Summary
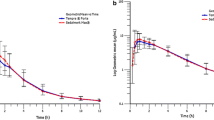
After oral administration of a single 50 mg dose of hydralazine (Apresoline®), the serum half-life (T1/2) and bioavailability (AUC0−∞) were assessed in 16 healthy volunteers. The half-life was 2.57±0.14 h (S.E.) in 10 slow acetylators of sulphadimidine, and 2.18±0.15 h in 6 fast acetylators (difference not statistically significant). AUC0−∞ was significantly higher in slow acetylators, at 1.04±0.10 µg·hour·ml−1, compared to 0.66±0.12 µg·hour·ml−1 in the fast acetylators (p<0.025). Treatment with Apresoline® 25 mg tid produced minimum serum concentrations at steady-state of 57.3±7.3 ng·ml−1 and 33.4±4.2 ng·ml−1 in 8 slow and 5 fast acetylators, respectively (p<0.05). The corresponding maximum concentrations were 228.8±20.3 ng·ml−1 and 147.6±15.0 ng·ml−1 in slow and fast acetylators, respectively (p<0.025). First-pass metabolism of hydralazine could explain the difference in bioavailability of the drug between fast and slow acetylators, without any corresponding difference in the elimination rate of the drug in the post-distributive phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perry, H.M.: Late toxicity to hydralazine resembling lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis. Amer. J. Med.54, 58–72 (1973)
Evans, D.A.P., White, T.: Human acetylation polymorphism. J. Lab. clin. Invest.63, 394–403 (1964)
Reidenberg, M.M., Drayer, D., Demarco, A.L., Bello, C.T.: Hydralazine elimination in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.14, 970–977 (1973)
Zacest, R., Koch-Weser, J.: Relation of hydralazine plasma concentration to dosage and hypotensive action. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.13, 420–425 (1972)
Zak, S.D., Bartlett, M.F., Wagner, W.E., Gilleran, T.G., Lukas, G.: Disposition of hydralazine in man and a method for its determination in biological fluids. J. pharm. Sci.2, 225–229 (1974)
Schulert, A.R.: Physiological disposition of hydralazine (1-hydrazinophthalazine) and a method for its determination in biological fluids. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn.132, 1–15 (1961)
Lesser, J.M., Israili, Z.H., Davis, D.C., Dayton, P.G.: Metabolism and disposition of hydralazine-C14 in man and dog. Drug Metab. Dispos.2, 351–360 (1974)
Jack, D.B., Brechbühler, S., Degen, P.H., Zbinden, P., Riess, W.: The determination of hydralazine in plasma by gas-liquid-chromatography. J. Chromatogr.115, 87–92 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talseth, T. Studies on hydralazine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 10, 183–187 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558327
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558327