Summary
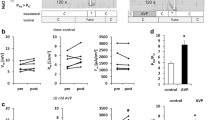
To asses passive permeability properties of distal, and proximal tubules of the rat kidney the tubular lumen was perfused with solutions of 1.5 and 150 mM Na/l while transtubular potential differences were recorded. Sodium transport numbers (T Na) were calculated.T Na in the distal tubule of adrenalectomized rats was acutely increased from 0.21 to 0.27 by aldosterone (5 μg/100 g B.W.). This effect of aldosterone could not be reduced by concomitant injection of cycloheximide (100 μg/100 g B.W.). Aldosterone was also effective in control rats. In the proximal tubule similar data were obtained. However, the aldosterone-induced increase of conductance was slightly reduced with cycloheximide.
These measurements of transepithelial sodium conductance indicate that aldosterone, in addition to the already known stimulation of active sodium transport, increases overall permeability of the tubular wall to sodium. In the distal tubule this effect indicates an increase of the luminal membrane permeability whereas in the proximal tubule aldosterone may facilitate the diffusion of sodium through the intercellular shunt path and/or the luminal membrane. The passive components of transepithelial electrolyte transfer seem to be less sensitive to inhibition of protein synthesis than the active transport components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulpaep, E. L., Seely, J. F.: Electrophysiology of proximal and distal tubules in the autoperfused dog kidney. Amer. J. Physiol.221, 1034–1096 (1971)
Civan, M. M., Hoffman, R. E.: Effect of aldosterone on electrical resistance of toad bladder. Amer. J. Physiol.220, 324–328 (1971)
Cuthbert, A. W., Painter, E.: Mechanism of action of aldosterone. Nature (Lond.)222, 280–281 (1969)
Feldman, D., Funder, J. W., Edelman, J. S.: Subcellular mechanisms in the action of adrenal steroids. Amer. J. Med.53, 545–560 (1972)
Fimognari, G. M., Fanestil, D. D., Edelman, I. S.: Induction of RNA and protein synthesis in the action of aldosterone. Amer. J. Physiol.213, 954–962 (1967)
Frömter, E., Müller, C. W., Wick, T.: Permeability properties of the proximal tubular epithelium of the rat kidney studied with electrophysiological methods. In: Electrophysiology of Epithelial Cells, Symposium, Schloß Reinhardshausen, edited by G. Giebisch, pp. 119–146 Stuttgart-New York: Schattauer 1971
Giebisch, G., Malnic, G., Klose, R. M., Windhager, E. E.: Effect of ionic substitution on distal potential differences in rat kidney. Amer. J. Physiol.211, 560–568 (1966)
Gutsche, H. U., Lange, S., Hegel, U.: Influx of electrolytes into the proximal tubule of rat kidney under the influence of aldosterone (Electrical measurements). V. Int. Congr. Nephrol. Mexico,. Abstract No. 646 (1972)
Handler, J. S., Preston, A. S., Orloff, J.: Effect of ADH, aldosterone, ouabain and amiloride on toad bladder epithelial cells. Amer. J. Physiol.222, 1071–1074 (1972)
Hierholzer, K., Wiederholt, M., Holzgreve, H., Giebisch, G., Klose, R. M., Windhager, E. E.: Micropunctures study of renal transtubular concentration gradients of sodium and potassium in adrenalectomized rats. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.285, 193–210 (1965)
Hodgkin, A. L., Horowicz, P.: The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)148, 127–160 (1959)
Knauf, H., Gruber, W. D., Nowzohour, B.: Actinomycin D als Antagonist der Aldosteronwirkung am Speichedrüsengang. Pflügers Arch.320, R93, (1970)
Leaf, A., Macknight, A. D. C.: The site of the aldosterone induced stimulation of sodium transport. J. Steroid Biochem.3, 237–245 (1972)
Lipton, P., Edelman I. S.: Effects of aldosterone and vasopressin on electrolytes of toad bladder epithelial cells. Amer. J. Physiol.221, 733–741, (1971)
Lynch, R. E., Schneider, E. G., Willis, L. R., Knox, F. G.: Absence of mineralocorticoid-dependent sodium reabsorption in dog proximal tubule. Amer. J. Physiol.223, 40–45 (1972)
Malnic, G., Giebisch, G.: Some electrical properties of distal tubular epithelium in the rat. Amer. J. Physiol.223, 791–808 (1972)
Martin, D. G., Berliner, R. W.: The effect of aldosterone on proximal tubular sodium reabsorption in the rat. Proc. Amer. Soc. Nephrol., Abstract No. 45 (1969)
Pelletier, M., Ludens, J. H., Fanestil, D. D.: The role of aldosterone in active sodium transport. Arch. intern. Med.129, 248–257 (1972)
Stolte, H., Wiederholt, M., Fuchs, G., Hierholzer, K.: Time course of development of transtubular sodium concentration differences in proximal surface tubules of the rat kidney. Pflügers Arch313, 252–270, (1969)
Uhlich, E., Halback, R., Ullrich, J. J.: Influence of aldosterone on24Na, efflux in collecting ducts of rats. Pflügers Arch.320, 261–264 (1970)
Wiederholt, M.: Mikropunktionsuntersuchungen am proximalen und distalen Konvolut der Rattenniere über den Einfluß von Actinomycin D auf den mineralocorticoidabhängigen Na-Transport. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.292, 334–342 (1966)
Wiederholt, M., Agulian, S. K., Khuri, R. N.: Intracellular potassium in the distal tubule of the adrenalectomized and aldosterone treated rat. Pflügers Arch.347, 117–123 (1974)
Wiederholt, M., Behn, C., Schoormans, W., Hansen, L.: Effect of aldosterone on sodium and potassium transport in the kidney. J. Steroid. Biochem.3, 151–159 (1972)
Wiederholt, M., Schoormans., W., Fischer, F., Behn, C.: Mechanism of action of aldosterone on potassium transfer in the, rat kidney. Pflügers Arch.345, 159–178 (1973)
Wiederholt, M., Stolte, H., Brecht, J.P., Hierholzer, K.: Mikropunktions-untersuchungen über den Einfluß von Aldosteron Cortison und Dexamethason auf die renale Natriumresorption adrenalektomierter Ratten. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.292, 316–333 (1966)
Wright, F. S.: Increasing magnitude of electrical potential along the renal distal tubule. Amer. J. Physiol.220, 624–638 (1971)
Yeh, S. D. J., Shils, M. E.: Quantitative aspects of cycloheximide inhibition of amino acid incorporation. Biochem. Pharmacol.18, 1919–1926 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiederholt, M., Schoormans, W., Hansen, L. et al. Sodium conductance changes by aldosterone in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 348, 155–165 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586477
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586477