Abstract
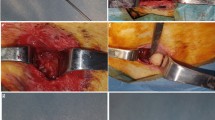
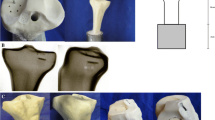
The tissue-implant interface at a self-reinforced poly-l-lactide (SR-PLLA) expansion plug implanted in distal rabbit femoral cancellous bone was studied histologically, histomorphometrically, and microradiographically in 35 rabbits during consolidation of a transverse transcondylar osteotomy fixed with the SR-PLLA expansion plug. The absorbable plug for internal fixation of fractures and osteotomies measured 4.5 mm in diameter and 30 mm in length and had an expandable distal locking blade system. The femoral specimens were harvested in groups of 5–10 rabbits after a follow-up time of 3, 6, 12, and 24 weeks. The intact controlateral femur served as a control. Vigorous osteogenic response to the implant was already observed at 3 weeks postoperatively, and the osteoid surface fraction at 24 weeks was still significantly higher than in the unoperated contralateral femur. Incomplete union of the osteotomy seemed to result in increased fibrous tissue formation at the tissue-implant boundary. No signs of degradation of the SR-PLLA was observed within the entire follow-up period. The number of inflammatory cells at the tissue-implant interface was low. Consequently, the short-term biocompatibility of the implant was deemed acceptable. Clinical application of the expansion plug is being planned.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böstman O (1991) Absorbable implants for the fixation of fractures. Current concepts review. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 73: 148–153
Böstman O, Vainionpää S, Hirvensalo E, Mäkelä A, Vihtonen K, Törmälä P, Rokkanen P (1987) Biodegradable internal fixation for malleolar fractures: a prospective randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 69:615–619
Böstman O, Hirvensalo E, Mäkinen J, Rokkanen P (1990) Foreign-body reactions to fracture fixation implants of biodegradable synthetic polymers. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 72:592–596
Böstman O, Päivärinta U, Partio E, Manninen M, Vasenius J, Majola A, Rokkanen P (1992) The tissue-implant interface during degradation of absorbable polyglycolide fracture fixation screws in the rabbit femur. Clin Orthop 285:263–272
Cutright DE, Hunsuck EE (1972) The repair of fractures of the orbital floor using biodegradable polylactic acid. Oral Surg 33:28–34
Eitenmüller J, Gerlach KL, Schmickal T, Muhr G (1987) Semirigide Plattenosteosynthesen unter Verwendung absorbierbarer Polymere als temporäre Implantate. II. Tierexperimentelle Untersuchungen. Chirurg 58:831–839
Frost HM (1983) Bone histomorphometry: analysis of trabecular bone dynamics. In: Recker RR (ed) Bone histomorphometry: techniques and interpretation. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 109–131
Gerlach KL (1990) Treatment of zygomatic fractures with biodegradable poly (l-lactide) plates and screws. In: Heimke G, Soltész U, Lee AJC (eds) Clinical implant materials. (Advances in biomaterials, vol 9). Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 573–578
Hollinger JO (1983) Preliminary report on the osteogenic potential of a biodegradable copolymer of polylactide (PLA) and polyglycolide (PGA). J Biomed Mater Res 17:71–82
Kulkarni RK, Pani KC, Neuman C, Leonard F (1966) Polylactic acid for surgical implants. Arch Surg 93:839–843
Majola A, Vainionpää S, Vihtonen K, Mero M, Vasenius J, Törmälä P, Rokkanen P (1991) Absorption, biocompatibility, and fixation properties of polylactic acid in bone tissue: an experimental study in rats. Clin Orthop 268:260–269
Mero M, Vainionpää S, Vasenius J, Vihtonen K, Rokkanen P (1989) Medetomidine-ketamine-diazepam anesthesia in the rabbit. Acta Vet Scand 85:135–137
Nelson JF, Stanford HG, Cutright DE (1977) Evaluation and comparisons of biodegradable substances as osteogenic agents. Oral Surg 43:836–843
Partio EK, Merikanto J, Heikkilä JT, Ylinen P, Mäkelä EA, Vainio J, Törmälä P, Rokkanen P (1992) Totally absorbable screws in fixation of subtalar extra articular arthrodesis in children with spastic neuromuscular disease: preliminary report of a randomized prospective study of fourteen arthrodeses fixed with absorbable or metallic screws J Pediatr Orthop 12:646–650
Pihlajamäki H, Böstman O, Hirvensalo E, Törmälä P, Rokkanen P (1992) Absorbable pins of self-reinforced poly-l-lactic acid for fixation of fractures and osteotomies. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 74:853–857
Rokkanen P, Böstman O, Vainionpää S, Vihtonen K, Törmälä P, Laiho J, Kilpikari J, Tamminmäki M (1985) Biodegradable implants in fracture fixation: early results of treatment of fractures of the ankle. Lancet 1:1422–1424
Rokkanen P, Böstman O, Hirvensalo E, Mäkelä EA, Partio E, Pätiälä H, Vainionpää S, Vihtonen K, Törmälä P (1992) Utilisation des implants biodégradables dans le treaement chirurgical des fractures et au cours des ostéotomies. Orthop Traumatol 2:107–110
Rozema FR, de Bruijn WC, Bos RRM, Boering G, Nijenhuis AJ, Pennings AJ (1992) Late tissue response to bone-plates and screws of poly (l-lactide) used for fracture fixation of the zygomatic bone. In: Doherty PJ, Williams RL, Williams DF, Lee AJC (eds) Biomaterial-tissue interfaces. (Advances in biomaterials, vol 10). Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 349–355
Schatzker J, Sanderson R, Murnaghan P (1975) The holding power of orthopaedic screws in vivo. Clin Orthop 108:116–126
Schenk R (1965) Zur histologischen Verarbeitung von unentkalkten Knochen. Acta Anat 60:3–19
Schmitz JP, Hollinger JO (1988) A preliminary study of the osteogenic potential of a biodegradable alloplastic-osteoinductive alloimplant. Clin Orthop 237:245–255
Törmälä P (1992) Biodegradable self-reinforced composite materials; manufacturing structure and mechanical properties. Clin Mater 10:29–34
Vert M, Christel P, Chabot F, Leray J (1984) Bioabsorbable plastic materials for bone surgery. In: Hastings GW, Ducheyne P (eds) Macromolecular biomaterials. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 119–142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pihlajamäki, H., Böstman, O., Manninen, M. et al. Tissue-implant interface at an absorbable fracture fixation plug made of polylactide in cancellous bone of distal rabbit femur. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 113, 101–105 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572915
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572915