Summary
-
1.
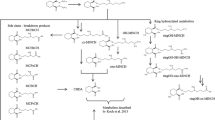
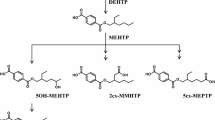
Free 2,4,5- and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (TCP) have been identified by co-crystallization with authentic carrier as constituents of the urine of rats given 3-H-labelled α-hexachlorocyclohexane (α-HCH). The two TCPs constituted 7% and 63%, respectively, of the free phenol fraction which was found to account for less than 5% of all urinary metabolites.
-
2.
75% of the label contained in the urine of rats collected for four weeks after an i.p. dose of 14-C-α-HCH could be extracted into an organic solvent after alkaline and acid hydrolysis. The radioactive material thus extracted was examined by TLC and GLC. It is shown to consist mainly of chlorophenols and chlorothiophenols.
-
3.
The extracts' major constituent was 2,4,6-TCP. Its amount was determined by GLC and was found to account for, on average, 45% of the total urinary metabolites. In conjunction with other evidence, this is considered to establish 2,4,6-TCP as the major product of α-HCH-biodegradation in the rat.
-
4.
Chromatographic evidence is presented for 2,3,4,5-tetrachlorophenol and 2,4,5-TCP being other components of the chlorophenol fraction isolated from hydrolysed urine.
-
5.
The amount of label associated with the chlorothiophenol fraction suggests a pathway involving endogenous thiol to be of significance in α-HCH-biodegradation in rats. Pretreatment with the drug itself increased the proportion of label associated with the fraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyland, E., Chasseaud, L. F.: The role of glutathione and glutathione-S-transferase in mercapturic acid biosynthesis. Advanc. Enzymol. 32, 173–219 (1969)
Bradbury, F. R., Standen, H.: Metabolism of benzene hexachloride by resistant houseflies Musca domestica. Nature (Lond.) 183, 983–984 (1959)
Chadwick, R. W., Freal, J. J.: The identification of five unreported lindane metabolites recovered from rat urine. Bull. environm. Contamin.Toxicol. 7, 137–146 (1972)
Freal, J. J., Chadwick, R. W.: Metabolism of hexachlorocyclohexane to chlorophenols and effect of isomer pretreatment on lindane metabolism in rat. Agr. Food Chem. 21, 424–427 (1973)
Grover, P. L., Sims, P.: The metabolism of γ-2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorocyclohex-1-ene and γ-hexachlorocyclohexane in rats. Biochem. J. 96, 521–525 (1965)
Jondorf, W. R., Parke, D. V., Williams, R. T.: Studies in detoxication. 66. The metabolism of halogenobenzenes. 1:2:3:-, 1:2:4- and 1:3:5-trichlorobenzenes. Biochem. J. 61, 512–521 (1955)
Jondorf, W. R., Parke, D. V., Williams, R. T.: Studies in detoxication. 76. The metabolism of halogenobenzenes. 1:2:3:4-, 1:2:3:5- and 1:2:4:5-tetrachlorobenzenes. Biochem. J. 69, 181–189 (1958)
Koransky, W., Portig, J.: Der Stoffwechsel der Hexachlorcyclohexan-Isomeren und seine Beeinflussung durch Mikrosomen aktivierende Pharmaka. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 243, 294–295 (1962)
Koransky, W., Portig, J., Vohland, H. W., Klempau, I.: Die Elimination von α- und γ-Hexachlorcyclohexan und ihre Beeinflussung durch Enzyme der Lebermikrosomen. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 247, 49–60 (1964)
Logie, D.: Analysis of chlorophenols by anion-exchange chromatography. Analyst 82, 563–581 (1957)
Noack, G., Portig, J.: Biodegradation of α-hexachlorcyclohexane. III. Decrease in liver non-protein thiol after intragastric application of the drug. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 280, 183–189 (1973)
Noack, G., Portig, J., Wirsching, M.: Biodegradation of α-hexachlorocyclohexane. IV. The extent of degradation of single doses in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. (in press, 1975)
Parke, D. V.: Studies in detoxication. 64. The synthesis of the isomeric dichlorophenylmercapturic acids. Biochem. J. 59, 422–426 (1955)
Parke, D. V., Williams, R. T.: Studies in detoxication. 81. The metabolism of halogenobenzenes: a) penta- and hexa-chlorobenzenes. b) further observations on 1:3:5-trichlorobenzene. Biochem. J. 74, 5–9 (1960)
Portig, J., Kraus, P., Sodomann, S., Noack, G.: Biodegradation of α-hexachlorocyclohexane. I. Glutathione-dependent conversion to a hydrophilic metabolite by rat liver cytosol. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 279, 185–198 (1973)
Van der Linden, T.: Über die Benzol-hexachloride und ihren Zerfall in Trichlorbenzole. Chem. Ber. 45, 231–247 (1912)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Aided by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koransky, W., Münch, G., Noack, G. et al. Biodegradation of α-hexachlorocyclohexane. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 288, 65–78 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501814
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501814