Summary
We report a detailed comparative immunocytochemical mapping of enkephalin, CCK and ACTH/gb-endorphin immunoreactive nerves in the central nervous system of rat and guinea pig. Enkephalin immunoreactivity was detected in many groups of nerve cell bodies, fibers and terminals in the limbic system, basal ganglia, hypothalamus, thalamus, brain stem and spinal cord. β-endorphin and ACTH immunoreactivity was limited to a single group of nerve cell bodies in and around the arcuate nucleus and in fibers and terminals in the midline areas of the hypothalamus, thalamus and mesencephalic periaqueductal gray with lateral extensions to the amygdaloid area. Cholecystokinin immunoreactive nerve fibers and terminals displayed a distribution similar to that of enkephalin in many regions; but striking differences were also found. An immunocytochemical doublestaining technique, which allowed simultaneous detection of two different peptides in the same tissue section, showed that enkephalin-, CCK- and ACTH/β-endorphin-immunoreactive nerves although closely intermingled in many brain areas, occurred separately. The distributions of nerve terminals containing these neuropeptides showed striking overlaps and also paralleled the distribution of opiate receptors. This may suggest that enkephalin, CCK, ACTH and β-endorphin may interact with each other and with opiate receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
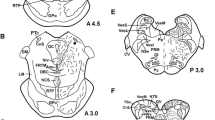
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Commissura anterior
- CAI:
-
Capsula interna
- CO:
-
Chiasma opticum
- CPF:
-
Cortex piriformis
- CSDD:
-
Commissura supraoptica dorsalis, pars dorsalis (Ganser)
- CSDV:
-
Commissura supraoptica dorsalis, pars ventralis (Meynert)
- FMP:
-
Fasciculus medialis prosencephali
- FOR:
-
Formatio reticularis
- GD:
-
Gyrus dentatus
- GP:
-
Glubus pallidus
- H:
-
Habenula
- HI:
-
Hippocampus
- S:
-
Subiculum
- SGCD:
-
Substantia grisea centralis, pars dorsalis
- SGCL:
-
Substantia grisea centralis, pars lateralis
- SGPV:
-
Substantia grisea periventricularis
- SNC:
-
Substantia nigra, zona compacta
- SNL:
-
Substantia nigra, pars lateralis
- ST:
-
Stria terminalis
- STP:
-
Stria terminalis, pars precommissuralis
- TD:
-
Tractus diagonalis (Broca)
- TO:
-
Tractus opticus
- TSHT:
-
Tractus septohypothalamicus
- TUOP:
-
Tuberculum olfactorium, pars corticalis
- SUM:
-
Decussatio supramamillaris
- a:
-
Nucleus accumbens
- ac:
-
Nucleus amygdaloideus centralis
- aco:
-
Nucleus amygdaloideus corticalis
- am:
-
Nucleus amygdaloideus medialis
- ar:
-
Nucleus arcuatus
- cp:
-
Nucleus caudatus putamen
- dcgl:
-
Nucleus dorsalis corporis geniculati lateralis
- em:
-
Eminentia mediana
- fm:
-
Nucleus paraventricularis, pars magnocellularis
- fp:
-
Nucleus paraventricularis, pars parvocellularis
- ha:
-
Nucleus anterior (hypothalami)
- hd:
-
Nucleus dorsomedialis (hypothalami)
- hl:
-
Nucleus lateralis (hypothalami)
- hp:
-
Nucleus posterior (hypothalami)
- hpv:
-
Nucleus periventricularis (hypothalami)
- hv:
-
Nucleus ventromedialis (hypothalami)
- ip:
-
Nucleus interpeduncularis
- mcgm:
-
Nucleus marginalis corporis geniculatic medialis
- mm:
-
Nucleus mammillaris medialis
- ml:
-
Nucleus mammillaris lateralis
- mh:
-
Nucleus medialis habenulae
- p:
-
Nucleus pretectalis
- pf:
-
Nucleus parafascicularis
- pom:
-
Nucleus preopticus medialis
- pop:
-
Nucleus preopticus periventricularis
- posc:
-
Nucleus preopticus, pars suprachiasmatica
- pt:
-
Nucleus paratenialis
- pvs:
-
Nucleus periventricularis stellatocellularis
- re:
-
Nucleus reuniens
- sc:
-
Nucleus suprachiasmaticus
- sl:
-
Nucleus septi lateralis
- so:
-
Nucleus supraopticus
- st:
-
Nucleus interstitialis striae terminalis
- tad:
-
Nucleus anterior dorsalis thalami
- tam:
-
Nucleus anterior medialis thalami
- tav:
-
Nucleus anterior ventralis thalami
- td:
-
Nucleus tractus diagonalis (Broca)
- th:
-
Nuclei thalami
- tl:
-
Nucleus lateralis thalami
- tlp:
-
Nucleus lateralis thalami, pars posterior
- tm:
-
Nucleus medialis thalami
- tml:
-
Nucleus medialis thalami, pars lateralis
- tmm:
-
Nucleus medialis thalami, pars medialis
- tpo:
-
Nucleus posterior thalami
- tr:
-
Nucleus reticularis thalami
- tv:
-
Nucleus ventralis thalami
