Summary
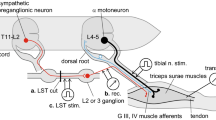
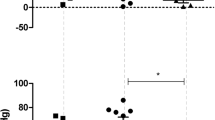
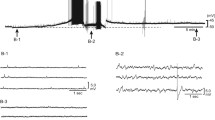
In Nembutal anesthetized cats single shock stimulation of the depressor area of the medulla oblongata evoked inhibition of spontaneous and glutamate-evoked activity of sympathetic preganglionic units. Single shocks to the lateral funiculus of the cervical or upper thoracic spinal cord in acute spinal cats evoked inhibition of the spontaneous and glutamate-evoked activity of single units and of the segmental reflex mass discharge evoked by spinal afferent stimulation. Cats studied 4 to 6 weeks after a complete transection of the spinal cord also showed, on stimulation of the lateral funiculus below the transection, an inhibition of the segmental reflex with time course similar to that seen in the acute spinal state, but of lower threshold and greater intensity. These results suggest that the inhibitory coupling between supraspinal levels and sympathetic preganglionic units is mediated, at least in part, by propriospinal neuronal systems which survive after chronic spinal section. On the assumption that the observed changes in the properties of inhibition are due to plastic changes consequent to partial denervation the results also suggest that continuous descending tracts exist, and that both the continuous and the propriospinal descending tracts may be converging onto some common neural element.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, R. S.: Tonic and reflex functions of medullary sympathetic cardiovascular centers. J. Neurophysiol.9, 205–217 (1946)
Beacham, W. S., Perl, E. R.: Characteristics of a spinal sympathetic reflex. J. Physiol. (Lond.)173, 431–448 (1964)
Burns, B. D., Ferch, W., Mandl, G.: A neurophysiological computer. Electron. Engng.37, 20–24 (1965)
Coote, J. H., Downman, C. B. B.: Central pathways of some autonomic reflex discharges. J. Physiol. (Lond.)183, 714–729 (1966)
Coote, J. H., Macleod, V. H.: The influence of bulbospinal monoaminergic pathways on symphatetic nerve activity. J. Physiol. (Lond.)241, 453–475 (1974a)
Coote, J. H., Macleod, V. H.: Evidence for the involvement in the baroreceptor reflex of a descending inhibitory pathway. J. Physiol. (Lond.)241, 477–496 (1974b)
Curtis, D. R., Phillis, J. W., Watkins, J. C.: The chemical excitation of spinal neurones by certain acidic amino acids. J. Physiol. (Lond.)150, 656–682 (1960)
Eccles, J. C.: The inhibitory pathways of the central nervous system. Liverpool: Univ. Press 1969
Gebber, G. L., Taylor, D. G., Weaver, L. C.: Electrophysiological studies on organization of central vasopressor pathways. Amer. J. Physiol.224, 470–481 (1973)
Gootman, P. M., Cohen, M. I.: Evoked splanchnic potentials produced by electrical stimulation of medullary vasomotor regions. Exp. Brain Res.13, 1–14 (1971)
Illert, M., Seller, H.: A descending sympathoinhibitory tract in the ventrolateral column of the cat. Pflügers Arch.313, 343–360 (1969)
Illert, M., Gabriel, M.: Descending pathways in the cervical cord of cats affecting blood pressure and sympathetic activity. Pflügers Arch.335, 109–124 (1972)
Illert, M., Gabriel, M.: Descending pathways in the spinal cord affecting sympathetic activity in spinalized cats. Acta physiol. pol.24, 115–117 (1973)
Kirchner, F., Kirchner, D., Polosa, C.: Spinal organization of sympathetic inhibition by spinal afferent volleys. Brain Res. (in press, 1975)
Kirchner, F., Sato, A., Weidinger, H.: Bulbar inhibition of spinal and supraspinal sympathetic reflex discharges. Pflügers Arch.326, 324–333 (1971)
Neumayr, R. J., Hare, B. D., Franz, D. N.: Evidence for bulbospinal control of sympathetic preganglionic neurons by monoaminergic pathways. Life Sci.14, 793–806 (1974)
Okada, H., Nakano, O., Nisida, I.: Effects of sciatic stimulation upon the efferent impulses in the long ciliary nerve of the cat. Jap. J. Physiol.10, 327–339 (1960)
Polosa, C.: The silent period of sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.45, 1033–1045 (1967)
Sato, A.: Spinal and supraspinal inhibition of somato-sympathetic reflexes by conditioning afferent volleys. Pflügers Arch.336, 121–133 (1972)
Sato, A., Schmidt, R. F.: Spinal and supraspinal components of the reflex discharges into lumbar and thoracic white rami. J. Physiol. (Lond.)212, 839–850 (1971)
Sato, A., Schmidt, R. F.: Ganglionic transmission of somatically induced sympathetic reflexes. Pflügers Arch.326, 240–253 (1971)
Sato, A., Schmidt, R. F.: Somatosympathetic reflexes: afferent fibers, central pathways, discharge characteristics. Physiol. Rev.53, 916–947 (1973)
Snyder, D. W., Gebber, G. L.: Relationships between medullary depressor region and central vasopressor pathways. Amer. J. Physiol.225, 1129–1137 (1973)
Snyder, D. W., Gebber, G. L.: Nature of sympathetic nervous silent period (SP). Fed. Proc.33, 430 (1974)
Szentágothai, J.: Short propriospinal neurons and intrinsic connections of the spinal gray matter. Acta morph. Acad. Sci. hung.1, 81–94 (1951)
Szentágothai, J.: Propriospinal pathways and their synapses. In: Organization of the spinal cord, pp. 155–177. Ed. by J. C. Eccles and J. P. Schade. Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 11. Amsterdam-New York: Elsevier 1964
Wyszogrodski, I., Polosa, C.: The inhibition of sympathetic preganglionic neurons by somatic afferents. Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.51, 29–38 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With MCR and DAAD support.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirchner, F., Wyszogrodski, I. & Polosa, C. Some properties of sympathetic neuron inhibition by depressor area and intraspinal stimulation. Pflugers Arch. 357, 349–360 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585988
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585988