Summary
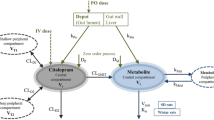
The pharmacokinetics of intravenous doxapram in healthy individuals is consistent with a three-compartment open model. Doxapram was administered by bolus injection (1.5 mg · kg−1) and by intravenous infusion (6.5 mg · kg−1 for 2 h) to 5 subjects on separate occasions. There was no significant difference in mean terminal plasma half-lives (355 and 448 min) or in mean total body clearances (5.9 and 5.6 ml · min−1 · kg−1) following i. v. bolus injection or infusion respectively. In 3 subjects plasma doxapram concentrations during and after i. v. infusion agreed with those predicted from pharmacokinetic values obtained from the bolus injection study. Since mean steady-state concentrations (9.9 µg · ml−1) would be reached only after an extended interval (mean 15.2 h), a variable-rate infusion regimen was calculated to produce and maintain a concentration of 2 µg · ml−1 from 15–25 min onwards. A regimen in which the infusion rate is reduced step-wise is recommended to achieve early near-constant plasma doxapram concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, K. S., Sedman, A. J., Wagner, J. G.: Pharmacokinetics of orally-administered acetaminophen in man. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.2, 381–393 (1974)
Benet, L. Z.: General treatment of linear mamillary models with elimination from any compartment as used in pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Sci.61, 536–540 (1972)
Boxenbaum, H. G., Riegelman, S., Elashoff, R. M.: Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.2, 123–148 (1974)
Brownlee, K. A.: Statistical theory and methodology in science and engineering, 2nd Ed. pp. 87–135. London: John Wiley and Sons 1965
Calverley, P. M. A., Robson, R. H., Wraith, P. K., Flenley, D. C. Prescott, L. F.: Effects of doxapram on hypoxic respiratory drive in man. Clin. Sci. Mol. Med.55, 23P (1978)
Gawley, T. H., Dundee, J. W., Gupta, P. K., Jones, C. J.: Role of doxapram in reducing pulmonary complications after major surgery. Br. Med. J.1976/I, 122–124
Gibaldi, M., Perrier, D.: Pharmacokinetics. pp. 89–96, 175–187. New York: Marcel Dekker 1975
Mueller, F. W., Lieberman, S. V.: Fitting a double-exponential curve to observed salicylate concentrations in blood. J. Pharm. Sci.59, 514–517 (1970)
Nelder, J. A., Mead, R.: A simplex method for function minimisation. Comput. J.7, 308–313 (1965)
Ottaway, J. H.: Normalisation in the fitting of data by iterative methods. Biochem. J.134, 729–736 (1973)
Riordan, J. F., Sillett, R. W., McNicol, M. W.: A controlled trial of doxapram in acute respiratory failure. Br. J. Dis. Chest69, 57–62 (1975)
Robson, R. H., Prescott, L. F.: A rapid gas-liquid chromatographic estimation of doxapram in plasma. J. Chromatogr. Biomed. Appl.143, 527–529 (1977)
Robson, R. H., Prescott, L. F.: A pharmacokinetic study of doxapram in patients and volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol.7, 81–87 (1979)
Vaughan, D. P., Tucker, G. T.: General derivation of the ideal intravenous drug input required to achieve and maintain a constant plasma drug concentration. Theoretical application to lignocaine therapy. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol.10, 433–440 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clements, J.A., Robson, R.H. & Prescott, L.F. The disposition of intravenous doxapram in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 16, 411–416 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00568202
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00568202