Summary
In slices of rat occipital cortex and hypothalamus preincubated with 3H-noradrenaline and superfused with various Ca2+-free solutions, the effect of introduction of CaCl2 on efflux of total tritium, 3H-noradrenaline and 3H-metabolites was studied.
-
1.
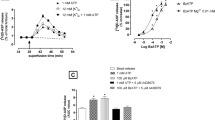
When slices of both brain regions were superfused with a Ca2+-free buffer containing 30 mM K+ and 119 mM Na+, introduction of 0.65–2.6 mM CaCl2 for 2 min induced a concentration-dependent overflow of tritium. Cocaine (100 μM) doubled the overflow of tritium evoked by 1.3 mM CaCl2. When slices were superfused with physiological salt solution after 100 min of superfusion with the Ca2+-free buffer and 2 stimulation periods with 1.3 mM CaCl2, electrical field stimulation (3 Hz, 13 mA, 2 ms, 2 min duration) still elicited on overflow of tritium which contained 59% 3H-noradrenaline. The CaCl2-induced overflow was not affected by tetrodotoxin (1 μM), but was inhibited by Mg2+ ions (10 mM).
-
2.
When cortical slices incubated with Ca2+-free solution containing 300 μM ionophore A 23187 (subsequent to preincubation with 3H-noradrenaline) were superfused with Ca2+-free solution containing 0.3 mM Mg2+ (otherwise composed like physiological salt solution), introduction of 1.3 or 2.6 mM CaCl2 for 5 min evoked a concentration-dependent overflow of tritium. The evoked overflow of 3H-noradrenaline was similar to that produced by the same Ca2+ concentrations after superfusion with K+-rich solution. The Ca2+-induced tritium overflow from slices preincubated with A 23187 was completely inhibited by 10 mM MgCl2.
-
3.
The Ca2+-induced overflow of tritium from cortex slices superfused with 30 mM K+ or preincubated with A 23187 was mainly represented by 3H-noradrenaline; the most important degradation products were 3H-dihydroxyphenylglycol and O-methylated deaminated metabolites. Under both conditions 100 μM cocaine increased the proportional 3H-noradrenaline overflow.
It is concluded that combined application of both methods of Ca2+-induced stimulation provides a tool for the determination of the site of action of drugs which alter stimulus-release coupling in noradrenergic neurons of the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, P. F., Rink, T. J.: Catecholamine release from bovine adrenal medulla in response to maintained depolarization. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 253, 593–620 (1975)
Breese, G. R., Chase, T. N., Kopin, I. J.: Metabolism of some phenylethylamines and their β-hydroxylated analogs in brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 165, 9–13 (1969)
Case, G. D., Vanderkooi, J. M., Scarpa, A.: Physical properties of biological membranes determined by the fluorescence of the calcium ionophore A 23187. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 161, 174–185 (1974)
Cochrane, D. E., Douglas, W. W., Mouri, T., Nakazato, Y.: Calcium and stimulus-secretion coupling in the adrenal medulla: contrasting stimulating effects of the ionophore X-537A and A 23187 on catecholamine output. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 252, 363–378 (1975)
Colburn, R. W., Thoa, N. B., Kopin, I. J.: Influence of ionophores which bind calcium on the release of norepinephrine from synaptosomes. Life Sci. 17, 1395–1400 (1976)
Cotman, C. W., Haycock, J. W., White, W. F.: Stimulus-secretion coupling processes in brain: analysis of noradrenaline and gamma-aminobutyric acid release. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 254, 475–505 (1976)
Farnebo, L.-O.: Histochemical demonstration of transmitter release from noradrenaline, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine nerve terminals in field stimulated rat brain slices. Z. Zellforsch. 122, 503–519 (1971)
Farnebo, L.-O., Hamberger, B.: Drug-induced changes in the release of 3H-monoamines from field stimulated rat brain slices. Acta Physiol. Scand., Suppl. 371, 35–44 (1971)
Garcia, A. G., Kirpekar, S. M., Prat, J. C.: A calcium ionophore stimulating the secretion of catecholamines from the cat adrenal. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 244, 253–262 (1975)
