine receptor antagonist, AF-DX 116, to membranes of peripheral tissues and brain in the rat. Life Sci 38:1653–1662
Hashiguchi T, Kobayashi H, Tosaka T, Libet B (1982) Two muscarinic mechanisms in mammalian sympathetic neurons. Brain Res 242:378–382
Higashida H, Brown DA (1986) Two polyphatidylinositide metabolites control two K+ currents in a neuronal cell. Nature 323:333–335
Jones SW (1985) Muscarinic and peptidergic excitation of bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 366:63–87
Kobayashi H, Libet B (1968) Generation of slow postsynaptic potentials without increases in ionic conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69:1304–1311
Kuba K, Koketsu K (1974) Ionic mechanism of the slow excitatory postsynaptic potential in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Brain Res 81:338–342
Kuba K, Koketsu K (1976) Analysis of the slow excitatory postsynaptic potential in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Jpn J Physiol 26:651–669
Kuba K, Koketsu K (1978) Synaptic events in sympathetic ganglia. Prog Neurobiol 11:77–169
Kuba K, Morita K, Nohmi M (1983) Origin of calcium ions in the generation of a slow afterhyperpolarization in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. Pflügers Arch 399:194–202
Kuffler LSW, Sejnowski TJ (1983) Peptidergic and muscarinic excitation at amphibian sympathetic synapses. J Physiol 341:257–278
Libet B (1964) Slow synaptic responses and excitatory changes in sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol 174:1–25
Murphy S, Pearce B, Morrow C (1986) Astrocytes have both M1 and M2 muscarinic receptor subtypes. Brain Res 364:177–180
Nishi S, Koketsu K (1960) Electrical properties and activities of single sympathetic neurones of frogs. J Cell Comp Physiol 55:15–30
Nishi S, Koketsu K (1968) Early and late afterdischarge, of amphibian sympathetic ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol 31:109–121
Nishizuka Y (1984) The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumor promotion. Nature 308:693–698
Tosaka T, Chichibu S, Libet B (1968) Intracellular analysis of slow inhibitory and excitatory postsynaptic potentials in sympathetic ganglia of the frog. J Neurophysiol 31:396–409
Tsuji S, Kuba K (1986) Excitatory muscarinic receptor and ion channels in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol Soc Jpn 48:207
Tsuji S, Minota S, Kuba K (1987) Regulation of two ion channels by a common muscarinic receptor-transduction system in a vertebrate neurone. Neurosci Lett 81:139–145
Weight F, Votava Z (1970) Slow synaptic excitation in sympathetic ganglion cells: evidence for synaptic inactivation of potassium conductance. Science 170:755–758
Wilson WA, Goldner MM (1975) Voltage clamping with a single microelectrode. J Neurobiol 6:411–422
Wise BC, Raynor RL, Kuo JF (1982) Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. I. Purification and general properties. J Biol Chem 257:8481–8488
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuji, S., Kuba, K. Muscarinic regulation of two ionic currents in the bullfrog sympathetic neurone. Pflugers Arch. 411, 361–370 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587714
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587714