Summary
The experiments were performed on 28 unanaesthetized, unrestrained cats of both sexes weighing 2.5–3.5 kg. For the operations pentobarbital anaesthesia (40 mg/kg) was used.
-
1.
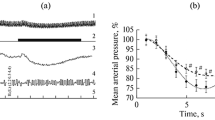
Weak electrical stimulation of the basolateral area of the nucleus amygdalae and the septum causes a decrease in blood pressure without alteration of the EMG (registered from the dorsal cervical muscles).
-
2.
Stimulation with medium intensity of these cerebral structures and of the nucleus amygdalae centralis evokes an isolated rise in blood pressure. The electrical threshold for the cardiovascular responses is lower than that for a behavioral reaction.
-
3.
Stronger stimulation of three limbic areas causes a latent psycho-motor reaction, which follows the rise in blood pressure. The time intervals between the onset of stimulation and i) the rise in blood pressure and ii) the first motor reaction depend upon the stimulus intensities. This means the higher the intensities of stimulation the shorter the latencies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand, B. K., Dua, S.: Stimulation of limbic system of brain in waking animals. Science122, 1139 (1955)
Anand, B. K., Dua, S.: Circulatory and respiratory changes induced by electrical stimulation of limbic system (visceral brain). J. Neurophysiol.19, 393–400 (1956)
Andy, O. J., Bonn, P., Chinn, McC., Allen, M.: Blood pressure alterations secondary to amygdaloid and periamygdaloid after-discharges. J. Neurophysiol.22, 51–60 (1959)
Baust, W., Heinemann, H.: The role of the baroreceptors and of blood pressure in the regulation of sleep and wakefulness. Exp. Brain Res.3, 12–24 (1967)
Brady, J. V., Nauta, W. J. H.: Subcortical mechanisms in emotional behavior; affective changes following septal forebrain lesions in the albino rat. J. comp. physiol. Psychol.46, 339–346 (1953)
Brady, J. V., Nauta, W. J. H.: Subcortical mechanisms in emotional behavior; duration of affective changes following septal and habenular lesions in the albino rat. J. comp. physiol. Psychol.48, 412–420 (1955)
Covian, M. R.: Studies on the neurovegetative and behavioral functions of the brain septal area. Progr. Brain Res.27, 189–217 (1967)
Covian, M. R., Antunes-Rodrigues, J., Flaherty, J. J. O': Effects of stimulation of the septal area upon blood pressure and respiration in the cat. J. Neurophysiol.27, 394–407 (1964)
Eliasson, S., Lindgren, P., Uvnäs, B.: Representation in the hypothalmus and the motor cortex in the dog of the sympathetic vasodilator outflow to the sceletal muscles. Acta physiol. scand.27, 18–37 (1959)
Fernandez de Molina, A., Hunsperger, R. W.: Central representation of affective reactions in forebrain and brain stem: electrical stimulation of amygdala, stria terminalis and adjacent structures. J. Physiol. (Lond.)145, 251–265 (1959)
Folkow, B., Johansson, B., Öberg, B.: A hypothalamic structure with a marked inhibitory effect on tonic sympathetic activity. Acta physiol. scand.47, 262–270 (1959)
Gastaut, H.: Corrélations entre le système nerveux végétatif et le système de la vie de relation dans le rhinencéphale. J. Physiol. (Paris)44, 431–470 (1952)
Gastaut, H., Vigouroux, R., Corriol, J., Badier, M.: Effects de la stimulation électrique (par électrodes à demeure) du complexe amygdalien chez le chat non narcosé. J. Physiol. (Paris)43, 740–746 (1951)
Harrison, J. M., Lyon, M.: The role of the septal nuclei and components of the fornix in the behavior of the rat. J. comp. Neurol.108, 121–137 (1957)
Kaada, B. R.: Somatomotor, autonomic and electrocorticographic responses to electrical stimulation of “rhinencephalic” and other structures in primates, cat and dog. Acta physiol. scand.24, Suppl. 83, 1–285 (1951)