- tvd:
-
Nucleus ventralis thalami, pars dorsomedialis
- tvm:
-
Nucleus ventralis medialis thalami, pars magnocellularis
References
Atweh SF, Kuhar MJ (1977a) Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. I. Spinal cord and medulla. Brain Res 124:53–67
Atweh SF, Kuhar MJ (1977b) Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. II. The brain stem. Brain Res 129:1–12
Atweh SF, Kuhar MJ (1977c) Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. III. The telencephalon. Brain Res 134:393–405
Baxter MG, Goff E, Miller AA, Saunders IA (1977) Effect of a potent synthetic opioid pentapeptide in some antinociceptive and behavioral tests in mice and rats. Br J Pharmacol 59:455–459
Bloom F, Battenberg E, Rossier J, Guillemin R (1978) Neurons containing β-endorphin in rat brain exist separately from those containing enkephalin: Immunocytochemical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:1591–1595
Bruce MK, Castellanos FX, Kastin AJ, Berzas MC, Marik MD, Olson GA, Olson RD (1979) Naloxone-induced suppression of food intake in normal and hypothalamic obese rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 11:729–732
Buscher HH, Hill RC, Römer D, Cardinaux A, Closse A, Hauser D, Pless J (1976) Evidence for analgesic activity of enkephalin in the mouse. Nature 261:423–425
Chang K-J, Cooper BR, Hazum E, Cuatrecasas P (1979) Multiple opiate receptors: Different regional distribution in the brain and differential binding of opiates and opioid peptides. Mol Pharmacol 16:91–104
Childers SR, Creese I, Snowman AM, Snyder SH (1979) Opiate receptor binding affected differentially by opiates and opioid peptides. Eur J Phamacol 55:11–18
Della-Ferra MA, Baile CA (1979) Cholecystokinin octapeptide: continuous picomole injections into the cerebral ventricles of sheep suppress feeding. Science 206:471–473
DeWied D (1977) Hormonal influences on motivation, learning and memory processes. Hosp Pract 11:123–131
DeWied D, Gispen WH (1977) Behavioral effects of peptides. In: Gainer H (ed) Peptides in neurobiology. Plenum Press, New York, pp 391–442
Dodd J, Kelly JS (1979) Cholecystokinin peptides: excitatory effect on hippocampal neurons. J Physiol (London) 195:61P
Duggan AW, Hall JG, Headly PR (1976) Morphine, enkephalin and the substantia gelatinosa. Nature 264:456–458
Graham RC, Karnovsky MJ (1966) The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubule of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem 14:291–302
Grandison L, Guidotti A (1977) Stimulation of food intake by muscimol and beta-endorphin. Neuropharmacology 16:533–536
Gähwiler BH (1980) Excitatory action of opioid peptides and opiates on cultured hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain Res 194:193–203
Hong JS, Wood PL, Gillin JC, Yang HYT, Costa E (1980) Changes of hippocampal met-enkephalin content after recurrent motor seizures. Nature 285:231–232
Hökfelt T, Elde R, Johansson D, Terenius L, Stein L (1977a) Distribution of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. I. Cell bodies. Neurosci Lett 5:25–31
Hökfelt T, Ljünadal H, Terenius L, Elde R, Nilsson G (1977b) Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possible related to pain and analgesia: Enkephalin and substance-P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:3081–3085
Innis RB, Correa FMA, Uhl GR, Schneider B, Snyder SH (1979) Cholecystokinin octapeptide-like immunoreactivity: histochemical localization in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:521–525
Larsson L-I (1977) Corticotropin-like peptides in central nerves and in endocrine cells of gut and pancreas. Lancet 2:1321–1323
Larsson L-I (1978) Distribution of ACTH-like immunoreactivity in rat brain and gastrointestinal tract. Histochemistry 55:225–233
Larsson L-I (1980) Immunocytochemical characterization of ACTH-like immunoreactivity in cerebral nerves and in endocrine cells of the pituitary and gastrointestinal tract by using region specific antisera. J Histochem Cytochem 28:133–141
Larsson L-I, Childers S, Snyder SH (1979) Methionine and leucine-enkephalin occur in separate neurons. Nature 282:407–411
Larsson L-I, Rehfeld JF (1977) Characterization of antral gastrin cells with region-specific antisera. J Histochem Cytochem 25:1317–1321
