Summary
-
1.
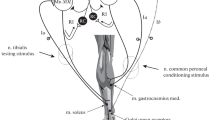
Tetanus toxin was injected into one triceps surae muscle of the cat to obtain symptoms of local tetanus. The contralateral homologous muscle was used as a control.
-
2.
The incubation time (20–40 h) was linearly related to the cube root of the weight of cat and showed a constant velocity (7–9 mm/h) of the spreading of toxin in the nerve fibres in cats of various sizes.
-
3.
The tension-extension curves of the tetanus muscle showed more stiffness and the base of the exponential passive tension-extension curve was always greater in the tetanus triceps surae muscle than in the control.
-
4.
With repeated stretches of the poisoned muscle the total tension-extension curve showed a progressive parallel shift to the right, indicating threshold increase of the stretch reflex. With antagonistic nerve stimulation the curve shiftet to the left (facilitation), which was never seen in the normal state.
-
5.
The total tension-extension curve of the poisoned muscle showed a progressive parallel shift to the left during the first few hours after the onset of symptoms, and to the right during selective blocking of the gamma fibres by procaine.
-
6.
The cats in which the toxin was injected into the flexor (tibialis anterior) muscle, had a longer incubation time and developed extensor spasticity instead of flexion of the leg.
-
7.
It is concluded that bias augmentation of the extensor gamma system is mainly responsible for the muscular stiffness in the early period of local tetanus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks, V. B., Curtis, D. R., Eccles, J. C.: The action of tetanus toxin on the inhibition of motoneurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 135, 655–672 (1957).
Granit, R.: Neuromuscular interaction in postural tone of the cat's isometic soleus muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 143, 387–402 (1958).
Kano, M., Sakurai, N., Takano, K.: Gamma activity of rigid cat in tetanus intoxication. J. Chiba med. Soc. 43, 388–389 (1967).
Kano, M., Takano, K.: Gamma activity of rigid cat caused by tetanus toxin. Jap. J. Physiol. 19, 1–10 (1969).
Koella, W. P., Nakao, H., Evans, R. L., Wada, J.: Interaction of vestibular and proprioceptive reflexes in the decerebrate cat. Amer. J. Physiol. 185, 607–613 (1956).
Kryzhanovskyi, G. N.: The neural pathway of toxin: Its transport to the central nervous system and the state of the spinal reflex apparatus in tetanus intoxication, pp. 155–168. In: Principles on Tetanus, L. Eckmann, ed. Bern: H. Huber 1967.
Liddell, E. G. T., Sherrington, S. C.: Reflexes in response to stretch (myotatic reflexes). Proc. roy. Soc. B 96, 212–242 (1924).
Liddell, E. G. T., Sherrington, S. C.: Further observations on myotatic reflexes. Proc. roy. Soc. B 97, 267–283 (1925).
Liljestrand, G., Magnus, R.: Über die Wirkung des Novokains auf den normalen und den tetanusstarren Skelettmuskel und über die Entstehung der lokalen Muskelstarre beim Wundstarrkrampf. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 176, 168–208 (1919).
Matthews, P. B. C.: A study of certain factors influencing the stretch reflex of the decerebrate cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 147, 547–564 (1959).
Matthews, P. B. C.: Mammalian muscle receptors and their central actions, pp. 448–451. London: Edward Arnold Ltd. 1972.
Matthews, P. B. C., Rushworth, G.: The relative sensitivity of muscle nerve fibres to procaine. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 135, 263–269 (1957).
Parsons, R. L., Hofmann, W. W., Feigen, G. A.: Mole of action of tetanus toxin on the neuromuscular junction. Amer. J. Physiol. 210, 84–90 (1966).
Pompeiano, O.: Alpha types of “release” studied in tension-extension diagrams from cat's forelimb triceps muscle. Arch. ital. Biol. 98, 91–117 (1960).
Ranson, S. W.: Local tetanus, a study of muscle and contracture. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 20, 663–700 (1928).
Ranson, S. W., Dixon, H. H.: The elasticity and ductility of muscle in the myostatic contracture caused by tetanus toxin. Amer. J. Physiol. 86, 312–319 (1928).
Schottelius, B. A., Schottelius, D. D.: Force-velocity relationship of tetanus toxin treated skeletal muscle. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.) 100, 282–285 (1959).
Student, C.: Das Längen-Aktivspannungs-Diagramm des gedehnten Katzen-Wadenmuskels bei kontrollierter Variation der Eingangs- und Ausgangs-Reizparameter. Med. Diss., Göttingen 1972.
Sverdlov, Y. S., Alekseeva, V. I.: Effect of tetanus toxin on presynaptic inhibition in the spinal cord. Fed. Proc. 25, 931–936 (Transl. Suppl.) (1966).
Takano, K.: Phasic, tonic and static components of the reflex tension obtained by stretch at different rates. In: Nobel Symposium I, Muscular afferents and motor control, pp. 461–463. R. Granit, ed. Stockholm: Almqvist and Wiksell 1966.
Takano, K., Henatsch, H.-D.: The effect of the rate of stretch upon the development of active reflex tension in hind limb muscles of the decerebrate cat. Exp. Brain Res. 12, 422–434 (1971).
Takano, K., Kano, M.: Reflex activity of the muscle in tetanus intoxication. J. Physiol. Soc. Japan 30, 122–123 (1968).
Takano, K., Kano, M.: Gamma-bias of the muscle poisoned by tetanus toxin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 276, 413–420 (1973).
Zacks, I., Sheff, F.: Tetanus toxin: Fine structure localization of binding sites in striated muscle. Science 159, 643–644 (1968).
Zacks, I., Sheff, F.: Tetanism: Pathobiological aspects of the action of tetanal toxin in the nervous system and skeletal muscle. Neurosci. Res. 3, 209–287 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takano, K., Henatsch, HD. Tension-extension diagram of the tetanus-intoxicated muscle of the cat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 276, 421–436 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00499895
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00499895