Abstract
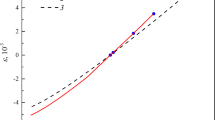
Simultaneous measurements of the specific heat capacity, c p, electrical resistivity, ρ, and hemispherical total emittance, ε, of tungsten-3 (wt%) rhenium alloy in the temperature range 1500–3600 K by a subsecond-duration pulse heating technique are described. The results are expressed by the relations
where T is in K, cp is in J·g−1·K−1, and ρ is in μΩ·cm. The melting temperature (solidus temperature) was also measured and was determined to be 3645 K. Uncertainties of the measured properties are estimated to be not more than ±3 % for specific heat capacity, ±1 % for electrical resistivity, ± 5 % for hemispherical total emittance, and ±20 K for the melting temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Cezairliyan, Int. J. Thermophys. 5:177 (1984).
G. M. Foley, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 41:827 (1970).
A. Cezairliyan, J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 75C:7 (1971).
A. Cezairliyan, M. S. Morse, H. A. Berman, and C. W. Beckett, J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 74A:65 (1970).
International Committee for Weights and Measures Metrologia 5:35 (1969).
A. Cezairliyan and J. L. McClure, J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 75A:283 (1971).
K. S. Sukhovei, Soviet Phys. Solid State 9:2893 (1968).
Ya. A. Kraftmakher and A. G. Cherevko, High Temp-High Press. 7:283 (1975).
A. V. Logunov and A. I. Kovalev, High Temp.-High Press. 5:625 (1973).
A. Cezairliyan, High Temp. Sci. 4:248 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
An alloy has a melting range instead of a melting temperature. For convenience, in the present work the solidus temperature of the alloy is referred to as the melting temperature.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cezairliyan, A., Miiller, A.P. Thermophysical measurements on tungsten-3 (wt %) rhenium alloy in the range 1500–3600 K by a pulse heating technique. Int J Thermophys 6, 191–202 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500031
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500031