Summary
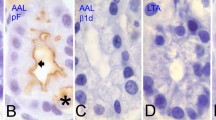
Lectin histochemical study was performed on twenty-eight specimens of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissues of proximal duodenum from human, cat, dog and Rhesus (macaque) monkey to demonstrate the pattern of carbohydrate residues in submucosal glands of Brunner as compared to that of the duodenal absorptive and goblet cells. Ten different biotinylated lectins were used as probes, and avidin-biotin-peroxidase (ABC) or avidin-gold-silver (AGS) complexes were used as “visualants”. Brunner's gland cells of the four species studied exhibited a similar lectin-binding pattern which differ from other duodenal cells. The epithelium of Brunner's gland stained intensely with Ricinus communis agglutinin-I (RCA-I), succinylated-WGA (S-WGA) and wheat-germ agglutinin (WGA), moderately with Bandeirea simplicifolia agglutinin-I (BS-I), Concanavalia ensiformis agglutinin (Con A) peanut agglutinin (PNA) and Ulex europaeus agglutinin-I (UEA-I) and occasionally with Dolichos biflorus agglutinin (DBA), Lens culinaris agglutinin (LCA) and soybean agglutinin (SBA). Desialylation with neuraminidase resulted in only a slight elevation in binding intensities of PNA, DBA and SBA, indicating that glycoconjugates of the Brunner's gland cells are rich in asialo-oligosaccharides, which differs from duodenal epithelial cells. In addition, these histochemical reagents were useful in localizing Brunner's gland elements in the duodenal mucosa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alroy J, Ucci AA, Pereira MEA (1984) Lectins: Histochemical probes for specific carbohydrate residues. In: DeLellis RA (ed) Diagnostic immunohistochemistry, vol 2. Masson, New York, pp 67–81
Alroy J, Ucci AA, Goyal V, Aurilio V (1986) Histochemical similarities between human and animal globoid cells in Krabbe's disease: A lectin study. Acta Neuropathol 71:26–31
Cochrane W, Davies DV, Palfrey AJ, Stockwell RA (1964) The histochemistry and electronmicroscopy of Brunner's glands in the guinea pig. J Anat 98:1–10
Cooke AR (1967) The glands of Brunner. In: Code CF (ed) Handbook of physiology, sect 6, vol 2. Am Physiol Soc, Washington, DC, pp 1087–1095
Cummings RD, Kornfeld S (1982) Fractionation of asparginelinked oligosaccharides by serial lectin-agarose affinity chromatography: A rapid, sensitive and specific technique. J Biol Chem 257:11235–11240
Danscher G, Norgaard RJO (1983) Light microscopic visualization of colloid gold on resin-embedded tissue. J Histochem Cytochem 31:1394–1398
Debrey H, Decout D, Strecker G, Spike G, Montruil J (1981) Specificity of twelve lectins towards oligosaccharides and glycoproteins related to N-glycoproteins. Eur J Biochem 117:41–55
Dellmann HD, Brown EM (1976) Textbook of veterinary histology. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia
Florey HW, Harding HE (1933) The functions of Brunner's glands and pyloric end of the stomach. J Pathol Bacteriol 37:431–453
Friend DS (1965) The fine structure of Brunner's glands in the mouse. J Cell Biol 25:563–576
Geleff S, Böck P (1984) Pancreatic duct glands. II. Lectin binding affinities of ductular epithelium, ductular glands and Brunner glands. Histochemistry 80:31–38
Goldstein IJ, Poretz RD (1986) Isolation, physicochemical characterization and carbohydrate-binding specificity of lectins. In: Liener IE, Sharon N, Goldstein IJ (eds) The lectins, properties, functions and applications in biology and medicine. Academic Press, New York, pp 33–247
Hosoda K (1956) Über die vergleichende Anatomie der Duodenaldrüsen bei den Rodentien, insbesondere die feinere Struktur der dunklen Endstücke derselben Drüsen. Yokohama Med Bull 7:170–181
Kornfeld K, Reitman ML, Kornfeld R (1981) The carbohydratebinding specificity of pea and lentile lectins: Fucose is an important determinant. J Biol Chem 256:6633–6640
Landboe-Christensen E (1944) Staining of the duodenal glands of Brunner in gross specimens of the duodenum in man. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 21:374–379
Moe H (1960) The ultrastructure of Brunner's gland of the cat. J Ultrastruct Res 4:58–72
Monsigny M, Roche AC, Sene C, Maget-Dona R, Delmotte F (1980) Sugar-lectin interactions: How does wheat-germ agglutinin bind sialoglycoconjugates? Eur J Biochem 104:147–153
Pereira MEA, Kiseilus EC, Gruezo F, Kabat EA (1978) Immunochemical studies on the combining site of blood group H-specific lectin I form Ulex europeus seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys 185:108–115
Posel P, Schumacher U, Frick H, Welsch U (1988) Histochemistry of mucosubstances in Brunner's gland cells and duodenal goblet cells of two new world monkey species (Saimiri sciureus and Saguinus fuscicollis). Histochemistry 88:327–332
Roth J (1984) Light and electron microscopic localization of antigens with protein A-gold (pAg) technique. In: DeLellis RA (ed) Diagnostic immunohistochemistry, vol 2. Masson, New York, pp 31–42
Rotterdam H, Sommers SH (1981) Duodenum. In: Blaustein A (ed) Biopsy interpretation series, biopsy diagnosis of the digestive tract. Raven Press, New York, pp 165–195
Schulte BA, Spicer SS (1985) Histochemical methods for characterizing secretory and cell surface sialoglycoconjugates. J Histochem 33:427–438
Schwalbe G (1872) Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Drüsen in den Darmwandungen, insbesondere der Brunnerschen Drüsen. Arch Mikrosk Anat 8:92–140
Skutelsky E, Goyal V, Alroy J (1986) The use of avidin-gold complex for light microscopic localization of lectin receptors. Histochemistry 86:291–294
Spicer SS, Schulte BA, Thomopoulos GN, Parmley RT, Takagi M (1983) Cytochemistry of complex carbohydrates by light and electron microscopy: Available methods and their application. In: Wagner BM, Fleischmayer R, Kaufman N (eds) Connective tissue diseases. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 163–211
Stoward PT, Spicer SS, Miller RC (1980) Histochemical reactivity of peanut lectin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate. J Histochem Cytochem 28:979–990
Suzuki S, Tsuyama S, Suganuma T, Yamamoto N, Murata F (1981) Postembedding staining of Brunner's glands with lectinferritin conjugates. J Histochem Cytochem 29:946–952
Trautmann A, Fiebiger J (1957) Fundamentals of the histology of domestic animals. Constock Publ Assoc, Ithaca, New York
Tschassownikow N (1926) Zur Frage über die Struktur der Brunnerschen und Pylorus-Drüsen und ihre Beziehung zueinander. Anat Anz 61:417–431
Whitehead R (1985) Mucosal biopsy of the gastrointestinal tract. In: Bennington JL (ed) Major problems in pathology, vol 3. WB Saunders Philadelphia, pp 121–122, 128–130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skutelsky, E., Moore, R.P. & Alroy, J. Lectin histochemistry of mammalian Brunner's glands. Histochemistry 90, 383–390 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508317
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00508317