Kaada, B. R., Andersen, P., Jansen, J., Jr.: Stimulation of amygdaloid nuclear complex in unanaesthetized cats. Neurology (Minneap.)4, 48–64 (1954)
Kabat, H., Magoun, H. W., Ranson, S. W.: Electrical stimulation of points in the forebrain and midbrain. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.)34, 931–955 (1935)
MacLean, P. D.: Some psychiatric implications of physiological studies on frontotemporal portion of limbic system (visceral brain). Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.4, 407–418 (1952)
MacLean, P. D., Delgado, J. M. R.: Electrical and chemical stimulation of frontotemporal portion of limbic system in the waking animal. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.5, 91–100 (1953)
MacLean, P. D., Ploog, D. W.: Cerebral representation of penile erection. J. Neurophysiol.25, 29–55 (1962)
Magnus, O., Lammers, H. J.: The amygdaloid nuclear complex. Part I: Electrical stimulation of the amygdala and periamygdaloid cortex in the waking cat. Folia psychiat. neerl.55, 555–581 (1956)
Manning, J. W., Charbon, G. A., Cotten, M. de V.: Inhibition of tonic cardiac sympathetic activity by stimulation of brain septal region. Amer. J. Physiol.205, 1221–1226 (1963)
Morin, G., Naquet, R., Badier, M.: Stimulation électrique de la région amygdalienne et pression artérielle chez le chat. J. Physiol. (Paris)44, 303–305 (1952)
Morison, R. S., Rioch, D. McK.: The influence of the forebrain on an autonomic reflex. Amer. J. Physiol.120, 257–276 (1937)
Naquet, R.: Sur les fonctions du rhinencéphale d'après les résultats de la stimulation chez le chat. Thesis, Marseille 1953
Olds, M. E., Olds, J.: Effect of lesions in medial forebrain bundle on self-stimulation behavior. Amer. J. Physiol.217, 1253–1264 (1969)
Poirier, L. J., Shulman, E.: Anatomical basis for the influence of the temporal lobe on respiration and cardiovascular activity. J. comp. Neurol.100, 99–109 (1954)
Ranson, S. W., Magoun, H. W.: The hypothalamus. Ergebn. Physiol.41, 56–163 (1939)
Reinoso-Suarez, F.: Topographischer Hirnatlas der Katze für experimentalphysiologische Untersuchungen. E. Merck AG, Darmstadt 1961
Shealy, C. N., Peele, T. L.: Studies on amygdaloid nucleus of cat. J. Neurophysiol.20, 125–139 (1957)
Spiegel, E. A., Miller, H. R., Oppenheimer, M. J.: Forebrain and rage reactions. J. Neurophysiol.3, 538–548 (1940)
Torii, S., Kawamura, H.: Effects of amygdaloid stimulation and blood pressure and electrical activity of hippocampus. Jap. J. Physiol.10, 374–348 (1960)
Tracy, W. H., Harrison, J. M.: Aversive behavior following lesion of the septal region of the brain in the cat. Amer. J. Psychol.69, 443–447 (1956)
Valenstein, E. S., Campbell, J. F.: Medial forebrain bundle-lateral hypothalamic area and reinforcing brain stimulation. Amer. J. Physiol.210, 270–274 (1966)
Vigouroux, R., Gastaut, H., Badier, M.: Les formes expérimentales de l'épilepsie. Provocation des principales manifestation cliniques de l'épilepsie de temporale par stimulation des structures rhinencéphaliques chez le chat non anesthésié. Rev. neurol.85, 505–508 (1951)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft with in the SFB 90 “Cardiovasculäres System”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinemann, H., Stock, G. & Schaefer, H. Temporal correlation of responses in blood pressure and motor reaction under electrical stimulation of limbic structures in unanaesthetized, unrestrained cats. Pflugers Arch. 343, 27–40 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586572
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586572