Summary
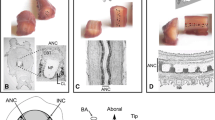
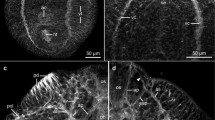
The presence and distribution of biogenic monoamines in the tube-wormChaetopterus variopedatus were investigated by a radioenzymatic method and HPLC with electrochemical detection, and the cellular localization of serotonin by peroxidase-antiperoxidase (PAP) immunohistochemistry with an antibody against serotonin-formaldehyde-protein conjugate. Dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, serotonin (5-HT) and some of their metabolites were detectable, dopamine and norepinephrine being present in substantially larger amounts than 5-HT and epinephrine. With few exceptions, the largest amounts of amines were localized in the most nerve-rich tissues such as tentacles, and those containing cerebral ganglia and the ventral nerve cord. Serotonin-immunoreactive unipolar neurons were widely distributed in the dorso-lateral cerebral ganglia, the neurosecretory pharyngeal ganglion and the segmental ganglia of the anterior (dorsolateral) and posterior (medioventral) nerve cords. Some nerve-fiber tracts stained in the cerebral ganglia, but the neuropiles of segmental ganglia were the most intensely reactive CNS structures. Numerous reactive fibers were also present in connectives, commissures and segmental nerves. All peripheral sensory structures included serotonin-immunoreactive cells and neurites, especially the parapodial cirri and the bristle receptors of the setae. Trunk and parapodial muscles contained reactive varicose fibers and neuronal somata. These results suggest that monoamines are abundant and widespread in these worms and that 5-HT appears to have a key sensory role.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez MC, Del Castillo J, Sanchez V (1969) Pharmacological responses of the dorsal longitudinal muscle ofSabellastarte magnifica. Comp Biochem Physiol 29: 931–942
Anctil M (1979) The epithelial luminescent system ofChaetopterus variopedatus. Can J Zool 57: 1290–1310
Anctil M, Laberge M, Martin N (1984) Neuromuscular pharmacology of the anterior intestine ofChaetopterus variopedatus, a filter-feeding polychaete. Comp Biochem Physiol 79C: 343–351
Belanger JH, Orchard I (1986) Leydig cells: octopaminergic neurons in the leech. Brain Res 382: 387–391
Belanger JH, Orchard I (1988) Release of octopamine by Leydig cells in the central nervous system of the leechMacrobdella decora, and its possible neurohormonal role. J Comp Physiol A 162: 405–412
Bullock TH, Horridge GA (1965) Structure and functions of the nervous system of invertebrates, Vol. 1. WH Freeman, San Francisco
Clark ME (1966) Histochemical localization of monoamines in the nervous system of the polychaeteNephthys. Proc R Sco Lond [Biol] 165: 308–325
David J-C, Coulon J-F (1985) Octopamine in invertebrates and vertebrates. A review. Progr Neurobiol 24: 141–185
DeWaele J-P, Anctil M, Carlberg M (1987) Biogenic catecholamines in the cnidarianRenilla Köllikeri: radioenzymatic and chromatographic detection. Can J Zool 65: 2458–2465
Dewhurst SA, Croker SG, Ikeda K, McCaman RE (1972) Metabolism of biogenic amines inDrosophila nervous tissue. Comp Biochem Physiol 43B: 975–981
Dorsett DA (1964) The sensory and motor innervation ofNereis. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 159: 652–667
Euler US von (1961) Occurrence of catecholamines in Acrania and Invertebrates. Nature 190: 170–171
Gardner CR, Walker RJ (1982) The roles of putative neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in annelids and related invertebrates. Progr Neurobiol 18: 81–120
Horridge GA (1963) Proprioceptors, bristle receptors, efferent sensory impulses, neurofibrils and number of axons in the parapodial nerve of the polychaeteHarmothoe. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 157: 199–222
Joyeux-Laffuie J (1890) Etude monographique du chétoptère (Chaetopterus variopedatus Renier). Arch Zool Exp Gén. Ser 2, 8: 245–360
