Summary
Spontaneous tension oscillations have been recorded from intact guinea-pig auricular trabeculae bathed in Na-poor and/or Ca-rich solutions.
The frequency of these oscillations and that of after-contractions (oscillations following an electrically induced contraction) evoked under identical experimental conditions was the same (33°C).
The amplitude of the oscillations rose when the [Ca2+]0/[Na+]0 2-ratio or the intracellular Na-concentration was increased. When the increase of the [Ca2+]0/[Na+]0 2-ratio was relatively small, tension oscillations only occured after a period of electrical stimulation.
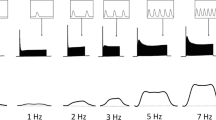
The oscillation-frequency increased slightly in media containing 70 instead of 5.4 mM KCl.
MnCl2 (3mM) did not affect either the amplitude or the frequency of the oscillations.
Caffeine (0.5–2.5 mM) decreased the amplitude and enhanced the frequency of the oscillations. After-contractions were diminished and, at higher concentrations, abolished.
It is demonstrated that the membrane potential does not participate in the process causing the tension oscillations. An increased [Ca2+]i is a prerequisite for the occurrence of these oscillations. Characteristics of intracellular Ca-movement probably determine the amplitude and frequency of the spontaneous oscillations of tension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassingthwaighte, J. B., Reuter, H.: Calcium movements and excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac cells. In: Electrical Phenomena in the Heart, edit. by W. C. De Mello. New York: Academic press 1972
Bloom, S.: Spontaneous rhythmic contractions of separated heart muscle cells. Science167, 1727–1729 (1970a)
Bloom, S.: Phylogenetic differences in spontaneous contractility of isolated heart muscle cells. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.37, 127–129 (1970b)
Bloom, S.: Requirements for spontaneous contractility in isolated adult mammalian heart muscle cells. Exp. Cell Res.69, 17–24 (1971)
Bloom, S., Brady, A. J., Langer, G. A.: Calcium metabolism and active tension in mechanically disaggregated heart muscle. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol.8, 137–147 (1974)
Chapman, R. A.: A study of the contractures induced in frog atrial trabeculae by a reduction of the bathing sodium concentration. J. Physiol. (Lond.)237, 295–313 (1974)
Fabiato, A., Fabiato, F.: Excitation-contraction coupling of isolated cardiac fibres with disrupted or closed sarcolemmas. Circulat. Res.31, 293–307 (1972)
Fabiato, A., Fabiato, F., Sonnenblick, E. H.: Calcium dependent cyclic contractions of cardiac and skeletal muscle cells with disrupted sarcolemmae. Fed. Proc.31, 373 (1972)
Ford, L. E., Podolsky, R. J.: Force development by skinned muscle fibres in EGTA buffered solutions. J. Physiol. (Lond.)223, 1–19 (1972a)
Ford, L. E., Podolsky, R. J.: Intracellular calcium movements in skinned muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)223, 21–33 (1972b)
Glitsch, H. G., Reuter, H., Scholz, H.: The effect of the internal sodium concentration on calcium fluxes in isolated guinea-pig auricles. J. Physiol. (Lond.)209, 25–43 (1970)
Jensen, R. A., Katzung, B. G.: Simultaneously recorded oscillations in membrane potential and isometric contractile force from cardiac muscle. Nature (Lond.)217, 961–963 (1968)
Kaufmann, R., Fleckenstein, A., Antoni, H., unter Mitarbeit von Wolf, H.: Ursachen und Auslösungsbedingungen von Myokard-Kontraktionen ohne reguläres Aktionspotential. Pflügers Arch.278, 435–446 (1963)
Kaufmann, R., Homburger, H., Tritthart, H.: Spezifische Hemmung des Erschlaffungsprozesses am stark gekühlten Warmblütermyokard. Pflügers Arch.305, 1–8 (1969)
Kerrick, W. G. L., Best, P. M.: Calcium ion release in mechanically disrupted heart cells. Science183, 435–438 (1974)
Langer, G. A.: Heart: Excitation-contraction coupling. Ann. Rev. Physiol.35, 55–86 (1973)
Lüttgau, H. C., Niedergerke, R.: The antagonism between Ca and Na ions on the frog's heart. J. Physiol. (Lond.)143, 486–505 (1958)
Mascher, D.: Electrical and mechanical events in depolarized cardiac muscle fibres during low sodium perfusion. Pflügers Arch.323, 284–296 (1971)
Miller, D. J.: Evidence for calcium-induced calcium release in intact depolarized frog heart muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)242, 93–95 P (1974)
Nakajima, Y., Endo, M.: Release of calcium induced by ‘depolarization’ of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Nature (Lond.)246, 216–218 (1973)
New, W., Trautwein, W.: The ionic nature of slow inward current and its relation to contraction. Pflügers Arch.334, 24–38 (1972)
Ohba, M.: Effects of caffeine on tension development in dog papillary muscle under voltage-clamp. Jap. J. Physiol.23, 47–58 (1973)
Reiter, M.: Die Entstehung von “Nachkontraktionen” im Herzmuskel unter Einwirkung von Calcium und von Digitalisglykosiden in Abhängigkeit von der Reizfrequenz. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.242, 497–507 (1962)
Reuter, H.: Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Progr. Biophys. molec. Biol.26, 1–43 (1973)
Reuter, H.: Exchange of calcium in the mammalian myocardium. Circulat. Res.34, 599–605 (1974)
Reuter, H., Seitz, N.: The dependence of calcium efflux from cardiac muscle on temperature and external ion composition. J. Physiol. (Lond.)195, 451–470 (1968)
Rougier, O., Vassort, G., Garnier, D., Gargouïl, Y. M., Corabœuf, E.: Données nouvelles concernant le rôle des ions Na+ et Ca2+ sur les propriétés électrophysiologiques des membranes cardiaques: existence d'un canal lent. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris)266, 802–805 (1968)
Scholz, H.: Über die Wirkung von Calcium und Natrium auf die Kaliumkontraktur isolierter Meerschweinchenvorhöfe. Pflügers Arch.308, 315–332 (1969)
Steiger, G. J.: Stretch activation and myogenic oscillation of isolated contractile structures of heart muscle. Pflügers Arch.330, 347–361 (1971)
Verdonck, F., Busselen, P., Carmeliet, E.: Ca-action potentials and contractions of heart muscle in Na-free solutions. Influence of caffeine. Arch. int. Physiol. Biochim.80, 167–169 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glitsch, H.G., Pott, L. Spontaneous tension oscillations in guinea-pig atrial trabeculae. Pflugers Arch. 358, 11–25 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584566
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584566