Larsson L-I, Rehfeld JF (1979) Localization and molecular heterogeneity of cholecystokinin in the central and peripheral nervous system. Brain Res 165:201–218
Lien EL, Fenichel RL, Garsky V, Sarantarkis D, Grant DH (1976) Enkephalin stimulated prolactin release. Life Sci 19:837–840
Loh HH, Tseng LF, Wei E, Li CH (1976) β-endorphin is a potent analgesic agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:2895–2898
Lord JAH, Waterfield AA, Hughes J, Kosterlitz HW (1977) Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonist and receptors. Nature 267:495–500
Mains RE, Eipper BA (1979) Synthesis and secretion of corticotropin, melanotrophins, and endorphins by rat intermediate pituitary cells. J Biol Chem 254:7885–7894
Nilaver G, Zimmerman CA, Defentini R, Liotta AS, Krieger DT, Brownstein MJ (1979) Adrenocortitropin and β-lipotropin in the hypothalamus. J Cell Biol 81:50–58
Pert A, Sivet C (1977) Neuroanatomical focus for morphine and enkephalin induced hypermotility. Nature 265:645–647
Plom GII, Van Ree JM (1978) Adrenocorticotropic hormone fragments mimic the effect of morphine in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 64:223–227
Rivier C, Vale W, Ling N, Brown M, Guillemin R (1977) Stimulation in vivo of the secretion of prolactin and growth hormone by β-endorphin. Endocrinology 100:238–241
Rodgers RJ, File SE (1979) Exploratory behaviour and aversive threshold following intra-amygdaloid application of opiates in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 11:505–511
Rossier J, Battenberg E, Dittman Q, Bayon A, Koda L, Miller R, Guillemin R, Bloom F (1979) Hypothalamic enkephalin neurons may regulate the neurohypophysis. Nature 27:653–655
Saito A, Sankaran H, Goldfine ID, Williams JA (1980) Cholecystokinin receptors in the brain: Characterization and distribution. Science 208:1155–1156
Sar M, Stumpf WE, Miller RJ, Chang K-J, Cuatrecasas P (1978) Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin in rat brain and spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 182:17–38
Schiller PW, Lipton A, Horrobin DF, Bodansky M (1978) Unsulfated C-terminal 7-peptide of cholecystokinin: A new ligand of the opiate receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 85:1332–1338
Simantov R, Kuhar MJ, Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1977) Opioid peptide enkephalin: Immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:2167–2171
Stengaard-Pedersen K, Larsson L-I (1981) Interaction of putative opioid peptides with opiate receptors. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 48:39–46
Sternberger LA (1974) Immunocytochemistry. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Storm-Mathisen J (1977) Localization of transmitter candidates in the brain: The hippocampal formation as a model. In: Progress in neurobiology, Vol 8. Pergamon Press, London, pp 119–181
Terenius L, Gispen WH, De Wied D (1975) ACTH-like peptides and opiate receptors in the rat brain: Structure-activity studies. Eur J Pharmacol 33:395–399
Vanderhaeghen JJ, Lotstra F, De May J, Gilles C (1980) Immunocytochemical localization of cholecystokinin- and gastrin-like peptides in the brain and hypophysis of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1190–1194
Wamsky JK, Young WS, Kuhar MJ (1980) Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin in rat forebrain. Brain Res 190:153–174
Watkins WB (1980) Presence of adrenocorticotropin and β-endorphin immunoreactivities in the magnocellular neurosecretory system of the rat hypothalamus. Cell Tissue Res 207:65–80
Zetler G (1979) Antagonism of cholecystokinin-like peptides by opioid peptides, morphine or tetrodotoxin. Eur J Pharmacol 60:67–77
Zieglgänsberger W, French ED, Siggins GR, Bloom FE (1979) Opioid peptides may excite hippocampal pyramidal neurons by inhibiting adjacent inhibitory interneurons. Science 205:414–417
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stengaard-Pedersen, K., Larsson, L.I. Comparative immunocytochemical localization of putative opioid ligands in the central nervous system. Histochemistry 73, 89–114 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00493136
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00493136