Garcia, A. G., Kirpekar, S. M., Sanchez-Garcia, P.: Release of noradrenaline from the cat spleen by nerve stimulation and potassium. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 261, 301–317 (1976)
Göthert, M.: Effects of presynaptic modulators on Ca2+-induced noradrenaline release from cardiac sympathetic nerves. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 300, 267–272 (1977)
Göthert, M., Nawroth, P., Pohl, I.-M.: Effects of verapamil and presynaptic modulators on calcium-induced noradrenaline release. Proceedings of the Fourth International Catecholamine Symposium, Pacific Grove, California. New York, Oxford: Pergamon (in press)
Göthert, M., Neumeyer, H.: Noradrenaline release from cardiac sympathetic nerves induced by Ca2+-dependent stimulation methods or by external Ca2+ itself: effects of Ca2+ antagonists, tetracaine and drugs modulating release. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 297II, R49 (1977)
Göthert, M., Pohl, I.-M., Wehking, E.: Effects of presynaptic modulators on Ca2+-induced noradrenaline release from central noradenergic neurons: noradrenaline and enkephalin inhibit release by decreasing depolarization-induced Ca2+-influx. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 307, 21–27 (1979)
Graefe, K. H., Stefano, F. J. E., Langer, S. Z.: Preferential metabolism of (−)-3H-norepinephrine through the deaminated glycol in the rat vas deferens. Biochem. Pharmacol. 22, 1147–1160 (1973)
Ito, S., Nakazato, Y., Ohga, A.: The effect of the ionophores X-537A and A 23187 on the noradrenaline output from peripheral adrenergic neurones in the presence of various divalent cations. Br. J. Pharmacol. 62, 91–98 (1978)
Krnjević, K.: Chemical nature of synaptic transmission in vertebrates. Physiol. Rev. 54, 418–540 (1974)
Langer, S. Z., Farah, M. B., Luchelli-Fortis, M. A., Adler-Graschinsky, E., Filinger, E. J.: Metabolism of endogenous noradrenaline. In: Neurotransmission (Ahtee L., ed.), pp. 17–31. Proc. 6th Int. Congr. Pharmacol., Vol. 2, Forssa: Forssan Krijapaino Oy 1975
Lidbrink, P., Jonsson, G.: Noradrenaline nerve terminals in the cerebral cortex: effects on noradrenaline uptake and storage following axonal lesion with 6-hydroxydopamine. J. Neurochem. 22, 617–626 (1974)
Lidbrink, P., Jonsson, G., Fuxe, K.: The effect of impiramine-like drugs and antihistamine drugs on uptake mechanisms in the central noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine neurons. Neuropharmacology 10, 521–536 (1971)
Pfeiffer, D. R., Reed, P. W., Lardy, H. A.: Ultraviolet and fluorescent spectral properties of the divalent cation ionophore A 23187 and its metal ion complexes. Biochemistry 13, 4007–4014 (1974)
Pfeiffer, D. R., Taylor, R. W., Lardy, H. A.: Ionophore A 23187: cation binding and transport properties. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 307, 402–421 (1978)
Rasmussen, H., Goodman, D. B. P.: Relationship between calcium and cyclic nucleotides in cell activation. Physiol. Rev. 57, 421–509 (1977)
Rubin, R. P.: The role of calcium in the release of neurotransmitter substances and hormones. Pharmacol. Rev. 22, 389–428 (1970)
Starke, K., Montel, H.: Alpha-receptor-mediated modulation of transmitter release from central noradrenergic neurons. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 279, 53–60 (1973)
Taube, H. D., Montel, H., Hau, G., Starke, K.: Phencyclidine and ketamine: comparison with the effect of cocaine on the noradrenergic neurones of the rat brain cortex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 291, 47–54 (1975)
Taube, H. D., Starke, K., Borowski, E.: Presynaptic receptor systems on the noradrenergic neurones of rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 299, 123–141 (1977)
Thoa, N. B., Costa, J. L., Moss, J., Kopin, I. J.: Mechanism of release of norepinephrine from peripheral adrenergic neurons by the calcium ionophore X537A and A 23187. Life Sci. 14, 1705–1719 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Göthert, M. Ca2+-induced noradrenaline release from central noradrenergic neurons promoted by high K+ concentration or ionophore A23187. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 307, 29–37 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00506548
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00506548