Summary
Pharmacokinetic processes have been studied using a recirculating rat liver perfusion system. Imipramine and its major metabolites have been determined at various times up to 3 h in perfusate, liver, bile and subcellular liver fractions.
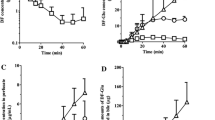
Imipramine undergoes a rapid hepatic uptake, the initial extraction being close to 100%. Most of the unchanged drug is then localized in the microsomal fraction. Metabolism is not limited by uptake and follows the pathways known from previous work. Like imipramine, its lipophilic metabolite, desmethylimipramine is bound to microsomes. Its concentration ratios, endoplasmic reticulum/cytosol and liver/perfusate, are around 200. In contrast, the polar glucuronides are easily released from the ER, their site of formation, into the cytosol and presumably from there excreted into the bile. A smaller amount of the glucuronides is increted into the perfusate where they reach a steady state level. Analogous experiments with a non-recirculating perfusion system yielded comparable results except for a more rapid imipramine uptake.
The results obtained in this study suggest that the pharmacokinetics of many drugs with high apparent volumes of distribution may be largely governed by intracellular binding of lipophilic compounds and translocation processes of polar metabolites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahr, C. von, Alexanderson, B., Azarnoff, D. L., Sjöqvist, F., Orrenius, S.: A comparative study of drug metabolism in the isolated perfused liver and in vivo in rats. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 9, 99–105 (1970)
Bahr, C. von, Bertilsson, L.: Hydroxylation and subsequent glucuronide conjugation of desmethylimipramine in rat liver microsomes. Xenobiotica 1, 205–212 (1971)
Bahr, C. von, Borga, O.: Uptake, metabolism and excretion of desmethylimipramine and its metabolites in the isolated perfused rat liver. Acta pharmacol. (Kbh.) 29, 359–374 (1971)
Bergmeyer, H. U.: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse. 2nd edit. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1970
Bickel, M. H., Baggiolini, M.: The metabolism of imipramine and its metabolites by rat liver microsomes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 15, 1155–1169 (1966)
Bickel, M. H., Gigon, P. L.: Metabolic interconversions and binding of imipramine, imipramine-N-oxide, and desmethylimipramine in rat liver slices. Xenobiotica 1, 631–641 (1971)
Bickel, M. H., Minder, R.: Metabolism and biliary excretion of the lipophilic drug molecules, imipramine and desmethylimipramine in the rat. I. Experiments in vivo and with isolated perfused livers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 19, 2425–2435 (1970a)
Bickel, M. H., Minder, R.: Metabolism and biliary excretion of the lipophilic drug molecules, imipramine and desmethylimipramine in the rat. II. Uptake into bile micelles. Biochem. Pharmacol. 19, 2437–2443 (1970b)
Bickel, M. H., Steele, J. W.: Binding of basic and acidic drugs to rat tissue subcellular fractions. Chemico-biol. Interactions 8, 151–162 (1974)
Bickel, M. H., Weder, H. J.: The total fate of a drug: Kinetics of distribution, excretion, and formation of 14 metabolites in rats treated with imipramine. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 173, 433–463 (1968)
Bickel, M. H., Weder, H. J.: Buccal absorption and other properties of pharmacokinetic importance of imipramine and its metabolites. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 21, 160–168 (1969)
Cordelli, A., Ferrari, M., Savonitto, E.: Metabolism of chlorpromazine and related psychotropic drugs in the isolated perfused rat liver. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 180, 121–125 (1969)
Crammer, J. L., Rolfe, B.: Metabolism of 14C-imipramine. III. Conversion by rat tissues. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 18, 26–37 (1970)
Dingell, J. V., Bass, A. D.: Inhibition of the hepatic metabolism of amphetamine by desipramine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 18, 1535–1538 (1969)
