Summary
-
1.
The transfer of 51CrEDTA and inulinsubstances which are distributed only in the extracellular space-across the rat colonic mucosa in vivo is increased by oxyphenisatin O (3.5 · 10−5 M) and deoxycholate D (3 · 10−3 M).
-
2.
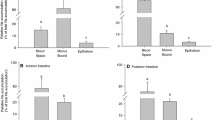
O and D do not change the size of the intra- and extracellular fluid compartments of the mucosa as measured with 51CrEDTA from the blood side. The sodium and potassium content of the mucosal tissue is not altered. Therefore the calculated intracellular concentrations of sodium and potassium remain constant.
-
3.
The time course of the 22Na uptake into the mucosal epithelium is not influenced by O and D up to 5 min after i.v. injection. The specific activity of sodium, however, in the luminal fluid increases under the influence of O (twofold) and D (fivefold). The uptake of 22Na into the mucosal tissue after administration of 22Na into the intestinal lumen is not changed in presence of O and D.
-
4.
We conclude that the net transport of sodium and water from blood to lumen under the influence of O and D occurs mainly via the intercellular way.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binder, H. J., Rawlins, C. L.: Effect of conjugated dihydroxy bile salts on electrolyte transport in rat colon. J. clin. Invest. 52, 1460–1466 (1973)
Cassidy, M. M., Tidball, C. S.: Cellular mechanism of intestinal permeability alterations produced by chelation depletion. J. Cell Biol. 32, 685–698 (1967)
Cofré, G., Crabbé, J.: Active sodium transport by the colon of Bufo marinus: Stimulation by aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 188, 177–190 (1967)
Edmonds, C. J., Nielson, O. E.: Transmembrane electrical potential differences and ionic composition of mucosal cells of rat colon. Acta physiol. scand. 72, 338–359 (1968)
Ehrenthal, W.: Der Phosphatstoffwechsel des Meerschweinchendünndarms unter der Einwirkung von Quabain. Thesis, Mathematisch-naturwissenschaftliche Fakultät der Universität des Saarlandes, Federal Republic of Germany 1974
Esposito, G., Faelli, A., Capravo, V.: The extracellular space of rat intestine “in vivo”. Pflügers Arch. 331, 70–76 (1972)
Ewe, K., Hölker, B.: Einfluß eines diphenolischen Laxans (Bisacodyl) auf den Wasser- und Elektrolyttransport im menschlichen Colon. Klin. Wschr. 52, 827–833 (1974)
Finn, A. L.: Separate effects of sodium and vasopressin on the sodium pump in toad bladder. Amer. J. Physiol. 215, 849–856 (1968)
Fordtran, J. S., Floyd, C. R., Carter, N. W.: The mechanisms of sodium absorption in the human small intestine. J. clin. Invest. 47, 884–900 (1968)
Forte, J. G., Nauss, A. H.: Effects of calcium removal on bull frog gastric mucosa. Amer. J. Physiol. 205, 631–637 (1963)
Forth, W., Leopold, G., Rummel, W.: Eisendurchtritt von der Mucosa- zur Serosaseite und umgekehrt an isolierten eisenarmen und normalen Segmenten von Jejunum und Ileum. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path. 261, 434–440 (1968)
Forth, W., Rummel, W., Baldauf, J.: Wasser- und Elektrolytbewegung am Dünn- und Dickdarm unter dem Einfluß von Laxantien, ein Beitrag zur Klärung ihres Wirkungsmechanismus. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path. 254, 18–32 (1966a)
Forth, W., Rummel, W., Glasner, H.: Zur resorptionshemmenden Wirkung von Gallensäuren. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path. 254, 363–380 (1966b)
Frazier, H. S., Dempsey, E. F., Leaf, A.: Movement of sodium across the mucosal surface of the isolated toad bladder and its modification by vasopressin. J. gen. Physiol. 45, 529–543 (1962)
Frizell, R. A., Schultz, S. G.: Effect of bile salts on transport across brush border of rabbit ileum. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 211, 589–592 (1970)
Higgins, J. T., Blair, N. P.: Intestinal transport of water and electrolytes during extracellular volume expansion in dogs. J. clin. Invest. 50, 2569–2579 (1971)
