Abstract
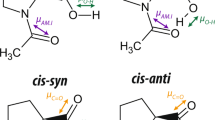
The OH ⋯ N ⇌ O− ⋯ H+N hydrogen bonds formed between tyrosine and lysine, and between glutamic acid and lysine residues are studied by infrared spectroscopy considering the following systems: (l-lys)n + phenol, copoly (l-lys, l-tyr)n, (l-lys)n + (l-tyr)n and (l-lys)n + (l-glu)n. The phenol-lysine hydrogen bonds are largely symmetrical in the average if the pKa of the protonated lysine is 2.2 units larger than that of the phenols. In the case of the hydrogen bonds between tyrosine and lysine residues in copoly (l-lys, l-tyr)n and (l-lys)n + (l-tyr)n, the weight of the proton limiting structure OH ⋯ N is 80–90%, and that of the polar O− ⋯ H+N structure 10–20%. Double minimum proton potentials occur but the proton is preferentially present at the tyrosine residues. In the (l-lys)n + (l-glu)n system, the protons are present at the lysine residues. Thus, these hydrogen bonds have very large dipole moments (about 10 D). With the lysine-phenole hydrogen bonds, hydration shifts the proton transfer equilibrium a little in favour of the polar proton limiting structure O− ⋯ H+N. These hydrogen bonds are broken to a large extent, however, when only about 3 water molecules are present per lysine residue. When less water is present, as in the copoly (l-lys, l-tyr)n and (l-lys)n + (l-tyr)n systems, these hydrogen bonds are, however, formed quantitatively. Thus — as discussed in this paper — the tyrosine-lysine hydrogen bonds can participate in proton conducting hydrogen bonded systems — as, for instance, present in bacteriorhodopsin — performing the proton transport through hydrophobic regions of biological membranes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blow DM (1976) Acc Chem Res 9: 145–152
Breuer MM, Kennerly MG (1971) J Colloid Interface Sci 37: 124–131
Brisette C, Sandorfy C (1960) Can J Chem 38: 34–44
ChirgadŽe YuN, Ovsepyan AM (1972) Biopolymers 11: 2179–2186
ChirgadŽe YuN, Brazhnikov EV, Nevskaya NA (1976) J Mol Biol 102: 781–792
Christensen JJ, Hansen LD, Izatt RM (eds) (1976) Handbook of proton ionisation heats. J. Wiley, New York
Drahonovski J, Vacek Z (1971) Collect Czech Chem Comm 36: 3431–3440
Elliot A (1954) Proc R Soc A221: 104–114
Evans JC (1960) Spectrochim Acta 16: 1382–1392
HadŽi D, Bratos S (1976) In: Schuster P, Zundel G, Sandorfy C (eds) The hydrogen bond — Recent developments in theory and experiments, vol. II. North Holland, Amsterdam
Hayd A, Weidemann EG, Zundel G (1979) J Chem Phys 70: 86–91
Hofmann KP, Zundel G (1971) Rev Sci Instrum 42: 1726–1727
Huyskens P, Zeegers-Huyskens Th (1964) J Chim Phys 61: 81–86
Ikeda S, Kito A, Imae T (1974) J Colloid Interface Sci 48: 256–262
Jadzyn J, Małeki J (1972) Acta Phys Pol A41: 599–616
Janoschek R, Weidemann EG, Pfeiffer H, Zundel G (1972) J Amer Chem Soc 94: 2387–2396
Janoschek R, Weidemann EG, Zundel G (1973) J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 2 69: 505–520
Katchalski E, Sela M (1953) J Am Chem Soc 75: 5284–5289
Katchalski E, Shavit N, Eisenberg H (1954) J Polymer Sci 13: 69–84
Katchalski E, Sela M, Silmann HI, Berger A (1964) In: Neurath H (ed) The proteins, vol. II. Academic Press, New York, pp 405–602
Kristof W, Zundel G (in preparation)
Kuhn J (1952) J Am Chem Soc 74: 2492–2499
Lindemann R, Zundel G (1977a) Biopolymers 16: 2407–2418
Lindemann R, Zundel G (1977b) J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 2 73: 788–803
Lindemann R, Zundel G (1978) Biopolymers 17: 1285–1304
Miyazawa T, Blout ER (1961) J Am Chem Soc 83: 712–719
Murray J, Gordon N (1935) J Am Chem Soc 57: 110–111
Nagasawa M, Holtzer A (1964) J Am Chem Soc 86: 538–543
Nouwen R, Huyskens P (1973) J Mol Struct 16: 459–471
Oakes J (1976) J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 1 72: 216–227
Ovchinnikov YuA (1979) Eur J Biochem 94: 321–336
Ovchinnikov YuA, Abdulaev NG, Feigina MJu, Kiselev AV, Lobanov NA (1979) FEBS Lett 100: 219–224
Pawlak Z, Magoński J (1980) J Solution Chem
Pfeiffer H, Zundel G, Weidemann EG (1979) J Phys Chem 83: 2544–2551
Ratajczak H, Sobczyk L (1969) J Chem Phys 50: 556–557
Schellman J, Schellman C (1974) In: Neurath H (ed) The proteins, vol. II. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–137
Schreiber M, Koll A, Sobczyk L (1978) Bull Acad Pol Sci Ser Sci Chim 26: 651–654
Sobczyk L (1976) In: Schuster P, Zundel G, Sandorfy C (eds) The hydrogen bond — Recent developments in theory and experiments, vol III. North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 936–963
Vinogradov SN (1970) Biochim Biophys Acta 214: 6–27
Vinogradov SN (1979) Biopolymers 18: 1559–1561
Weast RC (1977/78) Handbook of chemistry and physics. 58th ed. CRC-Press, West Palm Beach
Zundel G (1969) Hydration and intermolecular interaction. Academic Press, New York (1972): Mir. Moscov)
Zundel G (1976) In: Schuster P, Zundel G, Sandorfy C (eds) The hydrogen bond — Recent developments in theory and experiments, vol II. North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 683–766
Zundel G (1978) J Mol Struct 45: 55–73
Zundel G, Nagyrevi A (1978) J Phys Chem 82: 685–689
Zundel G, Weidemann EG (1971) In: Broda E, Locker A, Springer-Lederer H (eds) First European Biophysics Congress, vol 6. Wiener Medizinische Akademie, Wien, pp 43–47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kristof, W., Zundel, G. Proton transfer in and polarizability of hydrogen bonds in proteins. Tyrosine-lysine and glutamic acid-lysine hydrogen bonds — IR investigations. Biophys. Struct. Mechanism 6, 209–225 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00537294
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00537294