Summary
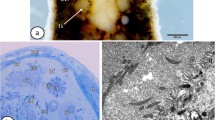
The ultrastructure of the cephalic labial kidney ofCampodea chardardi Condé has been studied. Each nephridium is subdivided into three segments: end-sac, coiled tubule and efferent-duct.
The cells of the sacculus are typical podocytes, and contain numerous pinocytotic vesicles and various vacuoles. The lumen contains micro-organisms.
The cells of the coiled tubule bear basal infoldings with numerous mitochondria and distal microvilli.
The efferent duct terminates close to the ventral face of labium, and possesses characteristic cuticular intima.
The labial kidney of Diplura is compared with published data on the nephridial organs of other Arthropods and Vertebrate nephron.
Résumé
L'ultrastructure du rein labial céphalique deCampodea chardardi Condé a été étudiée. Cette néphridie comprend trois parties: le saccule terminal, le labyrinthe et le canal excréteur.
Les cellules du saccule sont des podocytes typiques, contenant de nombreuses vacuoles de pinocytose et des inclusions diverses. La lumière est envahie par des micro-organismes bacilliformes.
Le labyrinthe possède des cellules à indentations basales profondes avec de nombreuses mitochondries, et des microvilli distaux.
Le canal excréteur débouchant sur la face ventrale du labium est caractérisé par la présence d'une intima cuticulaire.
Le rein labial des Diploures a été comparé avec des organes segmentaires néphridiens d'autres Arthropodes, et avec le néphron des Vertébrés.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliographie
Altner, H.: Die Ultrastruktur der Labialnephridien vonOnychiurus quadriocellatus (Collembola). J. Ultrastruct. Res.24, 349–366 (1968).
Bareth, C.: Les glandes exocrines céphaliques deCampodea remyi. Bull. Soc. Zool. Fr.93, 629–646 (1968).
Beams, H. W., Anderson, E.: Light and electron microscope studies on the cells of the distal portion of the crayfish nephron tubule. Cytologia (Tokyo)21, 50–57 (1956).
Bitsch, J.: Recherches anatomiques sur le labium des Diploures. Publ. Univ. Dijon, N. S.9, 5–26 (1952).
Bruntz, L.: Les reins labiaux et les glandes céphaliques des Thysanoures. Arch. Zool. exp. gén.39, 195–238 (1908).
Copeland, E.: A mitochondrial pump in the cells of the anal papillae of mosquito larvae. J. Cell Biol.23, 253–263 (1964).
El-Hifnawi, E. S., Seifert, G.: Über den Feinbau den Maxillarnephridien vonPolyxenus lagurus (L.) (Diplopoda, Penicillata). Z. Zellforsch.113, 518–530 (1971).
Ericsson, J. L. E., Trump, B. F.: Electron microscopy of the uriniferous tubules in: The kidney. Morphology, biochemistry, physiology (C. Rouiller et A. F. Muller edit.), vol.1, p. 351–447. New York and London: Academic Press 1969.
Fahlander, K.: Die Segmentalorgane der Diplopoda, Symphyla and Insecta Apterygota. Zool. Bidr. Upps.18, 243–251 (1939).
Fain-Maurel, M. A., Cassier, P.: Différenciations cytoplasmiques en relation avec la fonction excrétrice dans les reins céphaliques dePetrobius maritimus Leach (Insecte, Aptérygote). J. Microscopie10, 163–178 (1971).
François, J.: Squelette et musculature céphalique deCampodea chardardi Condé (Diplura: Campodeidae). Zool. Jb. (Abt. Anat. u. Ontog.)87, 331–376 (1970).
Gabe, M.: Données histologiques sur le rein céphalique des Thysanoures (Insectes Aptérygotes). Ann. Soc. ent. Fr.3, 681–713 (1967).
George, M.: Studies onCampodea (Diplura): the anatomy of the glands and sense-organs of the head. Quart. J. micr. Sci.104, 1–21 (1963).
Goodrich, E. S.: The study of nephridia and genital ducts since 1895. Quart. J. Micr. Sci.86, 112–293 (1945).
Grassi, B.: Note préliminaire sur l'anatomie des Thysanoures. Arch. ital. Biol.5, 381–389 (1884).
Grassi, B.: I progenitori dei Miriapodi e degli Insetti. II. Sistematica, morfologia e nota embriologica sull'Japyx e laCampodea. Atti Accad. gioenia Sci. nat.18, 1–83 (1886).
