Abstract
-
1.
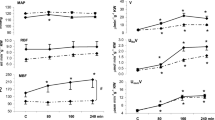
Renin-depletion, described as a decrease in renal cortex and plasma renin levels, was produced by clipping one renal artery of a rat and leaving the contralateral kidney in place (two kidney one clip hypertension). One month later the clipped kidney was removed and after 24 h recovery such rats were found to be renin depleted: renal cortex and plasma renin levels were 8 and 63% of normal respectively.
-
2.
Such renin depleted rats were incapable of releasing renin (as judged by increase in plasma renin level) in response to severly hypotensive haemorrhage and had very blunted renin release responses to pentobarbital and urethane anesthesia (59 and 17% of normal respectively).
-
3.
Our results confirm the hypothesis that a low renal renin status is associated with low basal and stimulated renin release. We suggest that the renin depleted rat may be a useful model for the study of the role of the renin angiotensin system in phenomena such as blood pressure compensation following hypotensive haemorrhage and drinking induced by beta-adrenoreceptor agonists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson J, Kaesermann HP, Lambelet J, Peters G, Peters-Haefeli L (1979) The role of circulating renin in drinking in response to isoprenaline. J Physiol (Lond) 291:61–73
Atkinson J, Kaesermann HP, Lambelet J, Lüthi P, Boillat N, Peters G (1980) Isoprenaline induced drinking without renin release. 7th Int. Food and Fluid Intake Conference Warsaw
Brough RB, Cowley AW, Guyton AC (1975) Quantitative analysis of the acute response to haemorrhage of the renin-angiotensin-vasoconstrictor feedback loop in areflexic dogs. Cardiovasc Res 9:722–733
Carvalho JS, Shapiro R, Hopper P, Page LB (1975) Methods for serial study of renin-angiotensin system in the unanesthetized rat. Am J Physiol 228:369–375
Essadki A, Boillat N, Atkinson J (1980) Failure of haemorrhage to stimulate renin release in renin-depleted rats. Experientia 36:706
Gross F (1971) Renin stores in the kidney and plasma renin activity. In: Fischer JW (ed) Kidney hormones. Academic Press, New York
Hartcroft PM (1957) Studies on renal juxtaglomerular cells. III. The effects of experimental renal disease and hypertension in the rat. J Exp Med 105:501–508
Helmchen U, Dienemann H, Kneissier U, Stahl R, Kirchertz EJ (1978) Renal hypotension in sodium and fluid deprivation: experimental findings in renin-depleted rats. Klin Wochenschr 56:253–255
Hess R, Regoli D (1964) Correlation of enzymatic activity of the juxtaglomerular complex with renin content in renal hypertensive rats. Br J Exp Pathol 45:666–671
Keeton TK, Campbell WB (1980) The pharmacologic alteration of renin release. Pharmacol Rev 32:81–227
Leenen FHH, De Jong W (1971) A solid silver clip for induction of predictable levels of renal hypertension in the rat. J Appl Physiol 31:142–144
Omae T, Masson GMC, Page IH (1961) Release of pressor substances from renal grafts originating from rats with renal hypertension. Circ Res 9:441–449
Peters-Haefeli L (1971) Renal cortical renin activity and renin secretion at rest and in response to hemorrhage. Am J Physiol 221:1331–1338
Pettinger WA (1978) Anesthetics and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis. Anesthesiology 48:393–396
Regoli D (1971) The role of the kidney and adrenal glands in the blood pressure response to haemorrhage. Rev Can Biol 30:35–43
Regoli D, Brunner H, Peters G, Gross F (1962a) Changes in renin content in kidneys of renal hypertensive rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 109:142–145
Regoli D, Hess R, Brunner H, Peters G, Gross F (1962b) Interrelationship of renin content in kidneys and blood pressure in renal hypertensive rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 140:416–426
Riedel B, Bucher O, Peters-Haefeli L, Baechtold-Fowler N, Peters G (1974) The replenishment of the juxtaglomerular renin store after temporary renin depletion. Pflügers Arch 347:125–135
Tobian L, Thompson J, Twedt R, Janecek J (1958) The granulation of juxtaglomerular cells in renal hypertension, desoxycorticosterone and post desoxycorticosterone hypertension adrenal regeneration hypertension and adrenal insufficiency. J Clin Invst 37:660–671
Weeks JR (1971) Cardiovascular techniques using unanaesthetized and freely moving rats. Upjohn Co., Int. Communication
Witty RT, Davis JO, Johnson A, Prewitt RL (1971) Effects of papaverine and haemorrhage on renin secretion in the nonfiltering kidney. Am J Physiol 221:1666–1671
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Swiss National Science Foundation, grant numbers 3.410.0.78 and 3.759.0.80
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Essadki, A., Atkinson, J. Renin release by renin-depleted rats following hypotensive haemorrhage and anesthetics. Pflugers Arch. 392, 46–50 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584581
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584581