Eling, T. E., Orton, T. C., Pickett, R. D., Anderson, M. A., Fouts, J. R.: Xenobiotic accumulation in the isolated perfused rabbit lung. Fed. Proc. 32, 748 (1973)
Evans, G. H., Wilkinson, G. R., Shand, D. G.: The disposition of propranolol. IV. A dominant role for tissue uptake in the dose-dependent extraction of propranolol by the perfused ratliver. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 186, 447–454 (1973)
Glaumann, H., Nilsson, R., Dallner, G.: Cytoplasmic location of certain small molecules after their metabolism by the endoplasmic reticulum of rat liver. FEBS Letters 10, 306–308 (1970)
Hahn, I., Krieglstein, G., Krieglstein, J., Tschentscher, K.: Distribution of chlorpromazine in a simplified blood influenced by various drugs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 278, 35–44 (1973)
Hargreaves, T., Piper, R. F., Trichey, R.: The effect of imipramine and desipramine on UDP-glucuronyltransferase. Experientia (Basel) 25, 725–726 (1969)
Herrmann, B., Schindler, W., Pulver, R.: Papierchromatographischer Nachweis von Stoffwechselprodukten des Tofranil. Med. exp. (Basel) 1, 381–385 (1960)
Jähnchen, E., Krieglstein, J., Kunkel, F., Samuelis, W. J., Wollert, U.: deDie Bedeutung der Bindung von Pharmaka an Albumin und Erythrocyten eines Perfusionsmediums der isolierten Rattenleber. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 269, 67–84 (1971)
Junod, A. F.: Accumulation of 14C-imipramine in isolated perfused rat lungs. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 183, 182–187 (1972)
Krieglstein, J.: Über die Wechselbeziehung der Plasma- und Gewebsproteinbindung von Promazin, untersucht an der isoliert perfundierten Rattenleber. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path. 262, 474–483 (1969)
Levine, W. G., Singer, R. W.: Hepatic intracellular distribution of foreign compounds in relation to their biliary excretion. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 183, 411–419 (1972)
Meijer, D. K. F., Arends, J. W., Weitering, J. G.: The cardiac glycoside sensitive step in the hepatic transport of the bisquaternary ammonium compound, hexafluorenium. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 15, 245–251 (1971)
Meijer, D. K. F., Wester, J., Gunnink, M.: Distribution of quaternary ammonium compounds between particulate and soluble constituents of rat liver, in relation to their transport from plasma into bile. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 273, 179–192 (1972)
Minder, R., Schnetzer, F., Bickel, M. H.: Hepatic and extrahepatic metabolism of the psychotropic drugs, chlorpromazine, imipramine, and imipramine-N-oxide. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 268, 334–347 (1971)
Nies, A. S., Branch, R. A., Wilkinson, G. R., Shand, D. G.: Propranolol (P)_ disposition, B: Flow-dependent hepatic elimination. Fed. Proc. 32, 715 (1973)
Nilsson, R., Pettersson, E., Dallner, G.: Permeability properties of rat liver endoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Letters 15, 85–87 (1971)
Rosenbloom, P. M., Bass, A. D.: A lung perfusion preparation for the study of drug metabolism. J. appl. Physiol. 29, 138–144 (1970)
Umbreit, W. W., Burris, R. H., Stauffer, J. F.: Manometric Techniques. Minneapolis: Burgess Publishing Co. 1959
Weibel, E. R., Stäubli, W., Gnägi, H. R., Hess, F. A.: Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J. Cell Biol. 42, 68–91 (1969)
Wilkinson, G. R., Branch, R. A., Nies, A. S., Shand, D. G.: Propranolol (P) disposition, A: Binding to a saturable, high affinity, hepatic site and its kinetic consequences. Fed. Proc. 32, 715 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bickel, M.H., Börner, H. Uptake, subcellular distribution, and transfer processes of imipramine and its metabolites formed in rat liver perfusion systems. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 284, 339–352 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00504703
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00504703