Summary
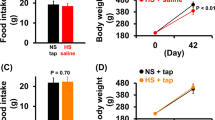
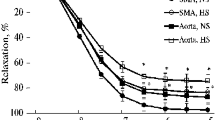
In previous experiments an altered PG biosynthesis as well as an increase in blood pressure, heart rate and plasma epinephrine could be found after a linoleic acid deficient diet compared with a linoleic acid rich diet in rats with a high salt intake. We injected rats with 200μg 6-hydroxydopamine into the right and left cerebral ventricles 17 days before a four-week linoleic acid deficient diet (0.5J% linoleic acid) and salt loading (1.5% NaCl). In these rats the elevation of blood pressure and plasma epinephrine compared with linoleic acid rich fed rats (13.3J% linoleic acid) was abolished and heart rate was reduced. PG biosynthesis in aorta and kidney medulla homogenate (PGE and PGF) and stomach fundus homogenate (6-Keto-PGF1α) was not influenced by chemical sympathectomy, neither were the food and fluid intakes. We conclude that an enhanced adrenergic activity (via alterations in PG metabolism?) is involved in the blood pressure increase after a linoleic acid deficient diet under high salt intake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam J, Scharf J-H, Enke H (1971) Methoden der statistischen Analyse in Medizin und Biologie. VEB Verlag Volk und Gesundheit, Berlin
Blass K-E, Block H-U, Förster W, Pönicke K (1980) Dipyridamole: A potent stimulator of prostacyclin (PGI2) biosynthesis. Br J Pharmacol 68:71–73
Block H-U, Taube Ch, Förster W (1975) Einfluß blutdrucksenkender Pharmaka auf die in vitro-Biosynthese der Prostaglandine E und F2α im Kaninchennierenmark. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 216:160–164
Boonayviroj P, Gutman Y (1977) Inhibition by prostaglandin E2 and by phenylephrine of catecholamine release from human adrenal in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 41:73–75
Friebel H, Vreden E (1957) Ein Gerät zur Blutdruckmessung an der Ratte. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol 232:419–422
Hoffmann P, Taube Ch, Pönicke K, Förster W, Somova L, Orbetzova V, Davidova F (1978) Influence of linoleic acid content of the diet on arterial pressure of salt loaded rats: I. Effects on prostaglandin metabolism and sympathetic nervous system. Acta Biol Med Germ 37:863–867
Hoffmann P, Poleshuk WS, Förster W, Markov HM (1981) Effect of prenatal linoleic acid (LA) deficient diet on blood pressure of salt loaded rats: I. Relationship with sympathetic nervous system. In: Förster W, Sarembe B, Mentz P (eds) Prostaglandins and thromboxanes in the cardiovascular system. VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena pp 215–217
Kostrzewa RM, Jacobowitz DM (1974) Pharmacological action of 6-hydroxydopamine. Pharmacol Rev 26:199–288
Matlina ES, Kiselewa SI, Sofijewa IE (1969) Metod opredelenija adrenalina, noradrenalina, dofamina i dofa w tkanich. In: Menschikov WW (ed) Metodi klinitscheskoi biochimii gormonov i mediatorov. Medizina, Moskau, pp 32–35
Reid JL, Zivin JA, Kopkin IJ (1975) Central and peripher adrenergic mechanisms in the development of desoxycorticosterone-saline-hypertension in rats. Circ Res 37:569–579
Rosenthal J, Simone PG, Silbergleit A (1974) Effects of prostaglandin deficiency on natriuresis, diuresis and blood pressure. Prostaglandins 5:435–440
Somova L, Orbetzova V, Davidova F, Hoffmann P, Taube Ch, Pönicke K, Förster W (1978) Influence of linoleic acid in the diet on arterial pressure of salt loaded rats. II. Effects on plasma catecholamine concentration, renin activity, and reactivity of isolated vessels. Acta Biol Med. Germ 37:869–873
Somova L, Hoffmann P, Förster W (1980) The reactivity of isolated blood vessels of salt loaded rats fed low or high linoleic acid diets. Eur J Pharmacol 64:79–84
Ten Hoor F, Van De Graaf HM (1978) The influence of a linoleic acid rich diet and of acetyl salicylic acid on NaCl induced hypertension, Na+- and H2O-balance and urinary prostaglandin excretion in rats. Acta Biol Med Germ 37:875–877
Triebe G, Block H-U, Förster W (1976) On the blood pressure response of salt-loaded rats under different content of linoleic acid in the food. Acta Biol Med Germ 35:1223–1224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffmann, P., Taube, C., Pönicke, K. et al. Chemical sympathectomy abolishes the increase in blood pressure of linoleic acid deficient fed rats induced by salt loading. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 317, 78–80 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00506261
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00506261