Abstract
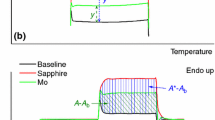
A Perkin-Elmer DSC-2 scanning calorimeter was operated by means of a PDP-11/34 computer with time-shared scanner and voltmeter. Special attention was paid to the problems of measurement below room temperature down to the low-temperature limit. It was found that Ne, rather than He, should be used as a purge gas, that scans should always be started at a standardized liquid nitrogen level, and that gas flow to the dry box should be stopped during measurements. Results on benzoic acid were then accurate to 0.6 % from 120 to 300 K. The specific heat of antimony was measured in the temperature interval 120–720 K.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. C. Mraw and D. F. Naas, J. Chem. Thermodyn. 11:567 (1979).
D. C. Ginnings and G. T. Furukawa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75:522 (1953).
Y. S. Touloukian and E. H. Buyco, Thermophysical Properties of Matter (Plenum, New York, 1970), Vol. 4, pp. 1–5.
J. M. G. Cowie, I. J. McEwen, and M. Y. Pedram, Macromolecules 16:1151 (1983).
Y. S. Touloukian and E. H. Buyco, Thermophysical Properties of Matter (Plenum, New York, 1970), Vol. 4, pp. 6–8.
W. Kramer and J. Nölting, Acta Metall. 20:1353 (1972).
S. Umino, Sci. Rep. Tohoku Impl. Univ. 15(Ser. 1):597 (1926).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fransson, Å., Bäckström, G. Automated differential scanning calorimetry at low temperatures. Int J Thermophys 6, 165–175 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500029
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500029