Groepler, W.: Feinstruktur der Coxalorgane bei der GattungOrnithodorus (Acari: Argasidae). Z. wiss. Zool.178, 235–275 (1969).
Haupt, J.: Zur Feinstruktur der Labialniere des SilberfischchensLepisma saccharina L. (Thysanura, Insecta). Zool. Beitr., N. F.15, 139–170 (1969a).
Haupt, J.: Zur Feinstruktur der Maxillarnephridien vonScutigerella immaculata Newport (Symphila, Myriapoda). Z. Zellforsch.101, 401–407 (1969b).
Hecker, H., Diehl, P. A., Aeschlimann, A.: Recherches sur l'ultrastructure et l'histochimie de l'organe coxald'Ornithodorus moubata (Murray) (Ixodoidea; Argasidae). Acta trop. (Basel)26, 346–359 (1969).
Hubert, M.: Etude des organes excréteurs chez les Diplopodes: morphologie des tubes de Malpighi et des reins labiaux ou maxillaires. Bull. Soc. zool. Fr.95, 847–860 (1970).
Kümmel, G.: Das Cölomsäckchen der Antennendrüse vonCambarus affinis Say (Decapoda, Crustacea). Eine elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchung mit einer Diskussion über die Funktion. Zool. Beitr., N. F.10, 227–252 (1964).
Marten, W.: Zur Kenntnis vonCampodea. Z. Morph. Ökol. Tiere36, 41–88 (1939).
Martoja, R.: Sur quelques aspects de la biologie des Orthoptères en relation avec la présence de concentrations microbiennes (Bactéries intestinales, Rickettsies). Ann. Soc. ent. Fr., N. S.2, 753–940 (1966).
Nassonow, N. W.: K morfologii nisschich nasekomychLepisma, Campodea iLipura. Izv. imp. Obshch. Estest. Antrop. Etnogr. imp. mosk. Univ.52, Trudy Lab. Zool. Mus.3, 15–86 (1887).
Oschman, J. L., Wall, B. J.: The structure of the rectal pads ofPeriplaneta americana L. with regard to fluid transport. J. Morph.127, 475–510 (1969).
Pease, D. C.: The fine structure of the kidney seen by the electron microscopy. J. Histochem. Cytochem.3, 295–301 (1955).
Philiptschenko, J.: Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Apterygoten. II. Über die Kopfdrüsen der Thysanuren. Z. wiss. Zool.91, 93–111 (1908).
Phillips, J. E., Dockrill, A. A.: Molecular sieving of hydrophilic molecules by the rectal intima. of the Desert Locust (Schistocerca gregaria). J. exp. Biol.48, 521–532 (1968).
Rasmont, R.: Structure et ultrastructure de la glande coxale d'un scorpion. Ann. Soc. r. zool. Belg.89, 239–272 (1960).
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.17, 208–212 (1963).
Rhodin, J. A. G.: Electron microscopy of the glomerular capillary wall. Exp. Cell Res.8, 572–574 (1955).
Rhodin, J. A. G.: Anatomy of kidney tubules. Int. Rev. Cytol.7, 485–534 (1958).
Schmidt-Nielsen, B., Gertz, H. H., Davis, L. E.: Excretion and ultrastructure of the antennal gland of the fiddler crabUca mordax. J. Morph.125, 473–493 (1968).
Toth, L.: The role nitrogen-active micro-organisms, in the nitrogen metabolism in Insects. Tijdschr. Ent.95, 43–59 (1952).
Tyson, G. E.: The fine structure of the maxillary gland of the brine shrimp,Artemia salina; The end-sac. Z. Zellforsch.86, 129–138 (1968).
Tyson, G. E.: The fine structure of the maxillary gland of the brine shrimp,Artemia salina; The efferent duct. Z. Zellforsch.93, 151–163 (1969a).
Tyson, G. E.: Intercoil connections of the kidney of the brine shrimp,Artemia salina. Z. Zellforsch.100, 54–59 (1969b).
Verhoeff, K. W.: Zur vergleichenden Morphologie und Systematik der Japygiden, zugleich zweiter Aufsatz über den Thorax der Insekten. Arch. Naturgesch.70, 63–114 (1904).
Yamada, E.: The fine structure of the renal glomerulus of the mouse. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.4, 551–566 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Nous tenons à remercier Monsieur le Professeur Noirot pour ses encouragements et conseils.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
François, J. Ultrastructure du rein labial céphalique deCampodea chardardi Condé (Diplura, Insecta). Z.Zellforsch 127, 34–49 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582758
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582758