Mekhjian, H. S., Phillips, S. F., Hofmann, A. F.: Colonic secretion of water and electrolytes induced by bile acids: perfusion studies in man. J. clin. Invest. 50, 1569–1577 (1971)
Nell, G., Forth, W., Rummel, W., Wanitschke, R.: Abolition of the apparent Na+ impermeability of the colon mucosa by deoxycholate. Bile acids in human diseases. II. Bile Acid Meeting, Freiburg i. Br., June 30–July 1, 1972 (P. Back and W. Gerok, eds.), pp. 263–267. Stuttgart-New York: F. K. Schattauer 1972b
Nell, G., Forth, W., Rummel, W., Wanitschke, R.: Pathway of sodium moving from blood to intestinal lumen under influence of oxyphenisatin and deoxycholate (J. W. L. Robinson, ed.). Lancaster, England: MTP 1975 (in press)
Nell, G., Overhoff, H., Forth, W., Kulenkampff, H., Specht, W., Rummel, W.: Influx and efflux of sodium in jejunal and colonic segments of rats under the influence of oxyphenisatin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 277, 53–60 (1973a)
Nell, G., Overhoff, H., Forth, W., Rummel, W.: The influence of water gradients and oxyphenisatin on the net transfer of sodium and water in the rat colon. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 277, 363–372 (1973b)
Nell, G., Rummel, W., Forth, W., Wanitschke, R.: Abolition of the apparent Na+ impermeability of the colon mucosa by oxyphenisatin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 274, Suppl. R 81 (1972a)
Overhoff, H., Forth, W., Nell, G., Pfleger, K., Rummel, W.: Zur Klärung der Ursachen des durch Oxyphenisatin bedingten Nettotransfers von Wasser und Na+ am Colon der Ratte. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 266, 419–420 (1970)
Parsons, D. S., Paterson, C. R.: Fluid and solute transport across rat colonic mucosa. Quart. J. Physiol. 50, 220–231 (1965)
Pfleger, K., Forth, W., Rummel, W.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur Resorption von Alkaliionen durch den Dünndarm. In: Radioisotope in der Gastroenterologie, pp. 191–192. Stuttgart: F. K. Schattauer 1967
Rummel, W.: Enterale Resorptionsvorgänge und ihre Beeinflussung. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak. 250, 189–209 (1965)
Rummel, W., Nell, G., Wanitschke, R.: Action mechanisms of antiabsorptive and hydragogue drugs. In: Intestinal absorption and malabsorption (T. Z. Csaky, ed.), pp. 209–227. New York: Raven Press 1975
Schultz, S. G., Fuisz, R. E., Curran, P. F.: Amino acid and sugar transport in rabbit ileum. J. gen. Physiol. 49, 849–866 (1966)
Sedar, A. W., Forte, J. G.: Effects of calcium depletion on the junctional complex between oxyntic cells of gastric glands. J. Cell Biol. 22, 173–188 (1964)
Stirling, C. E.: Radioautographic localization of sodium pump sites in rabbit intestine. J. Cell Biol. 53, 704–714 (1972)
Tormey, M. J., Diamond, J. M.: The ultrastructural route of fluid transport in rabbit gall bladder. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 2031–2060 (1967)
Ussing, H. H.: The alkali metal ions in biology. In: Handbuch der experimentellen Pharmakologie, pp. 131–138. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1960
Ussing, H. H., Erlij, D., Lassen, U.: Transport pathways in biological membranes. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 36, 17–49 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The results have already been presented in part on the occasion of the 13th spring meeting of the Deutsche Pharmakologische Gesellschaft, Mainz (Nell et al., 1972a), and on the II. Bile Acid Meeting, Freiburg i. Br., 1972 (Nell et al., 1972 b).
Supported by a grant from the Sonderforschungsbereich 38, Membrane Research, Universität des Saarlandes.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nell, G., Forth, W., Rummel, W. et al. Pathway of sodium moving from blood to intestinal lumen under the influence of oxyphenisatin and deoxycholate. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 293, 31–37 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498868
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498868