Kennedy MB (1978) Products of biogenic amine metabolism in the lobster: sulfate conjugates. J Neurochem 30: 315–320
Klemm N (1985) The distribution of biogenic monoamines in invertebrates. In: Gilles R, Balthazart J (eds) Neurobiology, Current Comparative Approaches. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 280–296
Lent CM, Dickenson MH (1984) Serotonin integrates the feeding behavior of the medicinal leech. J Comp Physiol A 154: 457–471
Manaranche R, L'Hermite P (1973) Etude des amines biogènes deGlycera convoluta K. (Annélide Polychète). Z Zellforsch 137: 21–36
Martin N (1983) Le système nerveux deChaetopterus variopedatus (Polychète tubicole): morphologie, neuropharmacologie et rôle dans le contrôle de l'activité lumineuse. M.Sc. thesis, University of Montreal, Montreal
Martin N, Anctil M (1984) The nervous system of the tube-wormChaetopterus variopedatus (Polychaeta). J Morphol 181: 161–173
Mason A, Sunderland AJ, Leake LD (1979) Effects of leech Retzius cells on body wall muscles. Comp Biochem Physiol 63C: 359–361
McAdoo DJ, Coggeshall RE (1976) Gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of biogenic amines in identified neurons and tissues ofHirudo medicinalis. J Neurochem 26: 163–167
Miron M-J, Anctil M (1988) Serotonin-like immunoreactivity in the central and peripheral nervous system of the scale wormHarmothoe imbricata (Polychaeta). J Comp Neurol 275: 429–440
Miron M-J, LaRivière L, Basot J-M, Anctil M (1987) Immunohistochemical and radioautographic evidence of monoamine-containing cells in bioluminescent elytra of the scale-wormHarmothoe imbricata (Polychaeta). Cell Tissue Res 249: 547–556
Myhrberg HE (1967) Monoaminergic mechanisms in the nervous systems ofLumbricus terrestris. Z Zellforsch 81: 322–343
Osborne NN, Briel G, Neuhoff V (1972) The amine and amino acid composition in the Retzius cells of leech,Hirudo medicinalis. Experientia 28: 1015–1018
Robertson HA (1975) Octopamine in the central nervous system of an annelidLumbricus terrestris. Experientia 31: 1006–1008
Robertson HA, Juorio AV (1976) Octopamine and some related non-catecholic amines in invertebrate nervous systems. Int Rev Neurobiol 19: 173–224
Sumida BH, Case JF (1983) Food recognition byChaetopterus variopedatus: synergy of mechanical and chemical stimulation. Mar Behav Physiol 9: 249–274
Vaughan PFT (1988) Amine transmitters and their associated second messenger systems. In: Lunt GG, Olsen RW (eds) Comparative Invertebrate Neurochemistry. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, NY, pp 124–174
Vaughan PFT, Neuhof V (1976) The metabolism of tyrosine, tyramine and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine by thoracic and cerebral ganglia of the locust (Schistocerca gregaria). Brain Res 117: 175–180
Warembourg M, Dhainaut-Courtois N (1969) Etude des monoamines biogènes dans le système nerveux des Néréides (Annélides, Polychètes). CR Acad Sci Paris 229: 654–655
Webb RA, Orchard I (1980) Octopamine in leeches. I. Distribution of octopamine inMacrobdella decora andErpobdella octoculata. Comp Biochem Physiol 67C: 135–140
Welsh JH, Moorhead M (1960) The quantitative distribution of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the invertebrates, especially in their nervous systems. J Neurochem 6: 146–149
White D, Marsden JR (1978) Microspectrofluorimetric measurements on cells containing biogenic amines in the cerebralganglion of the polychaeteNereis virens (Sars). Biol Bull 155: 395–409
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anctil, M., De Waele, J.P., Miron, M.J. et al. Monoamines in the nervous system of the tube-wormChaetopterus variopedatus (Polychaeta): Biochemical detection and serotonin immunoreactivity. Cell Tissue Res. 259, 81–92 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571433
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571433