Summary
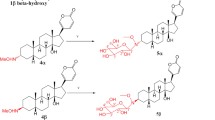
The inhibitory effect of formylated cardiac steroids (gitaloxin and its derivatives) on guinea-pig heart Na, K-ATPase was compared to that of other cardiac steroids with various hydroxy substituents. The decreasing order of potency of aglycones at equilibrium was as follows: gitaloxigenin > digitoxigenin > ouabagenin > digoxigenin > gitoxigenin > diginatigenin. This sequence was different to the sequence of drugs hydrophobic character. The compounds with hydroxy groups in the vicinity of the lactone ring (gitoxigenin, diginatigenin) were less potent than the hydrophilic compound ouabagenin. We propose that intramolecular bonding between 16β-OH and the lactone ring contributes to the relatively low potency of gitoxigenin and diginatigenin. The formylation of 16β-OH increased the potency of gitoxigenin by a factor of 41. The formylated compound (gitaloxigenin) was 5-fold more potent than digitoxigenin. The 3β-glycosylation of digoxigenin lead to pseudo-irreversible inhibitors of Na, K-ATPase. The half-time to achieve the equilibrium (for 5μmol/l) was equal to 54 s, 90 s and 108 s respectively for digoxigenin monodigitoxoside, digoxin and desacetyllanatoside C. However, at equilibrium the three glycosides were equipotent, suggesting the existence of steric effects at the sugar site of the receptor. The sequence of potency observed for monodigitoxosides, monodigitalosides and tridigitoxosides after 60 min incubation was similar to that observed for the corresponding aglycones. These results suggest that the strongly negative inductive group 16β-OCHO is tightly bound to Na, K-ATPase, possibly to the same receptor site than that which is thought forming hydrogen and ionic bonds with the lactone ring. They show that the high toxicity of gitaloxin in guineapig heart is likely due to its high potency as Na, K-ATPase inhibitor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clarck AF, Swanson PD, Stahl WL (1975) Increase in dissociation rate constants of cardiotonic steroid-brain (Na++K+)-ATPase complexes by reduction of the unsaturated lactone. J Biol Chem 250:9355–9359
De Pover A, Godfraind T (1979) Interaction of ouabain with (Na++K+)-ATPase preparations from human heart and guinea-pig heart. Biochem Pharmacol 28:3051–3056
Dolphen R, Lesne M (1980) Uptake and pharmacological effect of gitoxin and gitaloxin in rat and guinea-pig perfused hearts. Arzneim-Forsch (Drug Res) 30:614–618
Erdmann E, Schoner W (1974) Ouabain-receptor interactions in (Na++K+)-ATPase preparations. The molecular structure of different cardioactive steroids and other substances and their affinity to the glycoside receptor. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 283:335–356
Georges A (1967) Les hétérosides cardiotoniques de la digitale et leurs dérivés semi-synthétiques. Ed Arscia, Brussels
Godfraind T, De Pover A, Verbeke N (1977) Influence of pH and sodium on the inhibition of gunea-pig heart (Na++K+)-ATPase by calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta 481:202–211
Godfraind T, Ghysel-Burton J (1980) Independence of the positive inotropic effect of ouabain from the inhibition of the heart Na-K pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:3067–3069
Godfraind T, Tona Lutete D (1979) Inhibition by digoxin and SC4453 of (Na++K+)-ATPase prepared from human heart, guinea-pig heart and guinea-pig brain. Eur J Pharmacol 60:329–336
Güntert TW, Linde HHA (1981) Chemistry and structure-activity relationships of cardioactive steroids. Handb Exp Pharmacol 56/1:13–24
Hunter A, Downs CE (1945) The inhibition, of arginase by amino acids. J Biol Chem 157:427–446
Korolkovas A (1970) Essentials of molecular pharmacology. Background for drug design. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Langer GA (1981) Mechanism of action of the cardiac glycosides on the heart. Biochem Pharmacol 30:3261–3264
Lingner K, Küssner W (1962) Resorption und Abbau herzwirksamer Glykoside. Mitteilung: Abbau von Cardenolidglykosiden in vitro. Arzneim Forsch 12:835–841
Naaido BK, Witty TR, Remers WA, Besch HR Jr (1974) Cardiotonic steroids. Improtance of 14β-hydroxy group in digitoxigenin. J Pharm Sci 63:1391–1394
Portius HJ, Repke K (1964) Versuch einer Analyse der Beziehungen zwischen chemischer Struktur und digitalisähnlicher Wirksamkeit auf der Rezeptorebene. Arzneim-Forsch (Drug Res) 14:1073–1077
Schwartz A, Lindenmayer GE, Allen JC (1975) The sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase: pharmacological, physiological and biochemical aspects. Pharmacol Rev 27:1–134
Thomas R, Boutagy J, Gelbart A (1974) Synthesis and biological activity of semisynthetic digitalis analogs. J Pharm Sci 63:1649–1683
Thomas R, Allen JC, Pitts BJ Jr, Schwartz A (1979) Cardenolide analogs. An explanation for the unusual properties of AY 22241. Eur J Pharmacol 53:227–237
Wilson WE, Sivitz WI, Hanna LT (1970) Inhibition of calf brain membranal sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase by cardioactive sterols. A binding site model Mol Pharmacol 6:449–459
Yoda A (1973) Structure-activity relationships of cardiotonic steroids for the inhibition of sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. Dissociation rate constants of various enzymecardiac glycoside complexes formed in the presence of magnesium and phosphate. Mol Pharmacol 9:51–60
Yoda A, Yoda S (1980) The interaction of ouabagenum and (Na++K+)-ATPase in the presence of Na+, Mg+ and ATP. Mol Pharmacol 19:62–67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Pover, A., Godfraind, T. Influence of 16β formylation on Na, K-ATPase inhibition by cardiac glycosides. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 321, 135–139 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00518481
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00518481